Biology:Chromosome 17
| Chromosome 17 | |
|---|---|
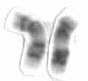 Human chromosome 17 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 17 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 84,276,897 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 1,124 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[2] (25.1 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 17 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 17 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 17 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 17 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000017 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000679 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 84 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 17 contains the Homeobox B gene cluster.
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 17. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). The most conservative estimate, from CCDS, represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[4]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 1,124 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,132 | 325 | 458 | [5] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 1,184 | 1,199 | 535 | [6] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 1,169 | — | — | [7] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 1,199 | 757 | 566 | [8][9][10] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 17. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
The following are some of the genes and their corresponding Cytogenetic location on chromosome 17:
p-arm
q-arm
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are related to genes on chromosome 17:
- 17q12 microdeletion syndrome
- Koolen–de Vries syndrome
- Alexander disease
- Andersen–Tawil syndrome
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome
- Bladder cancer
- Breast cancer
- Bruck syndrome
- Campomelic dysplasia
- Canavan disease
- Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, tp53
- Corticobasal degeneration
- Cystinosis
- Depression
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
- Epidermodysplasia verruciformis
- Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17
- Galactosemia
- Glycogen storage disease type II (Pompe disease)
- Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies
- Howel–Evans syndrome
- Li–Fraumeni syndrome
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young type 5
- Miller–Dieker syndrome
- Multiple synostoses syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis type I
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Obsessive–compulsive disorder
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Potocki–Lupski syndrome
- Proximal symphalangism
- Sanfilippo syndrome
- Smith–Magenis syndrome
- Usher syndrome
- Very long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency
- Von Gierke's syndrome
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[17] | Band[18] | ISCN start[19] |
ISCN stop[19] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[20] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | p | 13.3 | 0 | 385 | 1 | 3,400,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | p | 13.2 | 385 | 550 | 3,400,001 | 6,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 17 | p | 13.1 | 550 | 784 | 6,500,001 | 10,800,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | p | 12 | 784 | 990 | 10,800,001 | 16,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 17 | p | 11.2 | 990 | 1499 | 16,100,001 | 22,700,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | p | 11.1 | 1499 | 1664 | 22,700,001 | 25,100,000 | acen | |
| 17 | q | 11.1 | 1664 | 1815 | 25,100,001 | 27,400,000 | acen | |
| 17 | q | 11.2 | 1815 | 2104 | 27,400,001 | 33,500,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 12 | 2104 | 2255 | 33,500,001 | 39,800,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 17 | q | 21.1 | 2255 | 2461 | 39,800,001 | 40,200,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 21.2 | 2461 | 2599 | 40,200,001 | 42,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 17 | q | 21.31 | 2599 | 2874 | 42,800,001 | 46,800,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 21.32 | 2874 | 3025 | 46,800,001 | 49,300,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 17 | q | 21.33 | 3025 | 3176 | 49,300,001 | 52,100,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 22 | 3176 | 3383 | 52,100,001 | 59,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 17 | q | 23.1 | 3383 | 3451 | 59,500,001 | 60,200,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 23.2 | 3451 | 3658 | 60,200,001 | 63,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 17 | q | 23.3 | 3658 | 3781 | 63,100,001 | 64,600,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 24.1 | 3781 | 3850 | 64,600,001 | 66,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 17 | q | 24.2 | 3850 | 4001 | 66,200,001 | 69,100,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 24.3 | 4001 | 4166 | 69,100,001 | 72,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 17 | q | 25.1 | 4166 | 4400 | 72,900,001 | 76,800,000 | gneg | |
| 17 | q | 25.2 | 4400 | 4510 | 76,800,001 | 77,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 17 | q | 25.3 | 4510 | 4950 | 77,200,001 | 83,257,441 | gneg |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Search results - 17[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2016-09-08. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=17%5BChr%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22has%20ccds%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes.". Genome Biol 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMID 20441615.
- ↑ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 17". 2017-05-12. https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=17.
- ↑ "Chromosome 17: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". 2017-03-29. http://mar2017.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=17.
- ↑ "Human chromosome 17: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". 2018-02-28. https://www.uniprot.org/docs/humchr17.txt.
- ↑ "Search results - 17[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=17%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 9[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=17%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%28%22genetype%20miscrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20ncrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20rrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20trna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20scrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snorna%22%5BProperties%5D%29%20NOT%20%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 17[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=17%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20pseudo%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Obsessive Compulsive Disorder". http://omim.org/entry/164230.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=lGCLrh0DIwEC.
- ↑ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261304470.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ↑ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ↑ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Gilbert F (1998). "Disease genes and chromosomes: disease maps of the human genome. Chromosome 17". Genet Test 2 (4): 357–81. doi:10.1089/gte.1998.2.357. PMID 10464617.
- Gene Card Website https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=SCN4A
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 17". Genetics Home Reference. http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=17.
- "Chromosome 17". http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo17.shtml.
 |




