Chemistry:Manganese(II) bromide
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Manganese(II) bromide
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MnBr2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.746 g/mol (anhydrous) 286.60 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | pink crystalline |
| Density | 4.385 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 698 °C (1,288 °F; 971 K) (anhydrous) 64 °C (tetrahydrate) |
| Boiling point | 1,027 °C (1,881 °F; 1,300 K) |
| 146 g/100 mL at 20 °C[1] | |
| +13,900·10−6 cm3/mol | |
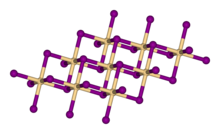
| Structure | |
| Trigonal, hP3, SpaceGroup = P-3m1, No. 164 | |
| octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P280 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Manganese(II) fluoride Manganese(II) chloride Manganese(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Iron(II) bromide Cobalt(II) bromide Manganese(III) bromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Manganese(II) bromide is the chemical compound composed of manganese and bromine with the formula MnBr2.
It can be used in place of palladium in the Stille reaction, which couples two carbon atoms using an organotin compound.[2]
References
- ↑ http://sites.chem.colostate.edu/diverdi/all_courses/CRC%20reference%20data/solubility%20of%20inorganic%20compounds.pdf [|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Cepanec, Ivica (2004). Synthesis of Biaryls. Elseveir. pp. 104. ISBN 0-08-044412-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=UMLOo1wXWdwC&q=%22Manganese(II)+bromide+%22&pg=PA104. Retrieved 2008-06-18.
 |

