Physics:Water of crystallization
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions.[1] In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.
Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks. Water of crystallization can generally be removed by heating a sample but the crystalline properties are often lost.
Compared to inorganic salts, proteins crystallize with large amounts of water in the crystal lattice. A water content of 50% is not uncommon for proteins.
Applications
Knowledge of hydration is essential for calculating the masses for many compounds. The reactivity of many salt-like solids is sensitive to the presence of water. The hydration and dehydration of salts is central to the use of phase-change materials for energy storage.[2]
Position in the crystal structure
File:H-bondingFeSO47aq.tif A salt with associated water of crystallization is known as a hydrate. The structure of hydrates can be quite elaborate, because of the existence of hydrogen bonds that define polymeric structures.[3] [4] Historically, the structures of many hydrates were unknown, and the dot in the formula of a hydrate was employed to specify the composition without indicating how the water is bound. Per IUPAC's recommendations, the middle dot is not surrounded by spaces when indicating a chemical adduct.[5] Examples:
- CuSO
4 · 5H2O – copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate - CoCl
2 · 6H2O – cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate - SnCl
2 · 2H2O – tin(II) (or stannous) chloride dihydrate
For many salts, the exact bonding of the water is unimportant because the water molecules are made labile upon dissolution. For example, an aqueous solution prepared from CuSO
4 · 5H2O and anhydrous CuSO
4 behave identically. Therefore, knowledge of the degree of hydration is important only for determining the equivalent weight: one mole of CuSO
4 · 5H2O weighs more than one mole of CuSO
4. In some cases, the degree of hydration can be critical to the resulting chemical properties. For example, anhydrous RhCl
3 is not soluble in water and is relatively useless in organometallic chemistry whereas RhCl
3 · 3H2O is versatile. Similarly, hydrated AlCl
3 is a poor Lewis acid and thus inactive as a catalyst for Friedel-Crafts reactions. Samples of AlCl
3 must therefore be protected from atmospheric moisture to preclude the formation of hydrates.
File:Ca(aq)6 improved image.tif
Crystals of hydrated copper(II) sulfate consist of [Cu(H
2O)
4]2+ centers linked to SO2−
4 ions. Copper is surrounded by six oxygen atoms, provided by two different sulfate groups and four molecules of water. A fifth water resides elsewhere in the framework but does not bind directly to copper.[6] The cobalt chloride mentioned above occurs as [Co(H
2O)
6]2+ and Cl−
. In tin chloride, each Sn(II) center is pyramidal (mean O/Cl–Sn–O/Cl angle is 83°) being bound to two chloride ions and one water. The second water in the formula unit is hydrogen-bonded to the chloride and to the coordinated water molecule. Water of crystallization is stabilized by electrostatic attractions, consequently hydrates are common for salts that contain +2 and +3 cations as well as −2 anions. In some cases, the majority of the weight of a compound arises from water. Glauber's salt, Na
2SO
4(H
2O)
10, is a white crystalline solid with greater than 50% water by weight.
Consider the case of nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate. This species has the formula NiCl
2(H
2O)
6. Crystallographic analysis reveals that the solid consists of [trans-NiCl
2(H
2O)
4] subunits that are hydrogen bonded to each other as well as two additional molecules of H
2O. Thus one third of the water molecules in the crystal are not directly bonded to Ni2+, and these might be termed "water of crystallization".
Analysis
The water content of most compounds can be determined with a knowledge of its formula. An unknown sample can be determined through thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) where the sample is heated strongly, and the accurate weight of a sample is plotted against the temperature. The amount of water driven off is then divided by the molar mass of water to obtain the number of molecules of water bound to the salt.
Other solvents of crystallization
Water is particularly common solvent to be found in crystals because it is small and polar. But all solvents can be found in some host crystals. Water is noteworthy because it is reactive, whereas other solvents such as benzene are considered to be chemically innocuous. Occasionally more than one solvent is found in a crystal, and often the stoichiometry is variable, reflected in the crystallographic concept of "partial occupancy". It is common and conventional for a chemist to "dry" a sample with a combination of vacuum and heat "to constant weight".
