Chemistry:Pyronaridine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
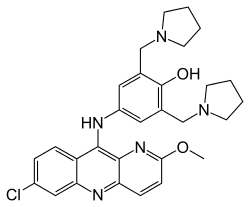 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pyronaridine tetraphosphate |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intramuscular injection, intravenous therapy |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H32ClN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 518.06 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Pyronaridine is an antimalarial drug.[1] It was first made in 1970 and has been in clinical use in China since the 1980s.[2]
In a small (n=88) malaria study in Camaroon, pyronaridine had a 100% cure rate, compared with 60% for chloroquine.[3]
It is one of the components of the artemisinin combination therapy pyronaridine/artesunate (Pyramax).[4]
It has also been studied as a potential anticancer drug,[5] and treatment for Ebola. The combination of pyronaridine and artesunate has been evaluated to have a synergistic effect of stronger antiviral effect and less toxicity.[6] The combination of pyronaridine and artesunate is being studied as a possible treatment for moderate to severe SARS-COV-2.[7]
References
- ↑ "Review of pyronaridine anti-malarial properties and product characteristics". Malaria Journal 11: 270. August 2012. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-11-270. PMID 22877082.
- ↑ "Studies on a new antimalarial compound: pyronaridine". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 86 (1): 7–10. 1992. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(92)90414-8. PMID 1566313.
- ↑ "Efficacy of oral pyronaridine for the treatment of acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria in African children". Clinical Infectious Diseases 26 (4): 946–953. April 1998. doi:10.1086/513942. PMID 9564481.
- ↑ "Pyramax". European Medicines Agency. 2016. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/medicine-outside-eu/pyramax-summary-public_en.pdf.
- ↑ "Pyronaridine exerts potent cytotoxicity on human breast and hematological cancer cells through induction of apoptosis". PLOS ONE 13 (11): e0206467. 2018. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0206467. PMID 30395606. Bibcode: 2018PLoSO..1306467V.
- ↑ "Repurposing the antimalarial pyronaridine tetraphosphate to protect against Ebola virus infection". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 13 (11): e0007890. November 2019. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007890. PMID 31751347.
- ↑ "Repurposing Antimalarials to Tackle the COVID-19 Pandemic". Trends in Parasitology 37 (1): 8–11. January 2021. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2020.10.003. PMID 33153922.
 |
