Chemistry:Hexylcaine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | <10 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
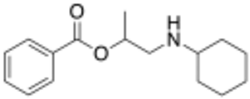
| Formula | C16H23NO2 |
| Molar mass | 261.365 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Hexylcaine hydrochloride, also called cyclaine (Merck) or osmocaine, is a short-acting local anesthetic. It acts by inhibiting sodium channel conduction. Overdose can lead to headache, tinnitus, numbness and tingling around the mouth and tongue, convulsions, inability to breathe, and decreased heart function.[1]
Synthesis
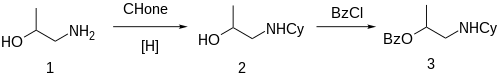
The reductive amination between 1-Amino-2-propanol [78-96-6] (1) and cyclohexanone gives 1-Cyclohexylamino-2-propanol [103-00-4] (2). Treatment with benzoyl chloride gives the ester, completing the synthesis of Hexylcaine (3).[citation needed]
References
- ↑ "Hexylcaine (cyclaine) as topical anesthetic in gastroscopy and esophagoscopy". Gastroenterology 36 (1): 120–1. January 1959. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(59)80102-5. PMID 13620024.
- ↑ Cope, Arthur C.; Hancock, Evelyn M. (1944). "1-Alkylamino-2-propanols and their p-Nitro- and p-Aminobenzoates". Journal of the American Chemical Society 66 (9): 1453–1456. doi:10.1021/ja01237a010.
- ↑ "Local Anesthetics". New England Journal of Medicine. 263 (19): 963–965.1960. doi:10.1056/NEJM196011102631912.
- ↑ Cope Arthur C, U.S. Patent 2,486,374 (1949 to Sharp & Dohme Inc).
 |