For other solvents of crystallization, analysis is conveniently accomplished by dissolving the sample in a deuterated solvent and analyzing the sample for solvent signals by NMR spectroscopy. Single crystal X-ray crystallography is often able to detect the presence of these solvents of crystallization as well. Other methods may be currently available.
Table of crystallization water in some inorganic halides
In the table below are indicated the number of molecules of water per metal in various salts.[7][8]
| Hydrated metal halides and their formulas |
Coordination sphere of the metal |
Equivalents of water of crystallization that are not bound to M |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium chloride CaCl 2(H 2O) 6 |
[Ca(μ-H 2O) 6(H 2O) 3]2+ |
none | example of water as a bridging ligand[9] |
| Titanium(III) chloride TiCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[TiCl 2(H 2O) 4]+ [10] |
two | isomorphous with VCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
| Titanium(III) chloride TiCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
[Ti(H 2O) 6]3+[10] |
none | isomeric with [TiCl 2(H 2O) 4]Cl.2H2O[11] |
| Zirconium(IV) fluoride ZrF 4(H 2O) 3 |
(μ–F) 2[ZrF 3(H 2O) 3] 2 |
none | rare case where Hf and Zr differ[12] |
| Hafnium tetrafluoride HfF 4(H 2O) 3 |
(μ–F) 2[HfF 2(H 2O) 2]n(H2O)n |
one | rare case where Hf and Zr differ[12] |
| Vanadium(III) chloride VCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[VCl 2(H 2O) 4]+ [10] |
two | |
| Vanadium(III) bromide VBr 3(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[VBr 2(H 2O) 4]+ [10] |
two | |
| Vanadium(III) iodide VI 3(H 2O) 6 |
[V(H 2O) 6]3+ |
none | relative to Cl− and Br− , I− competes poorly with water as a ligand for V(III) |
| Nb 6Cl 14(H 2O) 8 |
[Nb 6Cl 14(H 2O) 2] |
four | |
| Chromium(III) chloride CrCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[CrCl 2(H 2O) 4]+ |
two | dark green isomer, aka "Bjerrums's salt" |
| Chromium(III) chloride CrCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
[CrCl(H 2O) 5]2+ |
one | blue-green isomer |
| Chromium(II) chloride CrCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
trans-[CrCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | square planar/tetragonal distortion |
| Chromium(III) chloride CrCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
[Cr(H 2O) 6]3+ |
none | violet isomer. isostructural with aluminium compound[13] |
| Aluminum trichloride AlCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
[Al(H 2O) 6]3+ |
none | isostructural with the Cr(III) compound |
| Manganese(II) chloride MnCl 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[MnCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Manganese(II) chloride MnCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
cis-[MnCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | cis molecular, the unstable trans isomer has also been detected[14] |
| Manganese(II) bromide MnBr 2(H 2O) 4 |
cis-[MnBr 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | cis, molecular |
| Manganese(II) iodide MnI 2(H 2O) 4 |
trans-[MnI 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | molecular, isostructural with FeCl2(H2O)4.[15] |
| Manganese(II) chloride MnCl 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[MnCl 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging chloride |
| Manganese(II) bromide MnBr 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[MnBr 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging bromide |
| Iron(II) chloride FeCl 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[FeCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Iron(II) chloride FeCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
