Biology:Chromosome 7
| Chromosome 7 | |
|---|---|
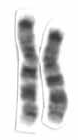 Human chromosome 7 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 7 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 160,567,428 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 862 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[2] (60.1 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 7 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 7 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 7 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 7 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000007 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000669 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 160 million[4] base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 7. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[5]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 862 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 870 | 245 | 703 | [6] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 984 | 973 | 889 | [7] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 944 | — | — | [8] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 948 | 905 | 933 | [9][10][11] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 7. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
- AASS: encoding enzyme Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase, mitochondrial
- ACTR3B: actin-related protein 3B
- AEBP1: AE binding protein 1
- AGK: encoding enzyme mitochondrial acylglycerol kinase
- ARHGEF35: encoding protein Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 35
- AVL9: encoding protein Avl9 cell migration associated
- BCAP29: B-cell receptor-associated protein 29
- BCC6: encoding protein basal cell carcinoma, susceptibility to, 6
- BRAT1: BRCA1-associated ATM activator 1
- C7orf25: protein UPF0415
- C7orf31: chromosome 7 open reading frame 31
- CALU: Calumenin
- CCL24: encoding protein C-C motif chemokine ligand 24
- CDCA7L: Cell division cycle-associated 7-like protein
- CFTR: anion channel membrane protein
- CNOT4: CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 4
- CPED1: cadherin like and PC-esterase domain containing 1
- CPVL: carboxypeptidase, vitellogenic like
- CROT: Peroxisomal carnitine O-octanoyltransferase
- DDX56: DEAD-box helicase 56
- DMTF1: Cyclin D binding myb like transcription factor 1
- ECOP: EGFR-coamplified and overexpressed protein
- EEPD1: encoding protein Endonuclease/exonuclease/phosphatase family domain containing 1
- EGFR-AS1: encoding protein EGFR antisense RNA 1
- EZH2: encoding enzyme histone-lysine N-methyltransferase for histone h3 lysine 27
- FAM71F2: family with sequence similarity 71 member F2
- FAM185A: family with sequence similarity 185 member A
- FAM200A: family with sequence similarity 200 member A
- FBXO24: F-box only protein 24
- GBAS: Glioblastoma amplified sequence; Protein NipSnap homolog 2
- GET4: encoding protein GET4
- GLCCI1: Glucocorticoid-induced transcript 1 protein
- HOXA@: encoding protein Homeobox a cluster
- HOXA10-HOXA9: readthrough gene unlikely to produce a protein product
- HPC4: Prostate cancer, hereditary, 4
- ICA1: islet cell autoantigen 1
- ING3: inhibitor of growth protein 3
- INTS1: encoding protein Integrator complex subunit 1
- IQCE: IQ domain-containing protein E
- KDM7A: encoding protein Lysine demethylase 7A
- LCHN: protein encoded by the KIAA1147 gene
- LHFPL3: LHFPL tetraspan subfamily member 3
- LINC01003: encoding long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1003
- LRRC17: leucine-rich repeat containing protein 17
- LRRC61: encoding protein Leucine rich repeat containing 61
- LRRD1: encoding protein Leucine-rich repeats and death domain containing 1
- LSM5: U6 small nuclear RNA and mRNA degradation associated
- LUC7L2: putative RNA-binding protein Luc7-like 2
- MACC1: encoding protein Macc1, met transcriptional regulator
- MAP11: encoding protein Microtubule-associated protein 11
- MDFIC: MyoD family inhibitor domain containing
- METTL2B: methyltransferase-like protein 2B
- MINDY4: MINDY lysine 48 deubiquitinase 4
- MIR93: encoding protein MicroRNA 93
- MIR148A: encoding protein MicroRNA 148a
- MIR196B: encoding protein MicroRNA 196b
- MIR548F4: encoding protein MicroRNA 548f-4
- MIR96: microRNA 96
- MOSPD3: motile sperm domain containing 3
- MTERF: mitochondrial transcription termination factor 1
- MTRNR2L6: encoding protein MT-RNR2-like 6
- NOM1: nucleolar protein with MIF4G domain 1
- NUDCD3: NudC domain-containing protein 3
- NUPL2: nucleoporin-like 2
- NXPH1: neurexophilin-1
- OPN1SW: blue-sensitive opsin
- PDAP1: PDGFA associated protein 1
- PHTF2: putative homeodomain transcription factor 2
- PLOD3: procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 3
- POM121: POM121 transmembrane nucleoporin
- POP7: ribonuclease P protein subunit p20
- PPP1R17: protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 17
- PSPH: phosphoserine phosphatase
- PURB: purine-rich element binding protein B
