Chemistry:Rebamipide
From HandWiki
Short description: Amino acid derivative
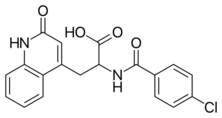 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mucosta (Japan ), Rebagen (South Korea , China , India ), Rebagit (Russia ), Rebamax (ID) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H15ClN2O4 |
| Molar mass | 370.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Rebamipide, an amino acid derivative of 2-(1H)-quinolinone, is used for mucosal protection,[1] healing of gastroduodenal ulcers, and treatment of gastritis.[2] It works by enhancing mucosal defense, scavenging free radicals,[3] and temporarily activating genes encoding cyclooxygenase-2.[4]
Studies have shown that rebamipide can fight the damaging effects of NSAIDs on the GIT mucosa,[5] and more recently, the small intestine, but not for naproxen-induced gastric damage.[6]
Availability
Rebamipide is used in a number of Asian countries including Japan (marketed as Mucosta), South Korea , China [7] and India (where it is marketed under the trade name Rebagen). It is also approved in Russia under the brand name Rebagit.[8]
References
- ↑ "Rebamipide: overview of its mechanisms of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing". Digestive Diseases and Sciences 43 (9 Suppl): 5S–13S. September 1998. PMID 9753220.
- ↑ "Rebamipide, novel prostaglandin-inducer accelerates healing and reduces relapse of acetic acid-induced rat gastric ulcer. Comparison with cimetidine". Digestive Diseases and Sciences 40 (11): 2469–72. November 1995. doi:10.1007/bf02063257. PMID 7587834.
- ↑ "Radical scavengers for elderly patients with age-related hearing loss". Acta Oto-Laryngologica 129 (1): 36–44. January 2009. doi:10.1080/00016480802008215. PMID 18607930.
- ↑ "Rebamipide activates genes encoding angiogenic growth factors and Cox2 and stimulates angiogenesis: a key to its ulcer healing action?". Digestive Diseases and Sciences 49 (2): 202–9. February 2004. doi:10.1023/b:ddas.0000017439.60943.5c. PMID 15104358.
- ↑ "Rebamipide helps defend against nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induced gastroenteropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Digestive Diseases and Sciences 58 (7): 1991–2000. July 2013. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2606-0. PMID 23456504.
- ↑ "Rebamipide does not protect against naproxen-induced gastric damage: a randomized double-blind controlled trial". BMC Gastroenterology 16 (1): 58. June 2016. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0472-x. PMID 27259970.
- ↑ "Rebamipide". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/international/rebamipide.html.
- ↑ "Registration Sertificate: Rebagit (rebamipide) Film-Coated Tablets" (in Russian). Russian State Register of Medicines.. http://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=bb32bbf8-84de-45c9-8ccf-df0789843d66&t=.
 |