trans-[FeCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | molecular |
| Iron(II) bromide FeBr 2(H 2O) 4 |
trans-[FeBr 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | molecular,[16] hydrates of FeI2 are not known |
| Iron(II) chloride FeCl 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[FeCl 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging chloride |
| Iron(III) chloride FeCl 3(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[FeCl 2(H 2O) 4]+ |
two | one of four hydrates of ferric chloride,[17] isostructural with Cr analogue |
| Iron(III) chloride FeCl 3(H 2O) 2.5 |
cis-[FeCl 2(H 2O) 4]+ |
two | the dihydrate has a similar structure, both contain FeCl− 4 anions.[17] |
| Cobalt(II) chloride CoCl 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[CoCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Cobalt(II) bromide CoBr 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[CoBr 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Cobalt(II) iodide CoI 2(H 2O) 6 |
[Co(H 2O) 6]2+ |
none[18] | iodide competes poorly with water |
| Cobalt(II) bromide CoBr 2(H 2O) 4 |
trans-[CoBr 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | molecular[16] |
| Cobalt(II) chloride CoCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
cis-[CoCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | note: cis molecular |
| Cobalt(II) chloride CoCl 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[CoCl 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging chloride |
| Cobalt(II) chloride CoBr 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[CoBr 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging bromide |
| Nickel(II) chloride NiCl 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[NiCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Nickel(II) chloride NiCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
cis-[NiCl 2(H 2O) 4] |
none | note: cis molecular[16] |
| Nickel(II) bromide NiBr 2(H 2O) 6 |
trans-[NiBr 2(H 2O) 4] |
two | |
| Nickel(II) iodide NiI 2(H 2O) 6 |
[Ni(H 2O) 6]2+ |
none[18] | iodide competes poorly with water |
| Nickel(II) chloride NiCl 2(H 2O) 2 |
trans-[NiCl 4(H 2O) 2] |
none | polymeric with bridging chloride |
| Platinum(IV) chloride [Pt(H 2O) 2Cl 4](H 2O) 3[19] |
trans-[PtCl 4(H 2O) 2] |
3 | octahedral Pt centers; rare example of non-first row chloride-aquo complex |
| Platinum(IV) chloride [Pt(H 2O) 3Cl 3]Cl(H 2O) 0.5[20] |
fac-[PtCl 3(H 2O) 3]+ |
0.5 | octahedral Pt centers; rare example of non-first row chloride-aquo complex |
| Copper(II) chloride CuCl 2(H 2O) 2 |
[CuCl 4(H 2O) 2] 2 |
none | tetragonally distorted two long Cu-Cl distances |
| Copper(II) bromide CuBr 2(H 2O) 4 |
[CuBr 4(H 2O) 2] n |
two | tetragonally distorted two long Cu-Br distances[16] |
| Zinc(II) chloride ZnCl 2(H 2O) 1.33[21] |
2 ZnCl 2 + ZnCl 2(H 2O) 4 |
none | coordination polymer with both tetrahedral and octahedral Zn centers |
| Zinc(II) chloride ZnCl 2(H 2O) 2.5[22] |
Cl 3Zn(μ-Cl)Zn(H 2O) 5 |
none | tetrahedral and octahedral Zn centers |
| Zinc(II) chloride ZnCl 2(H 2O) 3[21] |
[ZnCl 4]2− + Zn(H 2O) 6]2+ |
none | tetrahedral and octahedral Zn centers |
| Zinc(II) chloride ZnCl 2(H 2O) 4.5[21] |
[ZnCl 4]2− + [Zn(H 2O) 6]2+ |
three | tetrahedral and octahedral Zn centers |
Hydrates of metal sulfates
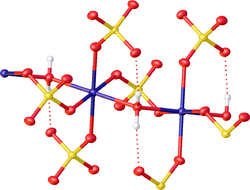
Transition metal sulfates form a variety of hydrates, each of which crystallizes in only one form. The sulfate group often binds to the metal, especially for those salts with fewer than six aquo ligands. The heptahydrates, which are often the most common salts, crystallize as monoclinic and the less common orthorhombic forms. In the heptahydrates, one water is in the lattice and the other six are coordinated to the ferrous center.[23] Many of the metal sulfates occur in nature, being the result of weathering of mineral sulfides.[24][25] Many monohydrates are known.[26]
