Chemistry:Pirenzepine
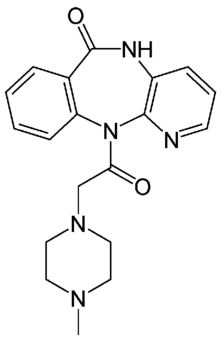 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gastrozepin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H21N5O2 |
| Molar mass | 351.410 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pirenzepine (Gastrozepin), an M1 selective antagonist, is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers, as it reduces gastric acid secretion and reduces muscle spasm. It is in a class of drugs known as muscarinic receptor antagonists; acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system which initiates the rest-and-digest state (as opposed to fight-or-flight), resulting in an increase in gastric motility and digestion; whereas pirenzepine would inhibit these actions and cause decreased gastric motility leading to delayed gastric emptying and constipation.[1] It has no effects on the brain and spinal cord as it cannot diffuse through the blood–brain barrier.
Pirenzepine has been investigated for use in myopia control.[2][3]
It promotes the homodimerization or oligomerisation of M1 receptors.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology. Springer. 2 August 2010. p. 811. ISBN 978-3-540-68698-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=qoyYobgX0uwC&pg=PA811. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ↑ "[Fundamentals of modern treatment of myopia]". Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis 51 (2): 5–9. 2005. PMID 16519089.
- ↑ "Interventions to slow progression of myopia in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1 (1): CD004916. January 2020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004916.pub4. PMID 31930781.
- ↑ "Dynamic Regulation of Quaternary Organization of the M1 Muscarinic Receptor by Subtype-selective Antagonist Drugs". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 291 (25): 13132–13146. June 2016. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.712562. PMID 27080256.
 |