- PVRIG: encoding protein Poliovirus receptor related immunoglobulin domain containing
- RADIL: ras-associating and dilute domain-containing protein
- RASA4B: encoding protein RAS p21 protein activator 4B
- RCP9: DNA-directed RNA polymerase III subunit RCP9
- REPIN1: replication initiator 1
- RNF216-IT1: encoding protein RNF216 intronic transcript 1
- SCIN: scinderin
- SCRN1: secernin 1
- SEMA3E: encoding protein Semaphorin 3E
- SOSTDC1: sclerostin domain containing 1
- SPDYE1: speedy/RINGO cell cycle regulator family member E1
- SSC4D: scavenger receptor cysteine rich family member with 4 domains
- STEAP1: six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1
- STEAP2: six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 2
- STEAP4: six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4
- STYXL1: serine/threonine/tyrosine-interacting-like protein 1
- SUMF2: sulatase-modifying factor 2
- SYPL1: synaptophysin-like protein 1
- TARP: TCR gamma alternate reading frame protein
- TBRG4: transforming growth factor beta regulator 4
- TECPR1 encoding protein Tectonin beta-propeller repeat containing 1
- TMED4: transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 4
- TMEM130: transmembrane protein 130
- TMEM196 encoding protein Transmembrane protein 196
- TMEM243: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 243
- TNRC18: encoding protein Trinucleotide repeat containing 18
- TRBC1 encoding protein T cell receptor beta constant 1
- TRBC2 encoding protein T cell receptor beta constant 2
- TRGV1: encoding protein T cell receptor gamma variable 1 (non-functional)
- TRIL: TRL4 interactor with leucine rich repeats
- UPK3B: encoding protein Uroplakin 3B
- URG4: up-regulated gene 4
- WBSCR17: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 17
- WDR91 encoding protein WD repeat domain 91
- WEE2-AS1: encoding protein WEE2 antisense RNA 1
- XKR5: encoding protein XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 5
- ZC3HAV1: zinc finger CCCH-type containing
- ZC3HC1: zinc finger C3HC-type containing 1
- ZNF106: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 106
- ZNF117: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 117
- ZNF394: zinc finger protein 394
- ZNF398: zinc finger protein 398
- ZNF679: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 679
- ZNF716: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 716
- ZNF727: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 727
- ZNF786: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 786
- ZNF853: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 853
- ZKSCAN1: zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 1
- ZKSCAN5: zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 5
- ZMIZ2: zinc finger MIZ domain-containing protein 2
- ZNF277P: zinc finger protein 277
- ZRF1: DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C2
- ZSCAN21: zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 21
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 7:
- 7p22.1 microduplication syndrome[12]
- argininosuccinic aciduria[13][14][15]
- cerebral cavernous malformation[13][15]
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease[13]
- Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic 3[13]
- Citrullinemia, type II, adult-onset,[13]
- congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens[13]
- cystic fibrosis[16][13][15]
- Developmental verbal dyspraxia[17]
- distal spinal muscular atrophy, type V[citation needed]
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
- hemochromatosis, type 3[13]
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC4[13]
- Lissencephaly syndrome, norman-roberts type[13]
- Marfan syndrome[13]
- maple syrup urine disease[citation needed]
- maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3[citation needed]
- mucopolysaccharidosis type VII or Sly syndrome[13]
- Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle, type 1D[13]
- myelodysplastic syndrome[18]
- Myotonia congenita[13][19]
- nonsyndromic deafness[13]
- osteogenesis imperfecta[citation needed]
- p47-phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease[citation needed]
- Pectus excavatum
- Pendred syndrome[13][20]
- Romano–Ward syndrome[citation needed]
- Shwachman–Diamond syndrome[13][15]
- Silver-Russell syndrome[21]
- Specific language impairment[13][17]
- Tritanopia or tritanomaly color blindness[13]
- Williams syndrome[16][13][22]
- Zellweger syndrome[23]
Chromosomal disorders
The following conditions are caused by changes in the structure or number of copies of chromosome 7:
- Williams syndrome is caused by the deletion of genetic material from a portion of the long (q) arm of chromosome 7. The deleted region, which is located at position 11.23 (written as 7q11.23), is designated as the Williams syndrome critical region. This region includes more than 20 genes, and researchers believe that the characteristic features of Williams syndrome are probably related to the loss of multiple genes in this region.
