Chemistry:Artemether
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Many[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular[2] Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H26O5 |
| Molar mass | 298.379 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 86 to 88 °C (187 to 190 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Artemether is a medication used for the treatment of malaria.[2] The injectable form is specifically used for severe malaria rather than quinine.[2] In adults, it may not be as effective as artesunate.[2] It is given by injection in a muscle.[2] It is also available by mouth in combination with lumefantrine, known as artemether/lumefantrine.[3][4]
Artemether causes relatively few side effects.[5] An irregular heartbeat may rarely occur.[5] While there is evidence that use during pregnancy may be harmful in animals, there is no evidence of concern in humans.[5] The World Health Organization (WHO) therefore recommends its use during pregnancy.[5] It is in the artemisinin class of medication.[5]
Artemether has been studied since at least 1981, and has been in medical use since 1987.[6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7]
Medical uses
Artemether is an antimalarial drug for uncomplicated malaria caused by P. falciparum (and chloroquine-resistant P. falciparum) or chloroquine-resistant P. vivax parasites.[8] Artemether can also be used to treat severe malaria.[2]
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum with artemisinin-based combination therapy.[9] Given in combination with lumefantrine, it may be followed by a 14-day regimen of primaquine to prevent relapse of P. vivax or P. ovale malarial parasites and provide a complete cure.[10]
Artemether can also be used in treating and preventing trematode infections of schistosomiasis when used in combination with praziquantel.[11]
Artemether is rated category C by the FDA based on animal studies where artemisinin derivatives have shown an association with fetal loss and deformity. Some studies, however, do not show evidence of harm.[12][13]
Side effects
Possible side effects include cardiac effects such as bradycardia and QT interval prolongation.[14] Also, possible central nervous system toxicity has been shown in animal studies.[15][16]
Drug interactions
Plasma artemether level was found to be lower when the combination product was used with lopinavir/ritonavir.[16] There is also decreased drug exposure associated with concurrent use with efavirenz or nevirapine.[17][18]
Artemether/lumefantrine should not be used with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4.[19]
Hormonal contraceptives may not be as efficacious when used with artemether/lumefantrine.[19]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Artemether is an artemisinin derivative and the mechanism of action for artemisinins is.
Artemether interact with ferriprotoporphyrin IX (heme) or ferrous ions in the acidic parasite food vacuole, and generates cytotoxic radical species
The accepted mode of action of the peroxide containing drug involve its interaction with heme (byproduct of hemoglobin degradation), derived from the proteolysis of haemoglobin. This interaction results in the formation of toxic oxygen and carbon centered radicals.
One of the proposed mechanisms is that through inhibiting anti-oxidant and metabolic enzymes, artemisinin derivatives inflict oxidative and metabolic stress on the cell. Some pathways affected may concern glutathione and glucose metabolism. As a consequence, lesions and reduced growth of the parasite may result.[20]
Another possible mechanism of action suggests that artemisinin drugs exert their cidal action by inhibiting PfATP6. Since PfATP6 is an enzyme regulating cellular calcium concentration, its malfunctioning will lead to intracellular calcium accumulation, which in turns causes cell death.[21]
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption of artemether is improved 2- to 3-fold with food. It is highly bound to protein (95.4%). Peak concentrations of artemether are seen 2 hours after administration.[4]
Artemether is metabolized in the human body to the active metabolite, dihydroartemisinin, primarily by hepatic enzymes CYP3A4/5.[4] Both the parent drug and active metabolite are eliminated with a half-life of about 2 hours.[4]
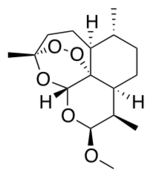
Chemistry
Artemether is a methyl ether derivative of artemisinin, which is a peroxide-containing lactone isolated from the antimalarial plant Artemisia annua. It is also known as dihydroartemisinin methyl ether, but its correct chemical nomenclature is (+)-(3-alpha,5a-beta,6-beta,8a-beta, 9-alpha,12-beta,12aR)-decahydro-10-methoxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-3,12-epoxy-12H-pyrano(4,3-j)-1,2-benzodioxepin. It is a relatively lipophilic and unstable drug,[22] which acts by creating reactive free radicals in addition to affecting the membrane transport system of the plasmodium organism.[14]
References
- ↑ "Artemether - Drugs.com". https://www.drugs.com/international/artemether.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "Artemether for severe malaria". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 6 (6): CD010678. June 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010678.pub3. PMID 31210357.
- ↑ "Artemether and Lumefantrine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/artemether-and-lumefantrine.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Coartem- artemether and lumefantrine tablet". 5 August 2019. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=7866ec19-dfac-47d4-a53f-511a12643cbf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "Treating severe malaria in pregnancy: a review of the evidence". Drug Safety 38 (2): 165–181. February 2015. doi:10.1007/s40264-014-0261-9. PMID 25556421.
- ↑ Tu Youyou and the Discovery of Artemisinin: 2015 Nobel Laureate in Physiology or Medicine. World Scientific. 2016. p. 162. ISBN 9789813109919. https://books.google.com/books?id=nmZtDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA162.
- ↑ World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2019. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ↑ "The clinical efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem)". Malaria Journal 8 (Suppl 1): S5. October 2009. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-8-S1-S5. PMID 19818172.
- ↑ Treatment of Uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. World Health Organization. 2015-01-01. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK294441/.
- ↑ Treatment Of Uncomplicated Malaria Caused By P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae or P. knowlesi. World Health Organization. 2015-01-01. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK294428/.
- ↑ "Systematic review and meta-analysis of artemisinin based therapies for the treatment and prevention of schistosomiasis". PLOS ONE 7 (9): e45867. 2012-01-01. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045867. PMID 23029285. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...745867P.
- ↑ "The safety of artemisinins during pregnancy: a pressing question". Malaria Journal 6: 15. February 2007. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-6-15. PMID 17300719.
- ↑ "Efficacy and safety of artemether-lumefantrine compared with quinine in pregnant women with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: an open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases 10 (11): 762–769. November 2010. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70202-4. PMID 20932805.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Artemether". http://www.antimicrobe.org/drugpopup/artemether.htm.
- ↑ "WHO Model Prescribing Information: Drugs Used in Parasitic Diseases - Second Edition: Protozoa: Malaria: Artemether". http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Jh2922e/2.5.10.html#Jh2922e.2.5.10.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Management of imported malaria in Europe". Malaria Journal 11: 328. September 2012. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-11-328. PMID 22985344.
- ↑ "Interactions between malaria and human immunodeficiency virus anno 2014". Clinical Microbiology and Infection 20 (4): 278–285. April 2014. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12597. PMID 24528518.
- ↑ "Clinical pharmacokinetic drug interactions associated with artemisinin derivatives and HIV-antivirals". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 53 (2): 141–153. February 2014. doi:10.1007/s40262-013-0110-5. PMID 24158666.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Artemether-lumefantrine: an option for malaria". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 46 (4): 567–577. April 2012. doi:10.1345/aph.1Q539. PMID 22496476.
- ↑ "Antischistosomal activity of artemisinin derivatives in vivo and in patients". Pharmacological Research 110: 216–226. August 2016. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.02.017. PMID 26902577.
- ↑ "Artemisinin anti-malarial drugs in China". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B 6 (2): 115–124. March 2016. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2016.01.008. PMID 27006895.
- ↑ "Relative response factor determination of β-artemether degradants by a dry heat stress approach". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 70: 111–116. November 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2012.06.002. PMID 22770733. https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/2938963.
 |