| Formula of hydrated metal ion sulfate |
Coordination sphere of the metal ion |
Equivalents of water of crystallization that are not bound to M |
mineral name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgSO4(H2O) | [Mn(μ-H2O)(μ4,-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | kieserite | see Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn analogues |
| MgSO4(H2O)4 | [Mg(H2O)4(κ′,κ1-SO4)]2 | none | sulfate is bridging ligand, 8-membered Mg2O4S2 rings[27] | |
| MgSO4(H2O)6 | [Mg(H2O)6] | none | hexahydrate | common motif[24] |
| MgSO4(H2O)7 | [Mg(H2O)6] | one | epsomite | common motif[24] |
| TiOSO4(H2O) | [Ti(μ-O)2(H2O)(κ1-SO4)3] | none | further hydration gives gels | |
| VSO4(H2O)6 | [V(H2O)6] | none | Adopts the hexahydrite motif[28] | |
| VOSO4(H2O)5 | [VO(H2O)4(κ1-SO4)4] | one | ||
| Cr(SO4)(H2O)3 | [Cr(H2O)3(κ1-SO4)] | none | resembles Cu(SO4)(H2O)3[29] | |
| Cr(SO4)(H2O)5 | [CR(H2O)4(κ1-SO4)2] | one | resembles Cu(SO4)(H2O)5[30] | |
| Cr2(SO4)3(H2O)18 | [Cr(H2O)6] | six | One of several chromium(III) sulfates | |
| MnSO4(H2O) | [Mn(μ-H2O)(μ4,-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | szmikite | see Fe, Co, Ni, Zn analogues |
| MnSO4(H2O)4 | [Mn(μ-SO4)2(H2O)4][31] | none | Ilesitepentahydrate is called jôkokuite; the hexahydrate, the most rare, is called chvaleticeite | with 8-membered ring Mn2(SO4)2 core |
| MnSO4(H2O)5 | ? | jôkokuite | ||
| MnSO4(H2O)6 | ? | Chvaleticeite | ||
| MnSO4(H2O)7 | [Mn(H2O)6] | one | mallardite[25] | see Mg analogue |
| FeSO4(H2O) | [Fe(μ-H2O)(μ4-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | see Mn, Co, Ni, Zn analogues | |
| FeSO4(H2O)7 | [Fe(H2O)6] | one | melanterite[25] | see Mg analogue |
| FeSO4(H2O)4 | [Fe(H2O)4(κ′,κ1-SO4)]2 | none | sulfate is bridging ligand, 8-membered Fe2O4S2 rings[27] | |
| FeII(FeIII)2(SO4)4(H2O)14 | [FeII(H2O)6]2+[FeIII(H2O)4(κ1-SO4)2]−2 | none | sulfates are terminal ligands on Fe(III)[32] | |
| CoSO4(H2O) | [Co(μ-H2O)(μ4-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | see Mn, Fe, Ni, Zn analogues | |
| CoSO4(H2O)6 | [Co(H2O)6] | none | moorhouseite | see Mg analogue |
| CoSO4(H2O)7 | [Co(H2O)6] | one | bieberite[25] | see Fe, Mg analogues |
| NiSO4(H2O) | [Ni(μ-H2O)(μ4-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | see Mn, Fe, Co, Zn analogues | |
| NiSO4(H2O)6 | [Ni(H2O)6] | none | retgersite | One of several nickel sulfate hydrates[33] |
| NiSO4(H2O)7 | [Ni(H2O)6] | morenosite[25] | ||
| (NH4)2[Pt2(SO4)4(H2O)2] | [Pt2(SO4)4(H2O)2]2- | none | Pt-Pt bonded Chinese lantern structure[34] | |
| CuSO4(H2O)5 | [Cu(H2O)4(κ1-SO4)2] | one | chalcantite | sulfate is bridging ligand[35] |
| CuSO4(H2O)7 | [Cu(H2O)6] | one | boothite[25] | |
| ZnSO4(H2O) | [Zn(μ-H2O)(μ4-κ1-SO4)4][26] | none | see Mn, Fe, Co, Ni analogues | |
| ZnSO4(H2O)4 | [Zn(H2O)4(κ′,κ1-SO4)]2 | none | sulfate is bridging ligand, 8-membered Zn2O4S2 rings[27][36] | |
| ZnSO4(H2O)6 | [Zn(H2O)6] | none | see Mg analogue[37] | |
| ZnSO4(H2O)7 | [Zn(H2O)6] | one | goslarite[25] | see Mg analogue |
| CdSO4(H2O) | [Cd(μ-H2O)2(κ1-SO4)4] | none | bridging water ligand[38] |
Hydrates of metal nitrates
Transition metal nitrates form a variety of hydrates. The nitrate anion often binds to the metal, especially for those salts with fewer than six aquo ligands. Nitrates are uncommon in nature, so few minerals are represented here. Hydrated ferrous nitrate has not been characterized crystallographically.
