Biology:Mathematical modelling of infectious diseases
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic (including in plants) and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc.
History
The modelling of infectious diseases is a tool that has been used to study the mechanisms by which diseases spread, to predict the future course of an outbreak and to evaluate strategies to control an epidemic.[1]
The first scientist who systematically tried to quantify causes of death was John Graunt in his book Natural and Political Observations made upon the Bills of Mortality, in 1662. The bills he studied were listings of numbers and causes of deaths published weekly. Graunt's analysis of causes of death is considered the beginning of the "theory of competing risks" which according to Daley and Gani [1] is "a theory that is now well established among modern epidemiologists".
The earliest account of mathematical modelling of spread of disease was carried out in 1760 by Daniel Bernoulli. Trained as a physician, Bernoulli created a mathematical model to defend the practice of inoculating against smallpox.[2] The calculations from this model showed that universal inoculation against smallpox would increase the life expectancy from 26 years 7 months to 29 years 9 months.[3] Daniel Bernoulli's work preceded the modern understanding of germ theory.[4]
In the early 20th century, William Hamer[5] and Ronald Ross[6] applied the law of mass action to explain epidemic behaviour.
The 1920s saw the emergence of compartmental models. The Kermack–McKendrick epidemic model (1927) and the Reed–Frost epidemic model (1928) both describe the relationship between susceptible, infected and immune individuals in a population. The Kermack–McKendrick epidemic model was successful in predicting the behavior of outbreaks very similar to that observed in many recorded epidemics.[7]
Recently, agent-based models (ABMs) have been used in exchange for simpler compartmental models.[8] For example, epidemiological ABMs have been used to inform public health (nonpharmaceutical) interventions against the spread of SARS-CoV-2.[9] Epidemiological ABMs, in spite of their complexity and requiring high computational power, have been criticized for simplifying and unrealistic assumptions.[10][11] Still, they can be useful in informing decisions regarding mitigation and suppression measures in cases when ABMs are accurately calibrated.[12]
Assumptions
Models are only as good as the assumptions on which they are based. If a model makes predictions that are out of line with observed results and the mathematics is correct, the initial assumptions must change to make the model useful.[13]
- Rectangular and stationary age distribution, i.e., everybody in the population lives to age L and then dies, and for each age (up to L) there is the same number of people in the population. This is often well-justified for developed countries where there is a low infant mortality and much of the population lives to the life expectancy.
- Homogeneous mixing of the population, i.e., individuals of the population under scrutiny assort and make contact at random and do not mix mostly in a smaller subgroup. This assumption is rarely justified because social structure is widespread. For example, most people in London only make contact with other Londoners. Further, within London then there are smaller subgroups, such as the Turkish community or teenagers (just to give two examples), who mix with each other more than people outside their group. However, homogeneous mixing is a standard assumption to make the mathematics tractable.
