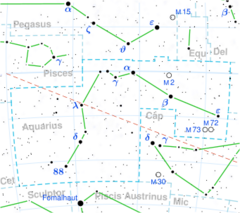
Astronomy:Chi Aquarii
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Right ascension | 23h 16m 50.93916s[1] |
| Declination | −07° 43′ 35.4023″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.75 - 5.10[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3 III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.60[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.60[4] |
| Variable type | SRb?[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −13.72 ± 0.86[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −19.18[1] mas/yr Dec.: −14.10[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 5.32 ± 0.37[1] mas |
| Distance | 610 ± 40 ly (190 ± 10 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.43[6] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 142[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,598[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.128[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,456[7] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Chi Aquarii, Latinized from χ Aquarii, is the Bayer designation of a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. The distance to this star, based upon parallax measurements with a 7% margin of error, is roughly 610 light-years (190 parsecs). It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 5.
This is a red giant star with a spectral classification of M3 III.[3] The interferometry-measured angular diameter of this star is 6.70 ± 0.15 mas,[10] which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about 137 times the radius of the Sun.[lower-alpha 1] It is classified as a semi-regular variable star and its brightness varies by an amplitude of 0.0636 in magnitude.[11] The identified pulsation periods are 32.3, 38.5, and 44.9 days.[12]
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009), "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)", VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1, Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Crampton, D.; Lloyd Evans, T. (1973), "Spectroscopic observations of M giant stars at the South Galactic Pole", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 162: 11–15, doi:10.1093/mnras/162.1.11, Bibcode: 1973MNRAS.162...11C.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nicolet, B. (1978), "Photoelectric photometric Catalogue of homogeneous measurements in the UBV System", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 34: 1–49, Bibcode: 1978A&AS...34....1N.
- ↑ Famaey, B. et al. (May 2009), "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations", Astronomy and Astrophysics 498 (2): 627–640, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698, Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..627F.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Watson, R. A. (15 June 2017), "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Tycho–Gaia stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 471 (1): 770–791, doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1433, ISSN 0035-8711, Bibcode: 2017MNRAS.471..770M.
- ↑ "chi Aqr -- Semi-regular pulsating Star", SIMBAD (Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg), http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=Chi+Aquarii, retrieved 2012-07-05.
- ↑ /ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats, Strasbourg astronomical Data Center, https://cdsarc.cds.unistra.fr/viz-bin/ftp-index?/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats, retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ↑ Richichi, A.; Percheron, I.; Khristoforova, M. (February 2005), "CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics 431 (2): 773–777, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042039, Bibcode: 2005A&A...431..773R.
- ↑ Koen, Chris; Eyer, Laurent (March 2002), "New periodic variables from the Hipparcos epoch photometry", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 331 (1): 45–59, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05150.x, Bibcode: 2002MNRAS.331...45K.
- ↑ Tabur, V. et al. (December 2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 400 (4): 1945–1961, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x, Bibcode: 2009MNRAS.400.1945T.
- ↑ Lang, Kenneth R. (2006), Astrophysical formulae, Astronomy and astrophysics library, 1 (3rd ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 3-540-29692-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=OvTjLcQ4MCQC&pg=PA41
External links
 |