| Formula of hydrated metal ion nitrate |
Coordination sphere of the metal ion |
Equivalents of water of crystallization that are not bound to M |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(NO3)3(H2O)9 | [Cr(H2O)6]3+ | three | octahedral configuration[39] isostructural with Fe(NO3)3(H2O)9 |
| Mn(NO3)2(H2O)4 | cis-[Mn(H2O)4(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration |
| Mn(NO3)2(H2O) | [Mn(H2O)(μ-ONO2)5] | none | octahedral configuration |
| Mn(NO3)2(H2O)6 | [Mn(H2O)6] | none | octahedral configuration[40] |
| Fe(NO3)3(H2O)9 | [Fe(H2O)6]3+ | three | octahedral configuration[41] isostructural with Cr(NO3)3(H2O)9 |
| Fe(NO3)3)(H2O)4 | [Fe(H2O)3(κ2-O2NO)2]+ | one | pentagonal bipyramid[42] |
| Fe(NO3)3(H2O)5 | [Fe(H2O)5(κ1-ONO2)]2+ | none | octahedral configuration[42] |
| Fe(NO3)3(H2O)6 | [Fe(H2O)6]3+ | none | octahedral configuration[42] |
| Co(NO3)2(H2O)2 | [Co(H2O)2(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration |
| Co(NO3)2(H2O)4 | [Co(H2O)4(κ1-ONO2)2 | none | octahedral configuration |
| Co(NO3)2(H2O)6 | [Co(H2O)6]2+ | none | octahedral configuration.[43] |
| α-Ni(NO3)2(H2O)4 | cis-[Ni(H2O)4(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration.[44] |
| β-Ni(NO3)2(H2O)4 | trans-[Ni(H2O)4(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration.[45] |
| Pd(NO3)2(H2O)2 | trans-[Pd(H2O)2(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | square planar coordination geometry[46] |
| Cu(NO3)2(H2O) | [Cu(H2O)(κ2-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration. |
| Cu(NO3)2(H2O)1.5 | uncertain | uncertain | uncertain[47] |
| Cu(NO3)2(H2O)2.5 | [Cu(H2O)2(κ1-ONO2)2] | one | square planar[48] |
| Cu(NO3)2(H2O)3 | uncertain | uncertain | uncertain [49] |
| Cu(NO3)2(H2O)6 | [Cu(H2O)6]2+ | none | octahedral configuration[50] |
| Zn(NO3)2(H2O)4 | cis-[Zn(H2O)4(κ1-ONO2)2] | none | octahedral configuration. |
Photos
-
Hydrated copper(II) sulfate is bright blue.
-
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate has a light turquoise tint.
See also
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Sharma, Atul; Tyagi, V.V.; Chen, C.R.; Buddhi, D. (2009). "Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 13 (2): 318–345. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2007.10.005.
- ↑ Wang, Yonghui; Feng, Liyun; Li, Yangguang; Hu, Changwen; Wang, Enbo; Hu, Ninghai; Jia, Hengqing (2002). "Novel Hydrogen-Bonded Three-Dimensional Networks Encapsulating One-Dimensional Covalent Chains: [M(4,4′-bipy)(H2O)4(4-abs)2·nH2O (4,4′-bipy = 4,4′-Bipyridine; 4-abs = 4-Aminobenzenesulfonate) (M = Co, n = 1; M = Mn, n = 2)"]. Inorganic Chemistry 41 (24): 6351–6357. doi:10.1021/ic025915o. PMID 12444778. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ic025915o.
- ↑ Maldonado, Carmen R.; Quirós, Miguel; Salas, J.M. (2010). "Formation of 2D water morphologies in the lattice of the salt with [Cu2(OH)2(H2O)2(phen)2]2+ as cation and 4,6-dimethyl-1,2,3-triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-5,7-dionato as anion". Inorganic Chemistry Communications 13 (3): 399–403. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2009.12.033.
