Chemistry:Rivaroxaban
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xarelto, others |
| Other names | BAY 59-7939 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a611049 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–100%; Cmax = 2–4 hours (10 mg oral)[3] |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4, CYP2J2 and CYP-independent mechanisms[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 5–9 hours in healthy subjects aged 20 to 45[3][6] |
| Excretion | 2/3 metabolized in liver and 1/3 eliminated unchanged[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molar mass | 435.88 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Rivaroxaban, sold under the brand name Xarelto among others, is an anticoagulant medication (blood thinner) used to treat and prevent blood clots.[7] Specifically it is used to treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary emboli and prevent blood clots in atrial fibrillation and following hip or knee surgery.[7] It is taken by mouth.[7]
Common side effects include bleeding.[7] Other serious side effects may include spinal hematoma and anaphylaxis.[7] It is unclear if use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is safe.[1] Compared to warfarin it has fewer interactions with other medications.[8] It works by blocking the activity of the clotting protein factor Xa.[7]
Rivaroxaban was patented in 2007 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2011.[9] In the United States, it will not be available as a generic medication until 2024.[10][11] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12] In 2020, it was the 86th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8 million prescriptions.[13][14]
Medical uses
In those with non-valvular atrial fibrillation, it appears to be as effective as warfarin in preventing ischemic strokes and embolic events.[15][16] Rivaroxaban is associated with lower rates of serious and fatal bleeding events than warfarin, though rivaroxaban is associated with higher rates of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.[17]
In July 2012, the UK's National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence recommended rivaroxaban to prevent and treat venous thromboembolism.[18]
Contraindications
Because of the difficulty associated with managing bleeding, rivaroxaban should be discontinued at least 24 hours before surgery, then restarted as soon as adequate hemostasis is established.[19]
Dosing recommendations do not recommend administering rivaroxaban with drugs known to be strong combined CYP3A4/P-glycoprotein inhibitors because this results in significantly higher plasma concentrations of rivaroxaban.[4][20]
Adverse effects
The most serious adverse effect is bleeding, including severe internal bleeding.[21][22][23] Rivaroxaban is associated with lower rates of serious and fatal bleeding events than warfarin but is associated with higher rates of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.[17]
(As of 2015), post-marketing assessments showed liver toxicity, and further studies are needed to quantify this risk.[24][25] In 2015, rivaroxaban accounted for the highest number of reported cases of serious injury among regularly monitored medications to the FDA's Adverse Events Reporting System (AERS).[26]
Reversal agent
In October 2014, Portola Pharmaceuticals completed Phase I and II clinical trials for andexanet alfa as an antidote for Factor Xa inhibitors with few adverse effects, and started Phase III trials.[27][28] Andexanet alfa was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in May 2018, under the trade name AndexXa.[29][30]
Mechanism of action
Rivaroxaban inhibits both free and bound Factor Xa in the prothrombinase complex.[31] It is a selective direct factor Xa inhibitor with an onset of action of 2.5 to 4 hours.[32] Inhibition of Factor Xa interrupts the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of the blood coagulation cascade, inhibiting both thrombin formation and development of thrombi. Rivaroxaban does not inhibit thrombin (activated Factor II), and no effects on platelets have been demonstrated.[3] It allows predictable anticoagulation and dose adjustments and routine coagulation monitoring;[3] dietary restrictions are not needed.[33]
Unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), and fondaparinux also inhibit the activity of factor Xa, indirectly, by binding to circulating antithrombin (AT III) and must be injected, whereas the orally active warfarin, phenprocoumon, and acenocoumarol are vitamin K antagonists (VKA), decreasing a number of coagulation factors, including factor X.[34]
