Chemistry:Lithium tetrachloroaluminate
| |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium tetrachloroaluminate
| |
| Other names
LAC
Lithium aluminium chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
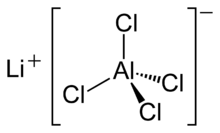
| Li[AlCl 4] | |
| Molar mass | 175.72 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White hygroscopic crystalline powder[1][2] |
| Odor | Odorless[1] |
| Melting point | 143 °C (289 °F; 416 K) [2] |
| Soluble.[1] Reacts violently with water.[3][2] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium tetrachloroaluminate is an inorganic compound with the formula Li[[[Chemistry:Aluminium |Al]]Cl
4].[4] It consists of lithium cations Li+
and tetrahedral tetrachloroaluminate anions [AlCl
4]−
.
Uses
Lithium tetrachloroaluminate is used in some lithium batteries. A solution of lithium tetrachloroaluminate in thionyl chloride is the liquid cathode and electrolyte in those baterries, e.g. the lithium-thionyl chloride cell. Another cathode-electrolyte formulation is lithium tetrachloroaluminate + thionyl chloride + sulfur dioxide + bromine.
Reactions
Reacts violently with water, alcohols and oxidizing agents. Upon exposure to heat or fire, it decomposes emitting irritating and toxic fumes and smoke of hydrogen chloride, lithium oxide and aluminium oxide.[3]
Toxicity
Upon contact with skin, causes burns. Inhalation causes coughing and corrosive injuries to the respiratory system, which can lead to pneumonia.[1][3] This compound is extremely destructive to the mucous tissues. May cause pulmonary edema and edema of the larynx, laryngitis and edema of bronchi, leading to shortness of breath. May cause damage to the eyes, headache and nausea. If swallowed, may cause damage.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Lithium tetrachloroaluminate". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lithium-tetrachloroaluminate.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Lithium Tetrachloroaluminate". https://www.americanelements.com/lithium-tetrachloroaluminate-14024-11-4.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/HR/en/sds/aldrich/451142 [bare URL]
- ↑ Perenthaler, E.; Schulz, Heinz; Rabenau, A. "Crystal structures of lithium tetrachloroaluminate and sodium tetrachloroaluminate as a function of temperature" Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (1982), 491, 259-65. doi:10.1002/zaac.19824910133
 |