Types of epidemic models
Stochastic
"Stochastic" means being or having a random variable. A stochastic model is a tool for estimating probability distributions of potential outcomes by allowing for random variation in one or more inputs over time. Stochastic models depend on the chance variations in risk of exposure, disease and other illness dynamics. Statistical agent-level disease dissemination in small or large populations can be determined by stochastic methods.[14] [15][16]
Deterministic
When dealing with large populations, as in the case of tuberculosis, deterministic or compartmental mathematical models are often used. In a deterministic model, individuals in the population are assigned to different subgroups or compartments, each representing a specific stage of the epidemic.[17]
The transition rates from one class to another are mathematically expressed as derivatives, hence the model is formulated using differential equations. While building such models, it must be assumed that the population size in a compartment is differentiable with respect to time and that the epidemic process is deterministic. In other words, the changes in population of a compartment can be calculated using only the history that was used to develop the model.[7]
Sub-exponential growth
A common explanation for the growth of epidemics holds that 1 person infects 2, those 2 infect 4 and so on and so on with the number of infected doubling every generation. It is analogous to a game of tag where 1 person tags 2, those 2 tag 4 others who've never been tagged and so on. As this game progresses it becomes increasing frenetic as the tagged run past the previously tagged to hunt down those who have never been tagged. Thus this model of an epidemic leads to a curve that grows exponentially until it crashes to zero as all the population have been infected. i.e. no herd immunity and no peak and gradual decline as seen in reality.[18]
Reproduction number
Endemic steady state
An infectious disease is said to be endemic when it can be sustained in a population without the need for external inputs. This means that, on average, each infected person is infecting exactly one other person (any more and the number of people infected will grow sub-exponentially and there will be an epidemic, any less and the disease will die out). In mathematical terms, that is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ R_0 S \ = 1. }[/math]
The basic reproduction number (R0) of the disease, assuming everyone is susceptible, multiplied by the proportion of the population that is actually susceptible (S) must be one (since those who are not susceptible do not feature in our calculations as they cannot contract the disease). Notice that this relation means that for a disease to be in the endemic steady state, the higher the basic reproduction number, the lower the proportion of the population susceptible must be, and vice versa. This expression has limitations concerning the susceptibility proportion, e.g. the R0 equals 0.5 implicates S has to be 2, however this proportion exceeds the population size.[citation needed]
Assume the rectangular stationary age distribution and let also the ages of infection have the same distribution for each birth year. Let the average age of infection be A, for instance when individuals younger than A are susceptible and those older than A are immune (or infectious). Then it can be shown by an easy argument that the proportion of the population that is susceptible is given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ S = \frac{A}{L}. }[/math]
We reiterate that L is the age at which in this model every individual is assumed to die. But the mathematical definition of the endemic steady state can be rearranged to give:
- [math]\displaystyle{ S = \frac {1} {R_0}. }[/math]
Therefore, due to the transitive property:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {1} {R_0} = \frac {A} {L} \Rightarrow R_0 = \frac {L} {A}. }[/math]
This provides a simple way to estimate the parameter R0 using easily available data.
For a population with an exponential age distribution,
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_0 = 1 + \frac {L} {A}. }[/math]
This allows for the basic reproduction number of a disease given A and L in either type of population distribution.
Compartmental models in epidemiology
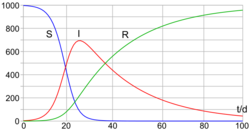
The SIR model
In 1927, W. O. Kermack and A. G. McKendrick created a model in which they considered a fixed population with only three compartments: susceptible, [math]\displaystyle{ S(t) }[/math]; infected, [math]\displaystyle{ I(t) }[/math]; and recovered, [math]\displaystyle{ R(t) }[/math]. The compartments used for this model consist of three classes:[19]
- [math]\displaystyle{ S(t) }[/math] is used to represent the individuals not yet infected with the disease at time t, or those susceptible to the disease of the population.
- [math]\displaystyle{ I(t) }[/math] denotes the individuals of the population who have been infected with the disease and are capable of spreading the disease to those in the susceptible category.
- [math]\displaystyle{ R(t) }[/math] is the compartment used for the individuals of the population who have been infected and then removed from the disease, either due to immunization or due to death. Those in this category are not able to be infected again or to transmit the infection to others.
