Chemistry:Ethylsarin
From HandWiki
Short description: Nerve agent
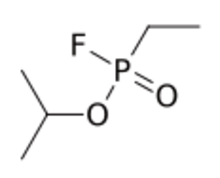
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propan-2-yl ethylphosphonofluoridate | |
| Other names
GE, EA-1209, TL-1620, T-2109
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12FO2P | |
| Molar mass | 154.121 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | −50 °C (−58 °F; 223 K) |
| Boiling point | 162 °C (324 °F; 435 K) |
| Vapor pressure | 1.97 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Extremely toxic |
| Flash point | 56.7 °C (134.1 °F; 329.8 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
690 mg/kg (mice, intraperitoneal)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethylsarin (GE), also known as EA-1209,[2] TL-1620 or T-2109,[3] is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It is the ethylphosphonofluoridate analog of sarin.[4][5] It has 1/8 the toxicity of sarin and is 2-3 times more persistent.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "ChemIDplus". https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/sid/0001189873.
- ↑ "Physical properties of standard agents, candidate agents, and related compounds at several temperatures". http://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/c033491.pdf.
- ↑ Chemical Warfare Agents, and Related Chemical Problems. Parts I-II. 1958. https://ntrl.ntis.gov/NTRL/dashboard/searchResults/titleDetail/PB158508.xhtml.
- ↑ Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents (2nd ed.). CRC Press. 24 August 2007. ISBN 9780849314346.
- ↑ Compendium of chemical warfare agents. Springer. 15 November 2006. ISBN 9780387346267.
- ↑ Franks, S. (1968). Manual of Military Chemistry. Volume 1. Chemistry of Chemical Warfare Agents.. Assistant Chief of Staff for Intelligence (Army), Washington, D.C.. pp. 247. https://ntrl.ntis.gov/NTRL/dashboard/searchResults/titleDetail/AD849866.xhtml.
- ↑ Department Of The Army Office Of The Chief, Chemical Corps. CMLWH. A1.13 - RLF/TSE/5190/blac. 17 February 1948.
 |
