Chemistry:Calcium cyanide
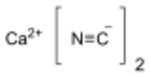
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca(CN)2 | |
| Molar mass | 92.1128 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | hydrogen cyanide |
| Density | 1.853 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 640 °C (1,184 °F; 913 K) (decomposes) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, weak acids |
| Structure | |
| rhombohedric | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly Toxic |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Non-flammable | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
39 mg/kg rat, oral[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Calcium cyanide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca(CN)2. It is the calcium salt derived from hydrocyanic acid. It is a white solid, although the pure material is rarely encountered. It hydrolyses readily (even in moist air) to release hydrogen cyanide and is very toxic.[3]
Preparation
Solutions of calcium cyanide can be prepared by treating calcium hydroxide with hydrogen cyanide. Solid calcium cyanide is produced commercially by heating calcium cyanamide with sodium chloride. The reaction is incomplete. The product is only of 50% purity, other components being sodium cyanide, calcium cyanamide, and carbon. Because of the carbon impurity, the solid is black, hence material is often called black cyanide.[3]
Reactivity
At temperatures around 600 °C, calcium cyanide converts to calcium cyanamide:[4][5]
- Ca(CN)2 → CaCN2 + C
It is suspected that this reaction is one step in the conversion of calcium carbide with nitrogen gas. The ratio of calcium cyanide to calcium cyanamide is sensitive to the presence of alkali metal halides, such as sodium chloride.
Calcium cyanide hydrolyzes upon acidification to form hydrogen cyanide:
- Ca(CN)2 + 2 H+ → Ca2+ + 2 HCN
Calcium cyanide reacts with ammonium carbonate to give produce ammonium cyanide:
- Ca(CN)2 + (NH4)2CO3 → 2 NH4CN + CaCO3
Uses
Calcium cyanide is used almost exclusively in the mining industry. It serves as an inexpensive source of cyanide in many leaching or vat operation to obtain precious metals such as gold and silver from their ores.[3][6]
Safety
Like other cyanide salts, this compound is highly toxic and its use is strictly regulated.
References
- ↑ "GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank". https://www.gestis.dguv.de.
- ↑ "CALCIUM CYANIDE | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA". http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/2775.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Gail, Ernst; Gos, Stephen; Kulzer, Rupprecht; Lorösch, Jürgen; Rubo, Andreas; Sauer, Manfred (2004). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_159.pub2.
- ↑ "Production of Hydrocyanic Acid" United States Patent Office. 1933.(accessed April 22, 2012).
- ↑ Thomas Güthner; Bernd Mertschenk (2006). "Cyanamides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_139.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.
- ↑ "Use of Cyanide for the Gold Industry" International Cyanide Management Code for the Use of Cyanide in the Gold . 2011. http://www.cyanidecode.org/cyanide_use.php (accessed April 22, 2012).
External links
 |

