Chemistry:Endomorphin-2
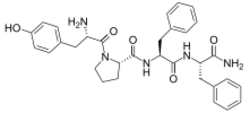
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
L-Tyrosyl-L-prolyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-phenylalaninamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H37N5O5 | |
| Molar mass | 571.667 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Endomorphin-2 (EM-2) is an endogenous opioid peptide and one of the two endomorphins.[1] It has the amino acid sequence Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2. It is a high affinity, highly selective agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, and along with endomorphin-1 (EM-1), has been proposed to be the actual endogenous ligand of this receptor (that is, rather than the endorphins).[1][2][3][4] Like EM-1, EM-2 produces analgesia in animals, but whereas EM-1 is more prevalent in the brain, EM-2 is more prevalent in the spinal cord.[1] In addition, the action of EM-2 differs from that of EM-1 somewhat, because EM-2 additionally induces the release of dynorphin A and [Met]enkephalin in the spinal cord and brain by an unknown mechanism, which in turn go on to activate the κ- and δ-opioid receptors, respectively, and a portion of the analgesic effects of EM-2 is dependent on this action.[5][6] Moreover, while EM-1 produces conditioned place preference, a measure of drug reward, EM-2 produces conditioned place aversion, an effect which is dynorphin A-dependent.[6] Similarly to the case of EM-1, the gene encoding for EM-2 has not yet been identified.[4][7]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Richard J. Bodnar; Kathryn Grace Commons; Donald W. Pfaff (3 April 2002). Central Neural States Relating Sex and Pain. JHU Press. pp. 67–. ISBN 978-0-8018-6827-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=4KeQEC4nHSkC&pg=PA67.
- ↑ H.-J. Krammer; M.V. Singer (31 May 2000). Neurogastroenterology - From the Basics to the Clinics. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 76–. ISBN 978-0-7923-8757-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=ghjN0L47QbwC&pg=PA76.
- ↑ Susan Brain; P.K. Moore (1999). Pain and Neurogenic Inflammation. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 28–. ISBN 978-3-7643-5875-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=6TNSAeTpkUMC&pg=PA28.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Stefan Offermanns; Walter Rosenthal (14 August 2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 904–. ISBN 978-3-540-38916-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=fGe6NDIGQpsC&pg=PA904.
- ↑ William D. Willis Jr.; Richard E. Coggeshall (31 January 2004). Sensory Mechanisms of the Spinal Cord: Volume 1 Primary Afferent Neurons and the Spinal Dorsal Horn. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 343–. ISBN 978-0-306-48033-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=uqnKCewO2voC&pg=PA343.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Austin (24 September 2010). Zen-Brain Reflections. MIT Press. pp. 125–. ISBN 978-0-262-26037-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=uZ4fyfH_t9EC&pg=PA125.
- ↑ Brian E. Cairns (1 September 2009). Peripheral Receptor Targets for Analgesia: Novel Approaches to Pain Management. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 520–. ISBN 978-0-470-52221-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=MTSvERxiCrIC&pg=PA520.
 |
