Chemistry:Lithium ruthenate
From HandWiki
| |
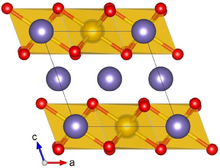
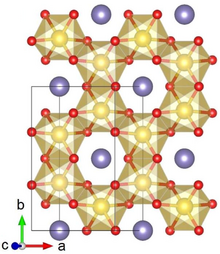 Crystal structure with Ru shown in yellow, Li in purple and O in red
| |
 Scale bar 0.1 mm[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium ruthenate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li2RuO3 | |
| Appearance | Dark blue crystals |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, P21/m[2] | |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lithium iridate, lithium platinate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium ruthenate, Li2RuO3, is a chemical compound of lithium, ruthenium and oxygen. It has a layered honeycomb crystal structure, and can be prepared by direct calcination of Ru metal and lithium carbonate at ca. 700 °C.[2] It is a potential lithium-ion battery electrode material,[2] though this application is hindered by the high costs of Ru, as compared to the cheaper Li2MnO3 alternative.[3]
References
- ↑ Freund, F.; Williams, S. C.; Johnson, R. D.; Coldea, R.; Gegenwart, P.; Jesche, A. (2016). "Single crystal growth from separated educts and its application to lithium transition-metal oxides". Scientific Reports 6: 35362. doi:10.1038/srep35362. PMID 27748402. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...635362F.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 O'Malley, Matthew J.; Verweij, Henk; Woodward, Patrick M. (2008). "Structure and properties of ordered Li2IrO3 and Li2PtO3". Journal of Solid State Chemistry 181 (8): 1803. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2008.04.005. Bibcode: 2008JSSCh.181.1803O.
- ↑ Yoshio, Masaki; Brodd, Ralph J.; Kozawa, Akiya (17 July 2010). Lithium-Ion Batteries: Science and Technologies. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-387-34445-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=gkYhDYk6ftQC&pg=PA10.
 |
