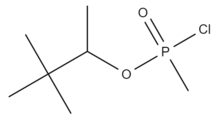
Chemistry:Chlorosoman
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,3-Dimethylbutan-2-yl methylphosphonochloridate | |
| Other names
Pinacolyl methylphosphonochloridate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16ClO2P | |
| Molar mass | 198.63 g·mol−1 |
| 1,030 mg/L[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.207 mm Hg[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlorosoman is a chlorine analog of soman. It is a highly toxic organophosphorus compound and used as the precursor substance for soman nerve agent.[2] Its physical properties are estimated. Soman is insoluble in water, with a boiling point of 223 degrees Celsius and a melting point of -27 degrees Celsius. Chlorosoman is at least 2.5x less toxic than its analogue.[3]
The ClG series of compounds is used more as a precursor to highly toxic compounds. For example, soman is a precursor to EA-2613 and EA-3209.
Synthesis
ClGD follows the same synthetic route as soman, with fluoridation being omitted. Chlorosoman is prepared by the Finkelstein reaction between a solution of sodium chloride in DMF and soman.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 National Center for Biotechnology Information. "Chlorosoman - PubChem Compound Database". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/145983.
- ↑ Quagliano, Javier; Witkiewicz, Zygfryd; Sliwka, Ewa; Neffe, Slawomir (2018). "Precursors of Nerve Chemical Warfare Agents with Industrial Relevance: Characteristics and Significance for Chemical Security". ChemistrySelect 3 (10): 2703–2715. doi:10.1002/slct.201702763.
- ↑ Ledgard, J. A Laboratory History of Chemical Warfare Agents.
- ↑ cit-OPDC. The preparatory manual to chemical warfare. Vol 1:ClG-agents.
 |