Rivaroxaban has predictable pharmacokinetics across a wide spectrum of patients (age, gender, weight, race) and has a flat dose response across an eightfold dose range (5–40 mg).[35] The oral bioavailability is dose-dependent.[4] Doses of rivaroxaban under 10 mg can be taken with or without food, as it displayed high bioavailability independent of whether food was consumed or not.[36] If rivaroxaban is given at oral doses of 15 mg or 20 mg, it needs to be taken with food to aid in drug absorption and achieve appropriate bioavailability (≥ 80%).[36]
Chemistry
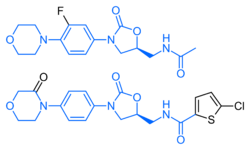
Rivaroxaban bears a striking structural similarity to the antibiotic linezolid: both drugs share the same oxazolidinone-derived core structure.[37] Accordingly, rivaroxaban was studied for any possible antimicrobial effects and for the possibility of mitochondrial toxicity, which is a known complication of long-term linezolid use.[38] Studies found that neither rivaroxaban nor its metabolites have any antibiotic effect against Gram-positive bacteria.[citation needed] As for mitochondrial toxicity, in vitro studies published before 2008 found the risk to be low.[37]
History
Rivaroxaban was initially developed by Bayer.[39] In the United States, it is marketed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals (a part of Johnson & Johnson).[39] It was the first available direct factor Xa inhibitor which is taken by mouth.[40]
Society and culture
Economics
Using rivaroxaban rather than warfarin costs 70 times more, according to Express Scripts Holding Co, the largest U.S. pharmacy benefits manager.[33] As of 2016, Bayer claimed that the drug was licensed in 130 countries and that more than 23 million patients had been treated.[41]
Legal status
In September 2008, Health Canada granted marketing authorization for rivaroxaban to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE) in people who have undergone elective total hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery.[42]
In the same month, the European Commission also granted marketing authorization of rivaroxaban to prevent venous thromboembolism in adults undergoing elective hip and knee replacement.[43][5]
On July 1, 2011, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved rivaroxaban for prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), in adults undergoing hip and knee replacement surgery.[44]
On November 4, 2011, the US FDA approved rivaroxaban for stroke prevention in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.[45]
Legal action
On March 25, 2019, over 25,000 lawsuits over rivaroxaban in the US were settled for $775 million to get paid out to those affected. Plaintiffs accused the drugmakers of not warning about the bleeding risks, claiming their injuries could have been prevented had doctors and patients been provided adequate information.[46]
Research
Researchers at the Duke Clinical Research Institute have been accused of withholding clinical data used to evaluate rivaroxaban.[47] Duke tested rivaroxaban in a clinical trial known as the ROCKET AF trial.[48] The clinical trial, published 2011 in the New England Journal of Medicine[49] and headed by Robert Califf, then Commissioner of the FDA,[50][49] found rivaroxaban to be more effective than warfarin in reducing the likelihood of ischemic strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation.[49] The validity of the study was called into question in 2014, when pharmaceutical sponsors Bayer and Johnson & Johnson revealed that the INRatio blood monitoring devices used were not functioning properly,[47][48] A subsequent analysis by the Duke team published in February 2016 found that this had no significant effect on efficacy and safety in the trial.[51]
Under-representation of racial minorities in clinical trials has been noted. Compared to warfarin, efficacy and safety was found to be similar across racial subgroups.[49]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Rivaroxaban Use During Pregnancy". https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/rivaroxaban.html.
- ↑ XARELTO (Bayer Australia Ltd)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "Xarelto 2.5 mg film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". 9 August 2022. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/3410/smpc.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Xarelto- rivaroxaban tablet, film coated Xarelto- rivaroxaban tablet, film coated Xarelto- rivaroxaban kit". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=10db92f9-2300-4a80-836b-673e1ae91610.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Xarelto EPAR". September 17, 2018. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/xarelto.
- ↑ "Rivaroxaban (xarelto) for the prevention of thromboembolic disease: an inside look at the oral direct factor xa inhibitor". P & T 34 (5): 238–44. May 2009. PMID 19561868.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 "Rivaroxaban Monograph for Professionals". American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/rivaroxaban.html.
