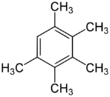
Chemistry:Pentamethylbenzene
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylbenzene | |||
| Other names
Pentamethylbenzene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C11H16 | |||
| Molar mass | 148.249 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.917 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 54.4 °C (129.9 °F; 327.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) | ||
| Solubility in organic solvents | soluble | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Flammable | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Pentamethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H(CH3)5. It is a colourless solid with a sweet odor. The compound is classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a relatively easily oxidized benzene derivative, with E1/2 of 1.95 V vs NHE.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
It is obtained as a minor product in the Friedel–Crafts methylation of xylene to durene (1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene).[2] Like durene, pentamethylbenzene is rather electron-rich and undergoes electrophilic substitution readily.[3] Indeed, it is used as a scavenger for carbocations.[4]
Pentamethylbenzene has been observed as an intermediate in the formation of hexamethylbenzene from phenol[5] and alkylation of durene or pentamethylbenzene has been reported as a suitable starting material for the synthesis of hexamethylbenzene.[2]
References
- ↑ Howell, J. O.; Goncalves, J. M.; Amatore, C.; Klasinc, L.; Wightman, R. M.; Kochi, J. K. (1984). "Electron transfer from aromatic hydrocarbons and their pi-complexes with metals. Comparison of the standard oxidation potentials and vertical ionization potentials". Journal of the American Chemical Society 106 (14): 3968–3976. doi:10.1021/ja00326a014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Smith, Lee Irvin (1930). "Durene". Organic Syntheses 10: 32. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.010.0032. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV2P0248.; Collective Volume, 2, pp. 248
- ↑ Griesbaum, Karl; Behr, Arno; Biedenkapp, Dieter; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Garbe, Dorothea; Paetz, Christian; Collin, Gerd; Mayer, Dieter et al. (2002). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_227.
- ↑ Okaya, Shun; Okuyama, Keiichiro; Okano, Kentaro; Tokuyama, Hidetoshi (2016). "Trichloroboron-Promoted Deprotection of Phenolic Benzyl Ether Using Pentamethylbenzene as a Non Lewis-Basic Cation Scavenger". Organic Syntheses 93: 63-74. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.093.0063. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=v93p0063.
- ↑ Landis, Phillip S.; Haag, Werner O. (1963). "Formation of Hexamethylbenzene from Phenol and Methanol". Journal of Organic Chemistry 28 (2): 585. doi:10.1021/jo01037a517.
 |