While a few of the specific genes related to Williams syndrome have been identified, the relationship between most of the genes in the deleted region and the signs and symptoms of Williams syndrome is unknown.
- Other changes in the number or structure of chromosome 7 can cause delayed growth and development, mental disorder, characteristic facial features, skeletal abnormalities, delayed speech, and other medical problems. These changes include an extra copy of part of chromosome 7 in each cell (partial trisomy 7) or a missing segment of the chromosome in each cell (partial monosomy 7). In some cases, several DNA building blocks (nucleotides) are deleted or duplicated in part of chromosome 7. A circular structure called ring chromosome 7 is also possible. A ring chromosome occurs when both ends of a broken chromosome are reunited.[24]
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[29] | Band[30] | ISCN start[31] |
ISCN stop[31] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[32] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | p | 22.3 | 0 | 227 | 1 | 2,800,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 22.2 | 227 | 397 | 2,800,001 | 4,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 7 | p | 22.1 | 397 | 610 | 4,500,001 | 7,200,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 21.3 | 610 | 908 | 7,200,001 | 13,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 7 | p | 21.2 | 908 | 965 | 13,700,001 | 16,500,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 21.1 | 965 | 1121 | 16,500,001 | 20,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 7 | p | 15.3 | 1121 | 1419 | 20,900,001 | 25,500,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 15.2 | 1419 | 1589 | 25,500,001 | 27,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 7 | p | 15.1 | 1589 | 1816 | 27,900,001 | 28,800,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 14.3 | 1816 | 1986 | 28,800,001 | 34,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | p | 14.2 | 1986 | 2043 | 34,900,001 | 37,100,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 14.1 | 2043 | 2327 | 37,100,001 | 43,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | p | 13 | 2327 | 2639 | 43,300,001 | 45,400,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 12.3 | 2639 | 2838 | 45,400,001 | 49,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | p | 12.2 | 2838 | 2909 | 49,000,001 | 50,500,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 12.1 | 2909 | 3093 | 50,500,001 | 53,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | p | 11.2 | 3093 | 3306 | 53,900,001 | 58,100,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | p | 11.1 | 3306 | 3448 | 58,100,001 | 60,100,000 | acen | |
| 7 | q | 11.1 | 3448 | 3689 | 60,100,001 | 62,100,000 | acen | |
| 7 | q | 11.21 | 3689 | 3973 | 62,100,001 | 67,500,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 11.22 | 3973 | 4171 | 67,500,001 | 72,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 7 | q | 11.23 | 4171 | 4597 | 72,700,001 | 77,900,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 21.11 | 4597 | 4994 | 77,900,001 | 86,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 7 | q | 21.12 | 4994 | 5108 | 86,700,001 | 88,500,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 21.13 | 5108 | 5292 | 88,500,001 | 91,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 21.2 | 5292 | 5406 | 91,500,001 | 93,300,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 21.3 | 5406 | 5661 | 93,300,001 | 98,400,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 22.1 | 5661 | 6129 | 98,400,001 | 104,200,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 22.2 | 6129 | 6300 | 104,200,001 | 104,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 7 | q | 22.3 | 6300 | 6470 | 104,900,001 | 107,800,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 31.1 | 6470 | 6683 | 107,800,001 | 115,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 31.2 | 6683 | 6867 | 115,000,001 | 117,700,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 31.31 | 6867 | 7094 | 117,700,001 | 121,400,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 31.32 | 7094 | 7208 | 121,400,001 | 124,100,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 31.33 | 7208 | 7364 | 124,100,001 | 127,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 32.1 | 7364 | 7449 | 127,500,001 | 129,600,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 32.2 | 7449 | 7576 | 129,600,001 | 130,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 7 | q | 32.3 | 7576 | 7803 | 130,800,001 | 132,900,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 33 | 7803 | 8031 | 132,900,001 | 138,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 7 | q | 34 | 8031 | 8371 | 138,500,001 | 143,400,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 35 | 8371 | 8612 | 143,400,001 | 148,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 7 | q | 36.1 | 8612 | 8910 | 148,200,001 | 152,800,000 | gneg | |
| 7 | q | 36.2 | 8910 | 9080 | 152,800,001 | 155,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 7 | q | 36.3 | 9080 | 9350 | 155,200,001 | 159,345,973 | gneg |
In popular culture
Novels
In the novel Performance Anomalies, researchers at Stanford University identify mutations in the long (q) arm of chromosome 7 as underlying the accelerated nervous system of the spy protagonist Cono,[33] who receives the moniker Cono 7Q
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Search results - 1[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2016-09-08. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=1%5BChr%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22has%20ccds%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ What is chromosome 7, "Genetics Home Reference" of U.S. National Library of Medicine. April 2008. [2014-05-14].
