Astronomy:HD 211575
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Aquarius
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Right ascension | 22h 18m 04.2722s[1] |
| Declination | −00° 14′ 15.557″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.40[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F3 V[3] |
| B−V color index | 0.441±0.003[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +14.8±0.5[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −41.997[1] mas/yr Dec.: +54.407[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 24.13 ± 0.29[6] mas |
| Distance | 135 ± 2 ly (41.4 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 3.31[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.27[7] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 4.30[4] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.15[2] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,574±224[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.11±0.11[5] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 19.0[2] km/s |
| Age | 150[5] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
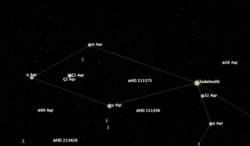
HD 211575 is a star in the constellation Aquarius in between "Gamma Aquarii", "Pi Aquarii" and "Sadalmelik". It is a member of the corona of the Ursa Major moving group.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brown, A. G. A. et al. (2016), "Gaia Data Release 1. Summary of the astrometric, photometric, and survey properties", Astronomy and Astrophysics 595: A2, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629512, Bibcode: 2016A&A...595A...2G.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Paunzen, E. et al. (July 2014), "Investigating the possible connection between λ Bootis stars and intermediate Population II type stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics 567: 8, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201423817, A67, Bibcode: 2014A&A...567A..67P.
- ↑ Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999), "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars", Michigan Spectral Survey 5, Bibcode: 1999MSS...C05....0H.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Casagrande, L. et al. (2011), "New constraints on the chemical evolution of the solar neighbourhood and Galactic disc(s). Improved astrophysical parameters for the Geneva-Copenhagen Survey", Astronomy & Astrophysics 530 (A138): 21, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201016276, Bibcode: 2011A&A...530A.138C.
- ↑ van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015), "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets", The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146, Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D.
- ↑ "HD 211575". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=HD+211575.
- ↑ Chupina, N. V. et al. (June 2006), "Kinematic structure of the corona of the Ursa Major flow found using proper motions and radial velocities of single stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics 451 (3): 909−916, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054009, Bibcode: 2006A&A...451..909C.
 |