Chemistry:Phosphorus pentasulfide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| P 4S 10 | |
| Molar mass | 444.50 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Odor | Rotten eggs[1] |
| Density | 2.09 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| Boiling point | 514 °C (957 °F; 787 K) |
| Hydrolyses | |
| Solubility in other solvents |
|
| Vapor pressure | 1 mmHg (300°C)[1] |
| Structure | |
| triclinic, aP28 | |
| P1 (No. 2) | |
| Td | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
389 mg/kg (oral, rat)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 ST 3 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
250 mg/m3[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
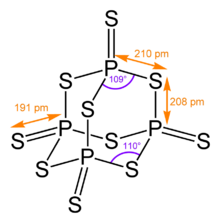
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P
2S
5 (empirical) or P
4S
10 (molecular). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF.[3]
Structure and synthesis
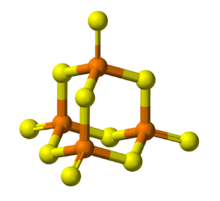
Its tetrahedral molecular structure is similar to that of adamantane and almost identical to the structure of phosphorus pentoxide.[4]
Phosphorus pentasulfide is obtained by the reaction of liquid white phosphorus (P
4) with sulfur above 300 °C. The first synthesis of P
4S
10 by Berzelius in 1843[5][6] was by this method. Alternatively, P
4S
10 can be formed by reacting elemental sulfur or pyrite, FeS
2, with ferrophosphorus, a crude form of Fe
2P (a byproduct of white phosphorus (P
4) production from phosphate rock):
- 4 Fe
2P + 18 S → P
4S
10 + 8 FeS - 4 Fe
2P + 18 FeS
2 P
4S
10 + 26 FeS
Applications
Approximately 150,000 tons of P
4S
10 are produced annually. The compound is mainly converted to other derivatives for use as lubrication additives such as zinc dithiophosphates.
It is widely used in the production of sodium dithiophosphate for applications as a flotation agent in the concentration of molybdenite minerals. It is also used in the production of pesticides such as Parathion and Malathion.[7] It is also a component of some amorphous solid electrolytes (e.g. Li
2S-P
2S
5) for some types of lithium batteries.
Phosphorus pentasulfide is a dual-use material, for the production of early insecticides such as Amiton and also for the manufacture of the related VX nerve agents.
Reactivity
Due to hydrolysis by atmospheric moisture, P
4S
10 evolves hydrogen sulfide H
2S, thus P
4S
10 is associated with a rotten egg odour. Aside from H
2S, hydrolysis of P
4S
10 eventually gives phosphoric acid:
- P
4S
10 + 16 H
2O → 4 H
3PO
4 + 10 H
2S
Other mild nucleophiles react with P
4S
10, including alcohols and amines. Aromatic compounds such as anisole, ferrocene and 1-methoxynaphthalene react to form 1,3,2,4-dithiadiphosphetane 2,4-disulfides such as Lawesson's reagent.
P
4S
10 is used as a thionation reagent. Reactions of this type require refluxing solvents such as benzene, dioxane, or acetonitrile with P
4S
10 dissociating into P
2S
5. Some ketones, esters, and imides are converted to the corresponding thiocarbonyls. Amides give thioamides. With 1,4-diketones the reagent forms thiophenes. It is also used to deoxygenate sulfoxides. The use of P
4S
10 has been displaced by the aforementioned Lawesson's reagent.[8]
P
4S
10 reacts with pyridine to form the complex P
2S
5(pyridine)
2.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0510". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0510.html.
- ↑ "Phosphorus pentasulfide". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/1314803.html.
- ↑ Scott D. Edmondson, Mousumi Sannigrahi "Phosphorus(V) sulfide" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2004 John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp166s.pub2
- ↑ Corbridge, D. E. C. (1995). Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology (5th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- ↑ Berzelius, J. (1843). "Ueber die Verbindungen des Phosphors mit Schwefel". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie 46 (2): 129–154. doi:10.1002/jlac.18430460202. https://zenodo.org/record/1426971.
- ↑ Berzelius, J. (1843). "Ueber die Verbindungen des Phosphors mit Schwefel". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie 46 (3): 251–281. doi:10.1002/jlac.18430460303. https://zenodo.org/record/1426973. (continuation of p. 154 of the same volume)
- ↑ Bettermann, G.; Krause, W.; Riess, G.; Hofmann, T. (2002). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_527. ISBN 3527306730.
- ↑ Ozturk, T.; Ertas, E.; Mert, O. (2010). "A Berzelius Reagent, Phosphorus Decasulfide (P4S10), in Organic Syntheses". Chemical Reviews 110 (6): 3419–3478. doi:10.1021/cr900243d. PMID 20429553.
- ↑ Bergman, Jan; Pettersson, Birgitta; Hasimbegovic, Vedran; Svensson, Per H. (2011). "Thionations Using a P4S10−Pyridine Complex in Solvents Such as Acetonitrile and Dimethyl Sulfone". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 76 (6): 1546–1553. doi:10.1021/jo101865y. PMID 21341727.
 |

