Astronomy:Iota Lyrae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Lyra |
| Right ascension | 19h 07m 18.13251s[2] |
| Declination | +36° 06′ 00.5592″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.22[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B6IV[4] |
| Variable type | Be star[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −26.0±4.6[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −1.437[2] mas/yr Dec.: −3.876[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.5858 ± 0.1924[2] mas |
| Distance | 910 ± 50 ly (280 ± 10 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.94[7] |
| Orbit[8] | |
| Period (P) | 216.93 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.172″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.637 |
| Inclination (i) | 145.5° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 171.4° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | B 1997.28 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 201.2° |
| Details | |
| Mass | 5.2[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 6.7[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 854[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.54[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 12,059[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.11[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 224[11] km/s |
| Age | 168[12] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
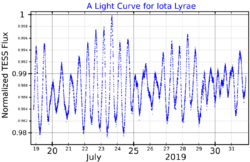
ι Lyrae, Latinised as Iota Lyrae, is a binary star[3] in the northern constellation of Lyra. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 5.22.[3] This object is located approximately 910 light years distant from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting nearer with a radial velocity of −26 km/s.[6]
This is a wide binary system with a computed orbital period of 217 years and an eccentricity of 0.6.[8] The primary component has a stellar classification of B6IV,[4] matching a B-type subgiant star. It is a Be star,[14] displaying emission lines in its spectrum, and is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 224 km/s.[11] The star ranges in brightness from magnitude 5.20 down to 5.27.[5] It has about five times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 854 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 12,059 K.
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x. Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lesh, Janet Rountree (December 1968). "The Kinematics of the Gould Belt: an Expanding Group?". Astrophysical Journal Supplement 17: 371. doi:10.1086/190179. Bibcode: 1968ApJS...17..371L.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Sixth Catalog of Orbits of Visual Binary Stars". United States Naval Observatory. http://www.usno.navy.mil/USNO/astrometry/optical-IR-prod/wds/orb6.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Anders, F. et al. (August 2019). "Photo-astrometric distances, extinctions, and astrophysical parameters for Gaia DR2 stars brighter than G = 18". Astronomy & Astrophysics 628: A94. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935765. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2019A&A...628A..94A.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Watson, R. A. (15 June 2017). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Tycho–Gaia stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 471 (1): 770–791. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1433. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2017MNRAS.471..770M.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy & Astrophysics 537: A120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. Bibcode: 2012A&A...537A.120Z.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (December 2012). "Dependence of kinematics on the age of stars in the solar neighborhood". Astronomy Letters 38 (12): 771–782. doi:10.1134/S1063773712120031. ISSN 0320-0108. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..771G.
- ↑ "iot Lyr". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=iot+Lyr.
- ↑ Abt, H. A.; Cardona, O. (October 1984), "Be stars in binaries", Astrophysical Journal 285: 190–194, doi:10.1086/162490, Bibcode: 1984ApJ...285..190A
 |