- ↑ Connelly, Neil G.; Damhus, Ture; Hartshorn, Richard M.; Hutton, Alan T. (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 (the "Red Book"). p. 56. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. https://iupac.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Red_Book_2005.pdf. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ↑ Moeller, Therald (Jan 1, 1980). Chemistry: With Inorganic qualitative Analysis. Academic Press Inc (London) Ltd. p. 909. ISBN 978-0-12-503350-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=uyjjgw_EmXEC&q=dehydration+of+copper(lI)+sulfate+pentahydrate. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ↑ K. Waizumi; H. Masuda; H. Ohtaki (1992). "X-Ray Structural Studies of FeBr2·4H2O, CoBr2·4H2O, NiCl2·4H2O, and CuBr2·4H2O. cis/trans Selectivity in Transition Metal(II) Dihalide Tetrahydrate". Inorganica Chimica Acta 192 (2): 173–181. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)80756-2.
- ↑ B. Morosin (1967). "An X-ray Diffraction Study on Nickel(II) Chloride Dihydrate". Acta Crystallographica 23 (4): 630–634. doi:10.1107/S0365110X67003305.
- ↑ Agron, P. A.; Busing, W. R. (1986). "Calcium and Strontium Dichloride Hexahydrates by Neutron Diffraction". Acta Crystallographica Section C 42 (2): 14. doi:10.1107/S0108270186097007.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Donovan, William F.; Smith, Peter W. (1975). "Crystal and Molecular Structures of Aquahalogenovanadium(III) Complexes. Part I. X-Ray Crystal Structure of trans-Tetrakisaquadibromo-Vanadium(III) Bromide Dihydrate and the Isomorphous Chloro- Compound". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (10): 894. doi:10.1039/DT9750000894.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 965. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 965. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Andress, K. R.; Carpenter, C. (1934). "Die Struktur von Chromchlorid- und Aluminiumchloridhexahydrat". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Kristallgeometrie, Kristallphysik, Kristallchemie 87: 446–463.
- ↑ Zalkin, Allan; Forrester, J. D.; Templeton, David H. (1964). "Crystal Structure of Manganese Dichloride Tetrahydrate". Inorganic Chemistry 3 (4): 529–533. doi:10.1021/ic50014a017. http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/7vf7p79j.
- ↑ Moore, J. E.; Abola, J. E.; Butera, R. A. (1985). "Structure of Manganese(II) Iodide Tetrahydrate, MnI2·4H2O". Acta Crystallographica Section C 41 (9): 1284–1286. doi:10.1107/S0108270185007466.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Waizumi, Kenji; Masuda, Hideki; Ohtaki, Hitoshi (1992). "X-ray Structural Studies of FeBr2·4H2O, CoBr2·4H2O, NiCl2·4H2O and CuBr2·4H2O. cis/trans Selectivity in Transition Metal(II) Dihalide Tetrahydrate". Inorganica Chimica Acta 192 (2): 173–181. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)80756-2.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Simon A. Cotton (2018). "Iron(III) Chloride and Its Coordination Chemistry". Journal of Coordination Chemistry 71 (21): 3415–3443. doi:10.1080/00958972.2018.1519188.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Louër, Michele; Grandjean, Daniel; Weigel, Dominique (1973). "Structure Cristalline et Expansion Thermique de l'Iodure de Nickel Hexahydrate" (Crystal structure and thermal expansion of nickel(II) iodide hexahydrate)". Journal of Solid State Chemistry 7: 222–228. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(73)90157-6.
- ↑ Rau, F.; Klement, U.; Range, K. -J. (1995). "Crystal Structure of trans-Diaquatetrachloroplatinum(IV) trihydrate, Pt(H2O)2Cl4(H2O)3". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials 210 (8): 606. doi:10.1524/zkri.1995.210.8.606. Bibcode: 1995ZK....210..606R.
- ↑ Rau, F.; Klement, U.; Range, K. -J. (1995). "Crystal Structure of fac-Triaquatrichloroplatinum(IV) Chloride Hemihydrate, (Pt(H2O)3Cl3)Cl(H2O)0.5". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials 210 (8): 605. doi:10.1524/zkri.1995.210.8.605. Bibcode: 1995ZK....210..605R.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Follner, H.; Brehler, B. (1970). "Die Kristallstruktur des ZnCl2.4/3H2O". Acta Crystallographica Section B 26 (11): 1679–1682. doi:10.1107/S0567740870004715.