Other compartmental models
There are many modifications of the SIR model, including those that include births and deaths, where upon recovery there is no immunity (SIS model), where immunity lasts only for a short period of time (SIRS), where there is a latent period of the disease where the person is not infectious (SEIS and SEIR), and where infants can be born with immunity (MSIR).[citation needed]
Infectious disease dynamics
Mathematical models need to integrate the increasing volume of data being generated on host-pathogen interactions. Many theoretical studies of the population dynamics, structure and evolution of infectious diseases of plants and animals, including humans, are concerned with this problem.[20]
Research topics include:
- antigenic shift
- epidemiological networks
- evolution and spread of resistance
- immuno-epidemiology
- intra-host dynamics
- Pandemic
- pathogen population genetics
- persistence of pathogens within hosts
- phylodynamics
- role and identification of infection reservoirs
- role of host genetic factors
- spatial epidemiology
- statistical and mathematical tools and innovations
- Strain structure and interactions
- transmission, spread and control of infection
- virulence
Mathematics of mass vaccination
If the proportion of the population that is immune exceeds the herd immunity level for the disease, then the disease can no longer persist in the population and its transmission dies out.[21] Thus, a disease can be eliminated from a population if enough individuals are immune due to either vaccination or recovery from prior exposure to disease. For example, smallpox eradication, with the last wild case in 1977, and certification of the eradication of indigenous transmission of 2 of the 3 types of wild poliovirus (type 2 in 2015, after the last reported case in 1999, and type 3 in 2019, after the last reported case in 2012).[22]
The herd immunity level will be denoted q. Recall that, for a stable state:[citation needed]
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_0 \cdot S = 1. }[/math]
In turn,
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_0=\frac{N}{S} = \frac{\mu N \operatorname E(T_L)}{\mu N \operatorname E[\min(T_L,T_S)]} = \frac{\operatorname E(T_L)}{\operatorname E[\min(T_L, T_S)]}, }[/math]
which is approximately:[citation needed]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\operatorname \operatorname E(T_L)}{\operatorname \operatorname E(T_S)} = 1+\frac{\lambda}{\mu} = \frac{\beta N }{v}. }[/math]
S will be (1 − q), since q is the proportion of the population that is immune and q + S must equal one (since in this simplified model, everyone is either susceptible or immune). Then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & R_0 \cdot (1-q) = 1, \\[6pt] & 1-q = \frac {1} {R_0}, \\[6pt] & q = 1 - \frac {1} {R_0}. \end{align} }[/math]
Remember that this is the threshold level. Die out of transmission will only occur if the proportion of immune individuals exceeds this level due to a mass vaccination programme.
We have just calculated the critical immunization threshold (denoted qc). It is the minimum proportion of the population that must be immunized at birth (or close to birth) in order for the infection to die out in the population.
- [math]\displaystyle{ q_c = 1 - \frac {1} {R_0}. }[/math]
Because the fraction of the final size of the population p that is never infected can be defined as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{t\to\infty} S(t) = e^{-\int_0^\infty \lambda(t) \, dt} = 1-p. }[/math]
Hence,
- [math]\displaystyle{ p = 1- e^{-\int_0^\infty \beta I(t) \, dt} = 1-e^{-R_0 p}. }[/math]
Solving for [math]\displaystyle{ R_0 }[/math], we obtain:
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_0 = \frac{-\ln(1-p)}{p}. }[/math]
When mass vaccination cannot exceed the herd immunity
If the vaccine used is insufficiently effective or the required coverage cannot be reached, the program may fail to exceed qc. Such a program will protect vaccinated individuals from disease, but may change the dynamics of transmission.[citation needed]
Suppose that a proportion of the population q (where q < qc) is immunised at birth against an infection with R0 > 1. The vaccination programme changes R0 to Rq where
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_q = R_0(1-q) }[/math]
This change occurs simply because there are now fewer susceptibles in the population who can be infected. Rq is simply R0 minus those that would normally be infected but that cannot be now since they are immune.
As a consequence of this lower basic reproduction number, the average age of infection A will also change to some new value Aq in those who have been left unvaccinated.
Recall the relation that linked R0, A and L. Assuming that life expectancy has not changed, now:[citation needed]
- [math]\displaystyle{ R_q = \frac{L}{A_q}, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ A_q = \frac{L}{R_q} = \frac{L}{R_0(1-q)}. }[/math]
But R0 = L/A so:
- [math]\displaystyle{ A_q = \frac{L}{(L/A)(1-q)} = \frac{AL}{L(1-q)} = \frac {A} {1-q}. }[/math]
Thus, the vaccination program may raise the average age of infection, and unvaccinated individuals will experience a reduced force of infection due to the presence of the vaccinated group. For a disease that leads to greater clinical severity in older populations, the unvaccinated proportion of the population may experience the disease relatively later in life than would occur in the absence of vaccine.
