Chemistry:Neuromedin N
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C38H63N7O8 | |
| Molar mass | 745.949 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
| Neuromedin N | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | NN |
| NCBI gene | 4922 |
| HGNC | 8038 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 12 q21 |
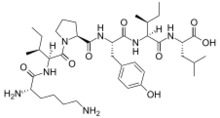
Neuromedin N is a neuropeptide derived from the same precursor polypeptide as neurotensin, and with similar but subtly distinct expression and effects.[2][3][4][5][6][7] Composed of the amino acid sequence Lys-Ile-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Leu, neuromedin N is homologous to neurotensin, both of whose sequences are found on the pro neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor C-terminus.[8][9] Both sequences of neuromedin N as well as neurotensin are flanked by Lys-Arg amino acids, which comprise a consensus sequence for the endoprotease proprotein convertase.[8] Neuromedin N is primarily synthesized in the neural and intestinal tissues of mammals; in studies performed in mice, neuromedin N's physiological effects were shown to include hypothermia and analgesia, arising from the peptide's ligand association to and interaction with neurotensin type 2 (NTS2) G protein-coupled receptors.[8][10]
References
- ↑ "Neuromedin N - Compound Summary". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=3025353.
- ↑ "Posttranslational processing of the neurotensin/neuromedin-N precursor". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 668 (1 The Neurobiol): 1–16. 1992. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27335.x. PMID 1463268. Bibcode: 1992NYASA.668....1C.
- ↑ "Biosynthesis, maturation, release, and degradation of neurotensin and neuromedin N". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 668 (1 The Neurobiol): 30–42. 1992. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27337.x. PMID 1463273. Bibcode: 1992NYASA.668...30K.
- ↑ "Neurotensin receptors: binding properties, transduction pathways, and structure". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 15 (5): 501–512. October 1995. doi:10.1007/BF02071313. PMID 8719037.
- ↑ "Differential effects of cocaine and methamphetamine on neurotensin/neuromedin N and preprotachykinin messenger RNA expression in unique regions of the striatum". Neuroscience 102 (4): 843–851. 2001. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00530-3. PMID 11182247.
- ↑ "Production of recombinant large proneurotensin/neuromedin N-derived peptides and characterization of their binding and biological activity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 290 (4): 1161–1168. February 2002. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.6308. PMID 11811984.
- ↑ "Differential processing of pro-neurotensin/neuromedin N and relationship to pro-hormone convertases". Peptides 27 (10): 2508–2514. October 2006. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2006.03.038. PMID 16904237.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Synthesis and binding characteristics of [(3)H]neuromedin N, a NTS2 receptor ligand". Neuropeptides 57: 15–20. June 2016. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2015.12.004. PMID 26707235.
- ↑ "Neuromedin N: a novel neurotensin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 122 (2): 542–549. July 1984. doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80067-4. PMID 6547840.
- ↑ "Hypothermic effect of neuromedin N in mice and its potentiation by peptidase inhibitors". European Journal of Pharmacology 151 (1): 117–121. June 1988. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(88)90699-1. PMID 3416919.
