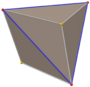
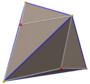
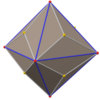
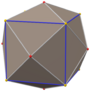
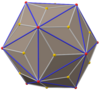
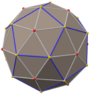
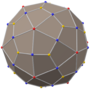
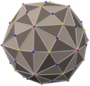
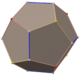
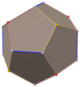
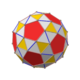
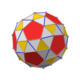
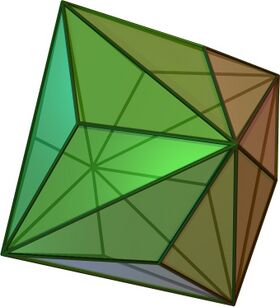
Triakis octahedron
| Triakis octahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Catalan solid |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Conway notation | kO |
| Face type | V3.8.8 isosceles triangle |
| Faces | 24 |
| Edges | 36 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Vertices by type | 8{3}+6{8} |
| Symmetry group | Oh, B3, [4,3], (*432) |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432) |
| Dihedral angle | 147°21′00″ arccos(−3 + 8√2/17) |
| Properties | convex, face-transitive |
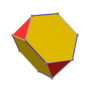
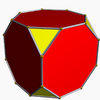 Truncated cube (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |
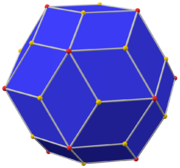
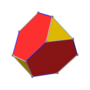
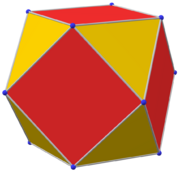
In geometry, a triakis octahedron (or trigonal trisoctahedron[1] or kisoctahedron[2]) is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the truncated cube.
It can be seen as an octahedron with triangular pyramids added to each face; that is, it is the Kleetope of the octahedron. It is also sometimes called a trisoctahedron, or, more fully, trigonal trisoctahedron. Both names reflect that it has three triangular faces for every face of an octahedron. The tetragonal trisoctahedron is another name for the deltoidal icositetrahedron, a different polyhedron with three quadrilateral faces for every face of an octahedron.
This convex polyhedron is topologically similar to the concave stellated octahedron. They have the same face connectivity, but the vertices are in different relative distances from the center.
If its shorter edges have length 1, its surface area and volume are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} A &= 3\sqrt{7+4\sqrt{2}} \\ V &= \frac{3+2\sqrt{2}}{2} \end{align} }[/math]
Cartesian coordinates
Let α = √2 − 1, then the 14 points (±α, ±α, ±α) and (±1, 0, 0), (0, ±1, 0) and (0, 0, ±1) are the vertices of a triakis octahedron centered at the origin.
The length of the long edges equals √2, and that of the short edges 2√2 − 2.
The faces are isosceles triangles with one obtuse and two acute angles. The obtuse angle equals arccos(1/4 − √2/2) ≈ 117.20057038016° and the acute ones equal arccos(1/2 + √2/4) ≈ 31.39971480992°.
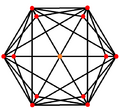
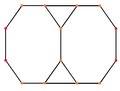
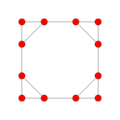
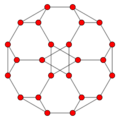
Orthogonal projections
The triakis octahedron has three symmetry positions, two located on vertices, and one mid-edge:
| Projective symmetry |
[2] | [4] | [6] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triakis octahedron |
|
|
|
| Truncated cube |
|
|
|
Cultural references
- A triakis octahedron is a vital element in the plot of cult author Hugh Cook's novel The Wishstone and the Wonderworkers.
Related polyhedra
The triakis octahedron is one of a family of duals to the uniform polyhedra related to the cube and regular octahedron.
The triakis octahedron is a part of a sequence of polyhedra and tilings, extending into the hyperbolic plane. These face-transitive figures have (*n32) reflectional symmetry.
File:Triakis octahedron.stl
The triakis octahedron is also a part of a sequence of polyhedra and tilings, extending into the hyperbolic plane. These face-transitive figures have (*n42) reflectional symmetry.
References
- ↑ "Clipart tagged: ‘forms’". etc.usf.edu. https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/keyword/forms.
- ↑ Conway, Symmetries of things, p. 284
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983), Dual Models, Cambridge University Press, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511569371, ISBN 978-0-521-54325-5 (The thirteen semiregular convex polyhedra and their duals, Page 17, Triakisoctahedron)
- The Symmetries of Things 2008, John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 [1] (Chapter 21, Naming the Archimedean and Catalan polyhedra and tilings, page 284, Triakis octahedron)
External links
- Eric W. Weisstein, Triakis octahedron (Catalan solid) at MathWorld.
- Triakis Octahedron – Interactive Polyhedron Model
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra www.georgehart.com: The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- VRML model
- Conway Notation for Polyhedra Try: "dtC"
 |