When mass vaccination exceeds the herd immunity
If a vaccination program causes the proportion of immune individuals in a population to exceed the critical threshold for a significant length of time, transmission of the infectious disease in that population will stop. If elimination occurs everywhere at the same time, then this can lead to eradication.[citation needed]
- Elimination
- Interruption of endemic transmission of an infectious disease, which occurs if each infected individual infects less than one other, is achieved by maintaining vaccination coverage to keep the proportion of immune individuals above the critical immunization threshold.[citation needed]
- Eradication
- Elimination everywhere at the same time such that the infectious agent dies out (for example, smallpox and rinderpest).[citation needed]
Reliability
Models have the advantage of examining multiple outcomes simultaneously, rather than making a single forecast. Models have shown broad degrees of reliability in past pandemics, such as SARS, SARS-CoV-2,[23] Swine flu, MERS and Ebola.[24]
See also
- Pandemic
- Compartmental models in epidemiology
- Contact tracing
- Critical community size
- Disease surveillance
- Ecosystem model
- Force of infection
- Landscape epidemiology
- Next-generation matrix
- Risk factor
- Sexual network
- WAIFW matrix
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Epidemic Modeling: An Introduction.. New York: Cambridge University Press. 2005.
- ↑ "The mathematics of infectious diseases". SIAM Review 42 (4): 599–653. 2000. doi:10.1137/S0036144500371907. Bibcode: 2000SIAMR..42..599H.
- ↑ "An attempt at a new analysis of the mortality caused by smallpox and of the advantages of inoculation to prevent it". Reviews in Medical Virology 14 (5): 275–88. 2004. doi:10.1002/rmv.443. PMID 15334536.
- ↑ "Germ Theory - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/mathematics/germ-theory.
- ↑ Epidemiology Old and New. London: Kegan Paul. 1928.
- ↑ Ross, Ronald (1910). The Prevention of Malaria. Dutton. http://catalog.hathitrust.org/Record/001587831.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Mathematical Models in Population Biology and Epidemiology.. New York: Springer. 2001.
- ↑ "Spatial pattern formation facilitates eradication of infectious diseases". The Journal of Applied Ecology 45 (2): 415–423. April 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01439.x. PMID 18784795. Bibcode: 2008JApEc..45..415E.
- ↑ "Special report: The simulations driving the world's response to COVID-19". Nature 580 (7803): 316–318. April 2020. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01003-6. PMID 32242115. Bibcode: 2020Natur.580..316A.
- ↑ "Computational Models That Matter During a Global Pandemic Outbreak: A Call to Action". Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 23 (2): 10. 2020. doi:10.18564/jasss.4298. ISSN 1460-7425. http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/23/2/10.html.
- ↑ "Modelling the pandemic". BMJ 369: m1567. April 2020. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1567. PMID 32317328. https://www.bmj.com/content/369/bmj.m1567.
- ↑ "Agent-based modelling for SARS-CoV-2 epidemic prediction and intervention assessment: A methodological appraisal". Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 26 (5): 1352–1360. October 2020. doi:10.1111/jep.13459. PMID 32820573.
- ↑ Huppert, A.; Katriel, G. (2013). "Mathematical modelling and prediction in infectious disease epidemiology". Clinical Microbiology and Infection 19 (11): 999–1005. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12308. PMID 24266045.
- ↑ Tembine, H. COVID-19: Data-Driven Mean-Field-Type Game Perspective. Games.. Games Journal. doi:10.3390/g11040051.
- ↑ Nakamura, Gilberto M.; Monteiro, Ana Carolina P.; Cardoso, George C.; Martinez, Alexandre S. (February 2017). "Efficient method for comprehensive computation of agent-level epidemic dissemination in networks" (in en). Scientific Reports 7 (1): 40885. doi:10.1038/srep40885. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 28106086. Bibcode: 2017NatSR...740885N.
- ↑ Nakamura, Gilberto M.; Cardoso, George C.; Martinez, Alexandre S. (February 2020). "Improved susceptible–infectious–susceptible epidemic equations based on uncertainties and autocorrelation functions" (in en). Royal Society Open Science 7 (2): 191504. doi:10.1098/rsos.191504. ISSN 2054-5703. PMID 32257317. Bibcode: 2020RSOS....791504N.
- ↑ Dietz, Klaus (1967). "Epidemics and Rumours: A Survey". Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series A (General) 130 (4): 505–528. doi:10.2307/2982521. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2982521.
- ↑ Maier, B. F.; Brockmann, D. (2020). "Effective containment explains subexponential growth in recent confirmed COVID-19 cases in China". Science 368 (6492): 742–746. doi:10.1126/science.abb4557. PMID 32269067. Bibcode: 2020Sci...368..742M.
- ↑ "Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics--I. 1927". Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 53 (1–2): 33–55. 1991. doi:10.1007/BF02464423. PMID 2059741. Bibcode: 1927RSPSA.115..700K.
- ↑ Brauer, Fred (2017). "Mathematical epidemiology: Past, present, and future". Infectious Disease Modelling 2 (2): 113–127. doi:10.1016/j.idm.2017.02.001. PMID 29928732.
- ↑ Britton, Tom; Ball, Frank; Trapman, Pieter (2020). "A mathematical model reveals the influence of population heterogeneity on herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2". Science 369 (6505): 846–849. doi:10.1126/science.abc6810. PMID 32576668. Bibcode: 2020Sci...369..846B.
- ↑ Pollard, Andrew J.; Bijker, Else M. (2021). "A guide to vaccinology: From basic principles to new developments". Nature Reviews Immunology 21 (2): 83–100. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-00479-7. PMID 33353987.
- ↑ Renz, Alina; Widerspick, Lina; Dräger, Andreas (2020). "FBA reveals guanylate kinase as a potential target for antiviral therapies against SARS-CoV-2". Bioinformatics 36 (Supplement_2): i813–i821. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa813. PMID 33381848. PMC 7773487. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa813.
- ↑ "Predicting COVID-19 using past pandemics as a guide: how reliable were mathematical models then, and how reliable will they be now?". Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 17 (6): 7502–7518. November 2020. doi:10.3934/mbe. PMID 33378907.
Further reading
- Keeling, Matt; Rohani, Pej. Modeling Infectious Diseases: In Humans and Animals. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- von Csefalvay, Chris. Computational Modeling of Infectious Disease. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier/Academic Press. https://chrisvoncsefalvay.github.io/computational-infectious-disease/. Retrieved 2023-02-27.
- Vynnycky, Emilia; White, Richard G.. An Introduction to Infectious Disease Modelling. http://anintroductiontoinfectiousdiseasemodelling.com/. Retrieved 2016-02-15. An introductory book on infectious disease modelling and its applications.
- "Mathematical models of infectious disease transmission". Nature Reviews. Microbiology 6 (6): 477–87. June 2008. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1845. PMID 18533288.
- "Mathematical models of disease transmission: a precious tool for the study of sexually transmitted diseases". Canadian Journal of Public Health 88 (4): 255–65. Jul–Aug 1997. doi:10.1007/BF03404793. PMID 9336095.
- Capasso, Vincenzo. Mathematical Structures of Epidemic Systems. Second Printing. Heidelberg, 2008: Springer.
External links
- Software
- Model-Builder: Interactive (GUI-based) software to build, simulate, and analyze ODE models.
- GLEaMviz Simulator: Enables simulation of emerging infectious diseases spreading across the world.
- STEM: Open source framework for Epidemiological Modeling available through the Eclipse Foundation.
- R package surveillance: Temporal and Spatio-Temporal Modeling and Monitoring of Epidemic Phenomena
 |