- ↑ Hennings, Erik; Schmidt, Horst; Voigt, Wolfgang (2014). "Crystal Structures of ZnCl2·2.5H2O, ZnCl2·3H2O and ZnCl2·4.5H2O". Acta Crystallographica Section E 70 (12): 515–518. doi:10.1107/S1600536814024738. PMID 25552980.
- ↑ Baur, W. H. (1964). "On the crystal chemistry of salt hydrates. III. The determination of the crystal structure of FeSO4(H2O)7 (melanterite)". Acta Crystallographica 17 (9): 1167–1174. doi:10.1107/S0365110X64003000.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Chou, I-Ming; Seal, Robert R.; Wang, Alian (2013). "The stability of sulfate and hydrated sulfate minerals near ambient conditions and their significance in environmental and planetary sciences". Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 62: 734–758. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.027. Bibcode: 2013JAESc..62..734C.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 25.6 Redhammer, G. J.; Koll, L.; Bernroider, M.; Tippelt, G.; Amthauer, G.; Roth, G. (2007). "Co2+–Cu2+ Substitution in Bieberite Solid-Solution Series, (Co1−xCuxSO4·7H2O, 0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.46: Synthesis, Single-Crystal Structure Analysis, and Optical Spectroscopy". American Mineralogist 92 (4): 532–545. doi:10.2138/am.2007.2229. Bibcode: 2007AmMin..92..532R.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 26.5 26.6 Wildner, M.; Giester, G. (1991). "The Crystal Structures of Kieserite-type Compounds. I. Crystal Structures of Me(II)SO4·H2O (Me = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn) (English translation)". Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie - Monatshefte: 296–306.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Baur, Werner H. (2002). "Zinc(II) Sulfate Tetrahydrate and Magnesium Sulfate Tetrahydrate. Addendum". Acta Crystallographica Section E 58 (4): e9–e10. doi:10.1107/S1600536802002192.
- ↑ Cotton, F. Albert; Falvello, Larry R.; Llusar, Rosa; Libby, Eduardo; Murillo, Carlos A.; Schwotzer, Willi (1986). "Synthesis and Characterization of Four Vanadium(II) Compounds, Including Vanadium(II) Sulfate Hexahydrate and Vanadium(II) Saccharinates". Inorganic Chemistry 25 (19): 3423–3428. doi:10.1021/ic00239a021.
- ↑ Dahmen, T.; Glaum, R.; Schmidt, G.; Gruehn, R. (1990). "Zur Darstellung und Kristallstruktur von CrSO4·3H2O". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 586: 141–8. doi:10.1002/zaac.19905860119.
- ↑ T. P. Vaalsta; E. N. Maslen (1987). "Electron density in chromium sulfate pentahydrate". Acta Crystallogr. B43: 448–454. doi:10.1107/S0108768187097519.
- ↑ Held, Peter; Bohatý, Ladislav (2002). "Manganese(II) Sulfate Tetrahydrate (Ilesite)". Acta Crystallographica Section E 58 (12): i121–i123. doi:10.1107/S1600536802020962.
- ↑ L. Fanfani; A. Nunzi; P. F. Zanazzi (1970). "The Crystal Structure of Roemerite". American Mineralogist 55: 78–89.
- ↑ Stadnicka, K.; Glazer, A. M.; Koralewski, M. (1987). "Structure, absolute configuration and optical activity of α-nickel sulfate hexahydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B 43 (4): 319–325. doi:10.1107/S0108768187097787.
- ↑ Pley, Martin; Wickleder, Mathias S. (2005). "Monomers, Chains and Layers of [Pt2(SO4)4] Units in the Crystal Structures of the Platinum(III) Sulfates (NH4)2[Pt2(SO4)4(H2O)2], K4[Pt2(SO4)5] and Cs[Pt2(SO4)3(HSO4)]". European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry 2005 (3): 529–535. doi:10.1002/ejic.200400755.
