Chemistry:Nizatidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Axid, Tazac |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694030 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >70% |
| Protein binding | 35% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
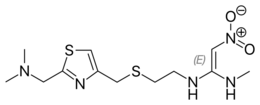
| Formula | C12H21N5O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 331.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nizatidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production, and is commonly used in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease.[1]
It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1988.[2][3] It was developed by Eli Lilly.
Medical use
Nizatidine is used to treat duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD/GORD), and to prevent stress ulcers.[4]
Adverse effects
Side effects are uncommon, usually minor, and include diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, drowsiness, headache, and muscle aches.[4]
History and development
Nizatidine was developed by Eli Lilly, and was first marketed in 1988.[2] It is considered to be equipotent with ranitidine and differs by the substitution of a thiazole ring in place of the furan ring in ranitidine. In September 2000, Eli Lilly announced they would sell the sales and marketing rights for Axid to Reliant Pharmaceuticals.[5] Subsequently, Reliant developed the oral solution of Axid, marketing this in 2004, after gaining approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[6] However, a year later, they sold rights of the Axid Oral Solution (including the issued patent[7] protecting the product) to Braintree Laboratories.[8]
Society and culture
Brand names
Brand names include Tazac and Axid.
References
- ↑ "[Nizatidine]" (in it). Medicina 9 (1): 93–96. 1989. PMID 2567957.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Nizatidine: FDA-Approved Drugs". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=019508.
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 44. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA444.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Nizatidine". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. NCBI Bookshelf. 25 January 2018. NBK548387. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548387/. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ↑ "Eli Lilly and Company and Reliant Pharmaceuticals Announce Agreement for U.S. Sales and Marketing Rights to Axid(R)". Encyclopedia.com. 7 September 2000. http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-65062714.html?Q=%22axid%22.
- ↑ "Reliant Pharmaceuticals to Launch AxidŽ Oral Solution". Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC. 26 July 2004. http://www.reliantrx.com/investor/press_releases/072604.htm.
- ↑ Bobotas G, Fawzy AA, "Liquid pharmaceutical composition", US patent 6930119, issued 24 June 2005, assigned to Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC
- ↑ "Reliant Pharmaceuticals Announces the Sale of Axid® Oral Solution to Braintree Laboratories". Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC. http://www.reliantrx.com/investor/press_releases/063005.htm.
 |
