Chemistry:Phosphorus acid
Phosphorus oxoacid is a generic name for any acid whose molecule consists of atoms of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen.[1] There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anions and organic groups are present in stable salts and esters. The most important ones — in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research — are the phosphoric acids, whose esters and salts are the phosphates. In general, any hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom is acidic, meaning that the –OH group can lose a proton H+ leaving a negatively charged –O− group and thus turning the acid into a phosphorus oxoanion. Each additional proton lost has an associated acid dissociation constant Ka1, Ka2 Ka3, ..., often expressed by its cologarithm (pKa1, pKa2, pKa3, ...). Hydrogen atoms bonded directly to phosphorus are generally not acidic.
Classification
The phosphorus oxoacids can be classified by the oxidation state(s) of the phosphorus atom(s), which may vary from +1 to +5. The oxygen atoms are usually in oxidation state -2, but may be in state -1 if the molecule includes peroxide groups.
Oxidation state +1
- Hypophosphorous or phosphinic acid, H3PO2 (or H2PO(OH)), a monoprotic acid (meaning that only one of the hydrogen atoms is acidic). Its salts and esters are called hypophosphites or phosphinites.
Oxidation state +3
- Phosphorous or phosphonic acid, H3PO3 (or HPO(OH)2), a diprotic acid (with only two acidic hydrogens). Its salts and esters are called phosphites or phosphonates.
Oxidation state +4
- Hypophosphoric acid, H4P2O6 (or (HO)2P–P(OH)2). All four hydrogens are acidic. Its salts and esters are hypophosphates.
Oxidation state +5
The most important members of this group are the phosphoric acids, where each phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. Their generic formula is Hn−x+2PnO3n−x+1, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure.
These acids, and their esters and salts ("phosphates") include some of the best-known and most important compounds of phosphorus.
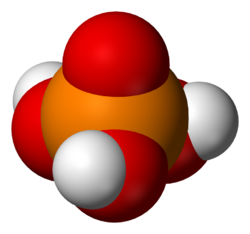
The simplest member of this class is
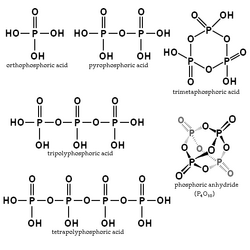
- Phosphoric acid proper, also called orthophosphoric or monophosphoric acid, H3PO4 (or OP(OH)3), a triprotic acid. It forms orthophosphate salt and esters, commonly called phosphates.
The smallest compounds of this class with two or more phosphorus atoms are called "oligophosphoric acids", and the larger ones, with linear –P–O– backbones, are "polyphosphoric acids"; with no definite separation between the two. Some of the most important members are:
- Pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7 (or (HO)2P–O–P(OH)2), with four acid hydrogens. Forms pyrophosphates.
- Triphosphoric or tripolyphosphoric acid, H5P3O10 (or (HO)2P–O–P(OH)–O–P(OH)2), with five acidic hydrogens. Forms triphosphates or tripolyphosphates.
- Tetraphosphoric acid, H6P4O13 (or (HO)2P(–O–P(OH))2–O–P(OH)2), with six acidic hydrogens. Forms tetraphosphates.
Thebackbone may be branched, as in
- triphosphono phosphoric acid, H6P4O13 or P(O)(–OP(O)(OH)2)3, a branched isomer of tetrapolyphosphoric acid.
The PO4 tetrahedra may be connected to form closed –P–O– chains, as in
- Trimetaphosphoric, or cyclo-triphosphoric acid, H3P3O9 (or (HPO3)3, (–P(O)(OH)–O–)3), a cyclic molecule with three acidic hydrogens. Forms the trimetaphosphate salts and esters.
Metaphosphoric acid is general term for phosphoric acids with a single cycle, (–P(O)(OH)–O–)n, whose elemental formula is HPO3.
-
Tetrapolyphosphoric acid
H6P4O13 -
Trimetaphosphoric acid
H3P3O9
Another compound that may be included in this class is
- Peroxomonophosphoric acid, H3PO5 (or OP(OH)2(OOH)), which can be seen as monophosphoric acid with a peroxide group replacing the oxygen atom in one of the hydroxyl groups
Mixed oxidation states
Some phosphorus oxoacids have two or more P atoms in different oxidation states. One example is
- Isohypophosphoric acid, H4P2O6 (or H(OH)(O)P−O−P(O)(OH)2), a tetraprotic acid and isomer of hypophosphoric acid, containing P in oxidation state +3 and +5
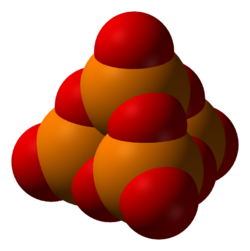
P4O10
See also
Further reading
- "Polyphosphate in bone". Biochemistry (Moscow) 65 (3): 296–303. Mar 2000. Archived from the original on 2011-08-25. https://web.archive.org/web/20110825053648/http://protein.bio.msu.su/biokhimiya/contents/v65/pdf/bcm_0296.pdf.
External links
- Determination of Polyphosphates Using Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection, Application Note 71 by Dionex
- US patent 3044851
- Phosphorus+Acids at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
| |
This article includes a list of related items that share the same name (or similar names). If an internal link incorrectly led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |