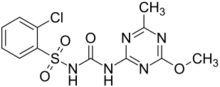
Chemistry:Chlorsulfuron
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-chloro-N-[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)carbamoyl]benzene-1-sulfonamide | |
| Other names
DPX4189
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 2588 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C12H12ClN5O4S | |
| Molar mass | 357.78 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.48 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 173 °C (343 °F; 446 K) |
| 12500 mg/L (20 °C) | |
| log P | -0.99 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.4 |
| Hazards[2] | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H400, H410 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlorsulfuron is an ALS (acetolactate synthase) inhibitor herbicide, and is a sulfonylurea compound.[3][4] It was discovered by George Levitt in February 1976 while working at DuPont, which was the patent assignee.[5][6][7]
Brand names
Originally introduced in 1982 under the brand name Glean by DuPont,[1][7] later also as Telar,[3] in North America.
Chemistry
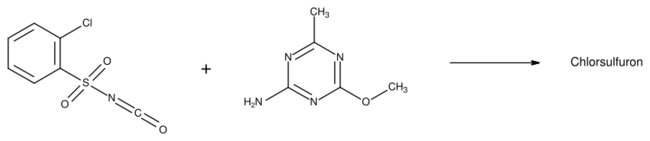
The first synthesis of chlorsulfuron was disclosed in a patent filed by DuPont in 1977. 2-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl isocyanate was condensed with 2-amino-4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazine to form the sulfonylurea product.[6]
Mode of action
Chlorsulfuron is an herbicide of the acetolactate synthase inhibitor (ALS inhibitor) class, HRAC (Herbicide Resistance Action Committee) group 2[4][3] (legacy HRAC Group B).[4]
Efficacy
Triticum aestivum is naturally resistant via aryl hydroxylation then conjugation with glucose compounds into non-herbicidal conjugates.[8] Widespread weed resistance to chlorsulfuron has been found across North America and around the world. T. aestivum's close relative Lolium rigidum was found to be using the same mechanism by Christopher et al 1991 and Cotterman & Saari 1992.[8] A North American population of Stellaria media was found by Hall and Devine 1990 to be resistant by way of an ALS target mutation rather than by improved disposal.[8] Increased P450 activity can also be effective, such as in Alopecurus myosuroides (found by Letouzé and Gasquez 2003), and L. rigidum (by Tardif and Powles 1999).[9] Another such mechanism - the acetolactate synthase target-site mutation Pro-197–Ser - was found by Roux et al 2004 to be accompanied by a 37% recessive fitness cost in a model (Arabidopsis thaliana).[10]
Use in genetic engineering
Genes conveying resistance to chlorsulfuron are used as selectable markers when attempting transformation with other genes,[11][12] for example in Dianthus caryophyllus[11] and Marchantia polymorpha.[12]
Crops have also been deliberately made resistant, for example in maize/corn by McCabe et al 1988 using bombardment with the relevant gene attached to tungsten particles.[13]
Applications
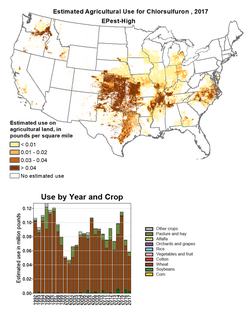
Chlorsulfuron has a broad spectrum of activity on commercially important broadleaf weeds and grasses but at the recommended use rate it is safe to important crops such as wheat. Its properties mean that it can be applied to soil so emerging weeds take it up and are controlled. Alternatively, spraying after weeds are already present in the crop will also lead to control. The product is used at application rates of 0.008–0.0155 pounds per acre (9.0–17.4 g/ha).[14] The estimated use in US agriculture is mapped by the US Geological Service and shows that from 1992 to 2017, the latest date for which figures are available, up to 120,000 pounds (54,000 kg) were applied each year. The compound is used mainly in wheat but also in pasture.[15]
Chlorsulfuron is recommended alone or with aminocyclopyrachlor for control of Centaurea solstitialis, Centaurea calcitrapa, and Centaurea iberica in the Pacific Northwest of North America.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Pesticide Properties Database. "Chlorsulfuron". University of Hertfordshire. http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/156.htm.
- ↑ PubChem Database. "Chlorsulfuron". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/175967.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Starthistle, yellow (Centaurea solstitialis), purple (Centaurea calcitrapa), and Iberian (Centaurea iberica)". Pacific Northwest Extension (Oregon, Washington, Idaho). 2015-11-10. http://pnwhandbooks.org/weed/problem-weeds/starthistle-yellow-centaurea-solstitialis-purple-centaurea-calcitrapa-iberian-centaurea-iberica.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "HRAC MOA 2020 Revision Description and Master Herbicide List". 2020-09-14. https://hracglobal.com/tools/hrac-moa-2020-revision-description-and-master-herbicide-list.
- ↑ George Levitt, "Herbicidal sulfonamides", DE patent 2715786, issued 1977, assigned to E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 George Levitt, "Herbicidal sulfonamides", US patent 4127405, issued 1978, assigned to E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Bhardwaj, Gaurab (2007). "From Pioneering Invention to Sustained Innovation: The Story of Sulfonylurea Herbicides". Chemical Heritage NewsMagazine 25 (1). http://faculty.babson.edu/gbhardwaj/Inventing%20Sulfonylurea%20Herbicides%20-%20CH.pdf.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Holt, Jodie S.; Powles, Steven B.; Holtum, Joseph A. M. (1993). "Mechanisms and Agronomic Aspects of Herbicide Resistance". Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology (Annual Reviews) 44 (1): 203–229. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.44.060193.001223. ISSN 1040-2519.
- ↑ Powles, Stephen B.; Yu, Qin (2010-06-02). "Evolution in Action: Plants Resistant to Herbicides". Annual Review of Plant Biology (Annual Reviews) 61 (1): 317–347. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112119. ISSN 1543-5008. PMID 20192743.
- ↑ Vila-Aiub, M M; Neve, P; Roux, F (2011-05-04). "A unified approach to the estimation and interpretation of resistance costs in plants". Heredity (The Genetics Society (Nature)) 107 (5): 386–394. doi:10.1038/hdy.2011.29. ISSN 0018-067X. PMID 21540885.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Tanaka, Yoshikazu; Brugliera, Filippa (2013-02-19). "Flower colour and cytochromes P450". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences (The Royal Society) 368 (1612): 20120432. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0432. ISSN 0962-8436. PMID 23297355.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Kohchi, Takayuki; Yamato, Katsuyuki T.; Ishizaki, Kimitsune; Yamaoka, Shohei; Nishihama, Ryuichi (2021-06-17). "Development and Molecular Genetics of Marchantia polymorpha". Annual Review of Plant Biology (Annual Reviews) 72 (1): 677–702. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-082520-094256. ISSN 1543-5008. PMID 33684298.
- ↑ Klein, Theodore M.; Arentzen, Rene; Lewis, Paul A.; Fitzpatrick-McElligott, Sandra (1992). "Transformation of Microbes, Plants and Animals by Particle Bombardment". Nature Biotechnology (Nature Portfolio) 10 (3): 286–291. doi:10.1038/nbt0392-286. ISSN 1087-0156. PMID 1368100.
- ↑ FMC Corporation (2019). "Glean XP herbicide US label". https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/ppls/000279-09600-20191120.pdf.
- ↑ US Geological Survey. "Estimated Agricultural Use for chlorsulfuron, 2017". https://water.usgs.gov/nawqa/pnsp/usage/maps/show_map.php?year=2017&map=CHLORSULFURON&hilo=H&disp=Chlorsulfuron.
 |