- ↑ Oral Anticoagulation Therapy: Cases and Clinical Correlation. Springer. 2017. p. 11. ISBN 9783319546438. https://books.google.com/books?id=byYmDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA11.
- ↑ "Generic Xarelto Availability". https://www.drugs.com/availability/generic-xarelto.html.
- ↑ "Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/Scripts/cder/ob/patent_info.cfm?Product_No=004&Appl_No=022406&Appl_type=N.
- ↑ "Bayer, J&J Win Ruling That Upholds Patent for Xarelto Drug". April 22, 2019. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-07-13/bayer-j-j-win-ruling-that-upholds-patent-for-xarelto-drug.
- ↑ World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. 2021. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Rivaroxaban - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Rivaroxaban.
- ↑ "Interventions for Preventing Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review". Annals of Internal Medicine 169 (11): 774–787. December 2018. doi:10.7326/M18-1523. PMID 30383133.
- ↑ "Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, or Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Subgroups". Thrombosis 2013: 640723. 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/640723. PMID 24455237.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "A review of traditional and novel oral anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy for dermatologists and dermatologic surgeons". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 72 (3): 524–34. March 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.10.027. PMID 25486915.
- ↑ "Rivaroxaban for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism". July 25, 2012. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/TA261.
- ↑ "Perioperative Management of Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): A Systemic Review". Health Services Insights 9 (Suppl 1): 25–36. 2016. doi:10.4137/HSI.S40701. PMID 28008269.
- ↑ "Co-administration of rivaroxaban with drugs that share its elimination pathways: pharmacokinetic effects in healthy subjects". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 76 (3): 455–66. September 2013. doi:10.1111/bcp.12075. PMID 23305158.
- ↑ "Medication Guide – Xarelto". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM280333.pdf.
- ↑ "Xarelto Side Effects". WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-156265/xarelto-oral/details/list-sideeffects.
- ↑ "Xarelto Side Effects Center". RxList. http://www.rxlist.com/xarelto-side-effects-drug-center.htm.
- ↑ "Liver injury with novel oral anticoagulants: assessing post-marketing reports in the US Food and Drug Administration adverse event reporting system". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 80 (2): 285–93. August 2015. doi:10.1111/bcp.12611. PMID 25689417.
- ↑ "Rivaroxaban postmarketing risk of liver injury". Journal of Hepatology 61 (2): 293–300. August 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.03.026. PMID 24681117. http://www.zora.uzh.ch/id/eprint/94814/1/2014_J_Hepatol_rivaroxaban_russmann.pdf.
- ↑ "ISMP Ranks Xarelto Most Dangerous Drug in the United States". https://www.drugnews.net/news/ismp-ranks-xarelto-most-dangerous-drug-in-US.
- ↑ "Possible Antidote Could Help Blood Thinner Patients In Bleeding Emergencies". https://www.drugnews.net/news/antidote-xarelto-blood-thinner-patients-emergency/.
- ↑ "Recent advances in the development of specific antidotes for target-specific oral anticoagulants". Pharmacotherapy 35 (2): 198–207. February 2015. doi:10.1002/phar.1532. PMID 25644580.
- ↑ "Accelerated Approval for AndexXa". https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM606693.pdf.
- ↑ "U.S. FDA Approves Portola Pharmaceuticals' Andexxa, First and Only Antidote for the Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors" (Press release). Portola Pharmaceuticals Inc. May 4, 2018. Retrieved August 1, 2018 – via GlobeNewswire.
- ↑ "Discovery of the novel antithrombotic agent 5-chloro-N-({(5S)-2-oxo-3- [4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl}methyl)thiophene- 2-carboxamide (BAY 59-7939): an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48 (19): 5900–8. September 2005. doi:10.1021/jm050101d. PMID 16161994.
