Astronomy:70 Aquarii
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Right ascension | 22h 48m 30.21043s[2] |
| Declination | –10° 33′ 19.7143″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.19[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | main sequencec |
| Spectral type | F0 V[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.28[3] |
| Variable type | δ Sct[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –5.8[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +31.535[2] mas/yr Dec.: +7.915[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 7.6654 ± 0.0704[2] mas |
| Distance | 425 ± 4 ly (130 ± 1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.88[7] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 4.17+0.17 −0.23[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 44.8±0.5[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.48[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,314+187 −144[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.02±0.15[8] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 110[9] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
70 Aquarii is a variable star located 425[2] light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It has the variable star designation FM Aquarii;[7] 70 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation. It is near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye, appearing as a dim, yellow-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 6.19.[3] This star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of –5.8 km/s.[6]
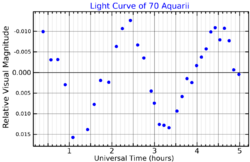
This is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F0 V.[4] Located in the lower part of the instability strip, it is a Delta Scuti-type variable that ranges in brightness from magnitude 6.16 down to 6.19 with a period of 125 minutes (0.087 days).[5] The star has a high rate of spin, showing a projected rotational velocity of 110 km/s.[9] It has four[2] times the Sun's radius and is radiating 45[2] times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of around 7,314 K.[2]
References
- ↑ Weiss, W. W. (November 1977). "HR 239 and HR 8676: Two delta Scuti-Type Variables". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1364: 1. Bibcode: 1977IBVS.1364....1W. http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1977IBVS.1364....1W/0000001.000.html. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Corben, P. M.; Stoy, R. H. (1968), "Photoelectric Magnitudes and Colours for Bright Southern Stars", Monthly Notes of the Astronomical Society of Southern Africa 27: 11, Bibcode: 1968MNSSA..27...11C.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999), "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars", Michigan Spectral Survey 5, Bibcode: 1999MSS...C05....0H.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Wilson, R. E. (1953), "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities", Carnegie Institute Washington D.C. Publication (Carnegie Institute of Washington, D.C.), Bibcode: 1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Paunzen, E. et al. (September 2002), "On the Period-Luminosity-Colour-Metallicity relation and the pulsational characteristics of lambda Bootis type stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics 392 (2): 515–528, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020854, Bibcode: 2002A&A...392..515P
- ↑ Gáspár, András et al. (2016), "The Correlation between Metallicity and Debris Disk Mass", The Astrophysical Journal 826 (2): 171, doi:10.3847/0004-637X/826/2/171, Bibcode: 2016ApJ...826..171G.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Royer, F. et al. (October 2002), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars in the northern hemisphere. II. Measurement of v sin i", Astronomy and Astrophysics 393: 897–911, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020943, Bibcode: 2002A&A...393..897R.
- ↑ "70 Aqr". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=70+Aqr.
External links
 |