- ↑ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes.". Genome Biol 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMID 20441615.
- ↑ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 7". 2017-05-12. https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=7.
- ↑ "Chromosome 7: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". 2017-03-29. http://mar2017.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=7.
- ↑ "Human chromosome 7: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". 2018-02-28. https://www.uniprot.org/docs/humchr07.txt.
- ↑ "Search results - 7[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=7%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 7[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=7%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%28%22genetype%20miscrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20ncrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20rrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20trna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20scrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snorna%22%5BProperties%5D%29%20NOT%20%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results - 7[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=7%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20pseudo%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Caselli, Rossella; Ballarati, Lucia; Vignoli, Aglaia; Peron, Angela; Recalcati, Maria Paola; Catusi, Ilaria; Larizza, Lidia; Giardino, Daniela (November 2015). "7p22.1 microduplication syndrome: Clinical and molecular characterization of an adult case and review of the literature". European Journal of Medical Genetics 58 (11): 578–583. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.08.003. ISSN 1878-0849. PMID 26297194. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26297194/.
- ↑ 13.00 13.01 13.02 13.03 13.04 13.05 13.06 13.07 13.08 13.09 13.10 13.11 13.12 13.13 13.14 13.15 13.16 13.17 13.18 13.19 "Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and biology". Science 300 (5620): 767–772. May 2003. doi:10.1126/science.1083423. PMID 12690205. Bibcode: 2003Sci...300..767S.
- ↑ "Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency". Genetics in Medicine 14 (5): 501–507. May 2012. doi:10.1038/gim.2011.1. PMID 22241104.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 "Chromosome 7". Genetic Testing 6 (2): 141–161. 2002. doi:10.1089/10906570260199429. PMID 12215256.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7". Nature 424 (6945): 157–164. Jul 2003. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948. Bibcode: 2003Natur.424..157H.</bn>"Supernumerary ring chromosome 7 mosaicism: case report, investigation of the gene content, and delineation of the phenotype". American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 132A (1): 93–100. Jan 2005. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30408. PMID 15580634. http://selab.janelia.org/publications/Hillier03/Hillier03-reprint.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-20.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Genetic advances in the study of speech and language disorders". Neuron 68 (2): 309–320. Oct 2010. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.001. PMID 20955937.
- ↑ "Incidence, characterization and prognostic significance of chromosomal abnormalities in 640 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Grupo Cooperativo Español de Citogenética Hematológica". British Journal of Haematology 108 (2): 346–356. Feb 2000. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.01868.x. PMID 10691865.
- ↑ Myotonia congenita. Advances in Genetics. 63. 2008. pp. 25–55. doi:10.1016/S0065-2660(08)01002-X. ISBN 9780123745279.
- ↑ "[Pendrin: physiology, molecular biology and clinical importance]" (in it). Giornale Italiano di Nefrologia 24 (4): 288–294. 2007. PMID 17659500.
- ↑ "Silver-Russell syndrome: genetic basis and molecular genetic testing". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 5: 19. 2010. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-5-19. PMID 20573229.
- ↑ "Auditory and visual processing in Williams syndrome". The Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Sciences 47 (2): 125–131. 2010. PMID 20733255.
- ↑ Steinberg, Steven J; Raymond, Gerald V; Braverman, Nancy E; Moser, Ann B (2017). "Zellweger Spectrum Disorder". GeneReviews®. University of Washington, Seattle. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1448/. Retrieved 2019-09-17.
- ↑ "De novo supernumerary ring chromosome 7: first report of a non-mosaic patient and review of the literature". Clinical Genetics 61 (3): 202–206. Mar 2002. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2002.610306.x. PMID 12000362.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=lGCLrh0DIwEC.
- ↑ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261304470.
- ↑ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ↑ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ↑ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- ↑ Lee, Victor Robert (2013-01-15) (in en). Performance Anomalies: A Novel. Perimeter Six Press. ISBN 9781938409202. https://books.google.com/books?id=R4xrWxfC_DUC&q=performance+anomalies+chromosome&pg=PT87.
Further reading
- "Pure partial trisomy 7q: two new patients and review". American Journal of Medical Genetics 113 (2): 218–224. Nov 2002. doi:10.1002/ajmg.10719. PMID 12407716.
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 7". Genetics Home Reference. http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=7.
- "Chromosome 7". http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo07.shtml.
 |