- ↑ "Outpatient Oral Anticoagulant Therapy". Consultative Hemostasis and Thrombosis (Fourth ed.). Elsevier. January 2019. pp. 747–777. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-46202-0.00037-6. ISBN 978-0-323-46202-0.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "New blood thinner 'antidote' to help doctors move past warfarin". Reuters. December 23, 2015. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-pharmaceuticals-bloodthinners-idUSKBN0U617320151223.
- ↑ "New oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation". European Heart Journal 29 (2): 155–65. January 2008. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm575. PMID 18096568.
- ↑ "A once-daily, oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor, rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939), for thromboprophylaxis after total hip replacement". Circulation 114 (22): 2374–2381. November 2006. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.642074. PMID 17116766.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "The effect of food on the absorption and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban". International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 51 (7): 549–561. July 2013. doi:10.5414/CP201812. PMID 23458226.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 European Medicines Agency (2008). "CHP Assessment Report for Xarelto (EMEA/543519/2008)". http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/xarelto/H-944-en6.pdf.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Singh AK, Noronha V, Gupta A, Singh D, Singh P, Singh A, Singh A. (2020). "Rivaroxaban: Drug review". Cancer Res Stat Treat 3 (2): 264–269. doi:10.4103/CRST.CRST_122_19.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Xarelto FDA Approval History". September 7, 2020. https://www.drugs.com/history/xarelto.html.
- ↑ "Rivaroxaban, the first oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 10 (18): 2945–2946. December 2009. doi:10.1517/14656560903413559. PMID 19925048.
- ↑ "Bayer comments on article in The British Medical Journal (BMJ) regarding Xarelto". Bayer AG Communications, Government Relations & Corporate Brand. September 29, 2016. http://www.press.bayer.com/baynews/baynews.nsf/id/6B53106BB5B7A379C125803C0060247B/$File/2016-0232E.pdf?open&mod=29.09.2016_07:31:43.
- ↑ "Bayer's Xarelto Approved in Canada" (Press release). Bayer. September 16, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ↑ "Bayer's Novel Anticoagulant Xarelto now also approved in the EU" (Press release). Bayer. February 10, 2008. Archived from the original on October 22, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Xarelto (rivaroxaban tablets) to Help Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients Undergoing Knee or Hip Replacement Surgery" (Press release). Janssen Pharmaceutica. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on November 5, 2011. Retrieved July 1, 2011.
- ↑ "FDA approves Xarelto to prevent stroke in people with common type of abnormal heart rhythm". US Food and Drug Association. November 4, 2011. https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm278646.htm.
- ↑ "Bayer, Johnson & Johnson settle more than 25,000 lawsuits over blood thinner Xarelto for $775 million". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/amphtml/business/economy/bayer-johnson-and-johnson-settle-more-than-25000-lawsuits-over-blood-thinner-xarelto-for-775-million/2019/03/25/53e2e6c8-4ef4-11e9-88a1-ed346f0ec94f_story.html.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 "Document Claims Drug Makers Deceived a Top Medical Journal". The New York Times. March 1, 2016. https://www.nytimes.com/2016/03/02/business/document-claims-drug-makers-deceived-a-top-medical-journal.html?_r=0.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 "Duke clinical trial under scrutiny in drug case". Duke Student Publishing Company. http://www.dukechronicle.com/article/2016/04/duke-clinical-trial-under-scrutiny-in-drug-case.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 "Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation". The New England Journal of Medicine 365 (10): 883–91. September 2011. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1009638. PMID 21830957.
- ↑ "Meet Robert M. Califf, M.D., Commissioner of Food and Drugs". https://www.fda.gov/AboutFDA/CentersOffices/ucm452317.htm.
- ↑ "Point-of-Care Warfarin Monitoring in the ROCKET AF Trial". The New England Journal of Medicine 374 (8): 785–8. February 2016. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1515842. PMID 26839968.
External links
- "Rivaroxaban". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/rivaroxaban.
 |