- ↑ V. P. Ting, P. F. Henry, M. Schmidtmann, C. C. Wilson, M. T. Weller "In situ Neutron Powder Diffraction and Structure Determination in Controlled Humidities" Chem. Commun., 2009, 7527-7529. doi:10.1039/B918702B
- ↑ Blake, Alexander J.; Cooke, Paul A.; Hubberstey, Peter; Sampson, Claire L. (2001). "Zinc(II) sulfate tetrahydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section E 57 (12): i109–i111. doi:10.1107/S1600536801017998.
- ↑ Spiess, M.; Gruehn, R. (1979). "Beiträge zum thermischen Verhalten von Sulfaten. II. Zur thermischen Dehydratisierung des ZnSO4·7H2O und zum Hochtemperaturverhalten von wasserfreiem ZnSO4". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 456: 222–240. doi:10.1002/zaac.19794560124.
- ↑ Theppitak, Chatphorn; Chainok, Kittipong (2015). "Crystal Structure of CdSO4(H2O): A Redetermination". Acta Crystallographica Section E 71 (10): i8–i9. doi:10.1107/S2056989015016904. PMID 26594423.
- ↑ Lazar, D.; Ribár, B.; Divjaković, V.; Mészáros, Cs. (1991). "Structure of Hexaaquachromium(III) Nitrate Trihydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C 47 (5): 1060–1062. doi:10.1107/S0108270190012628.
- ↑ Petrovič, D.; Ribár, B.; Djurič, S.; Krstanovič, I. (1976). "The crystal structure of hexaquomanganese nitrate, Mn(OH2)6(NO3)2". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials 144 (1–6): 334–340. doi:10.1524/zkri.1976.144.16.334.
- ↑ Hair, Neil J.; Beattie, James K. (1977). "Structure of Hexaaquairon(III) Nitrate Trihydrate. Comparison of Iron(II) and Iron(III) Bond Lengths in High-Spin Octahedral Environments". Inorganic Chemistry 16 (2): 245–250. doi:10.1021/ic50168a006.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Schmidt, H.; Asztalos, A.; Bok, F.; Voigt, W. (2012). "New iron(III) nitrate hydrates: Fe(NO3)3·xH2O with x = 4, 5 and 6". Acta Crystallographica Section C C68 (6): i29-33. doi:10.1107/S0108270112015855. PMID 22669180.
- ↑ Prelesnik, P. V.; Gabela, F.; Ribar, B.; Krstanovic, I. (1973). "Hexaaquacobalt(II) nitrate". Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2 (4): 581–583.
- ↑ Gallezot, P.; Weigel, D.; Prettre, M. (1967). "Structure du Nitrate de Nickel Tétrahydraté". Acta Crystallographica 22 (5): 699–705. doi:10.1107/S0365110X67001392.
- ↑ Morosin, B.; Haseda, T. (1979). "Crystal Structure of the β Form of Ni(NO3)2·4H2O". Acta Crystallographica Section B 35 (12): 2856–2858. doi:10.1107/S0567740879010827.
- ↑ Laligant, Y.; Ferey, G.; Le Bail, A. (1991). "Crystal Structure of Pd(NO3)2(H2O)2". Materials Research Bulletin 26 (4): 269–275. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(91)90021-D.
- ↑ Dornberger-Schiff, K.; Leciejewicz, J. (1958). "Zur Struktur des Kupfernitrates Cu(NO3)2·1.5H2O". Acta Crystallographica 11 (11): 825–826. doi:10.1107/S0365110X58002322.
- ↑ Morosin, B. (1970). "The Crystal Structure of Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O". Acta Crystallographica B26 (9): 1203–1208. doi:10.1107/S0567740870003898.
- ↑ J. Garaj, Sbornik Prac. Chem.-Technol. Fak. Svst., Cskosl. 1966, pp. 35–39.
- ↑ Zibaseresht, R.; Hartshorn, R. M. (2006). "Hexaaquacopper(II) dinitrate: absence of Jahn-Teller distortion". Acta Crystallographica E62: i19–i22. doi:10.1107/S1600536805041851.
 |


