Astronomy:2007 VK184
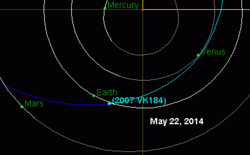 The 2014 close approach of 2007 VK184[1] | |
| Discovery[2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Catalina Sky Survey (703) |
| Discovery date | 12 November 2007 |
| Designations | |
| Minor planet category | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 2022-Aug-09 (JD 2459800.5)[1] | |
| Uncertainty parameter 1[1] | |
| Observation arc | 6.37 years |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.7098 AU |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.74286 AU |
| 1.7263 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.56969 |
| Orbital period | 828.5 d (2.27 yr) |
| Average Orbital speed | 22.8 km/s[lower-alpha 1] |
| Mean anomaly | 201.99° |
| Inclination | 1.2208° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 253.57° |
| 73.649° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00044 AU (66,000 km) |
| Venus MOID | 0.055 AU (8,200,000 km)[3] |
| Mars MOID | 0.033 AU (4,900,000 km) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | ~130 meters (430 ft)[4] |
| Mass | 3.3×109 kg (assumed)[4] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 22.0[1] |
2007 VK184 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, and estimated to be approximately 130 meters (430 ft) in diameter.[4] It was listed on the Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1 for a potential impactor in June 2048.[4] It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 28 March 2014.[5]
2023
The asteroid will come to opposition on 24 April 2023 when it will have a solar elongation of 177 degrees and an apparent magnitude of 22.[6] Then on 15 July 2023 the asteroid will harmlessly pass 0.2275 astronomical unit|AU (34.03 million km) from Earth.[1]
Description
2007 VK184 was discovered on 12 November 2007 by the Catalina Sky Survey.[2] It was recovered on 26 March 2014 by Mauna Kea,[7][3] and removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 28 March 2014.[5] By 4 January 2008, with an observation arc of 52 days, there was a 1 in 2700 chance of an impact with Earth on 3 June 2048.[8] The Sentry Risk Table, using an observation arc of 60 days, showed the asteroid had a 1 in 1820 chance (0.055%) of impacting Earth on 3 June 2048.[4] Since the March 2014 recovery, it is known that the asteroid will pass 0.013 astronomical unit|AU (1,900,000 km; 1,200,000 mi) from Earth on 2 June 2048.[1]
2014 passage
Before the 2014 close approach, the asteroid had a modest observation arc of 60 days,[4] and the imprecise trajectory of this asteroid was complicated by close approaches to Earth, Venus and Mars.[1] On 23 May 2014, the asteroid passed 0.17 AU (25,000,000 km; 16,000,000 mi) from Earth[1] and reached an apparent magnitude of ~20.8.[9] As expected the close approach allowed astronomers to recover the asteroid on 26 March 2014 and refine the odds of a future collision.[3] As the asteroid gets closer to Earth, the positional uncertainty becomes larger.[10] By recovering the asteroid well before closest approach you can avoid searching a larger region of the sky.[10] Most asteroids rated 1 on the Torino Scale are later downgraded to 0 after more observations come in.
Risk assessments were calculated based on a diameter of 130 meters.[4] It was estimated that, if it were ever to impact Earth, it would enter the atmosphere at a speed of 19.2 km/s and would have a kinetic energy equivalent to 150 megatons of TNT.[4] Assuming the target surface is sedimentary rock, the asteroid would impact the ground with the equivalent of 40 megatons of TNT and create a 2.1 kilometers (1.3 mi) impact crater.[11] Asteroids of approximately 130 meters in diameter are expected to impact Earth once every 11000 years or so.[11]
2048
On 26–27 March 2014, additional observations were made which ruled out the chance of an impact in 2048.[10] On 2 June 2048 the asteroid will pass 5 lunar distances from Earth[1] with a 3-sigma uncertainty region of ±20000 km.[12]
2118
By the Earth approach of June 2118 the known approaches become more divergent.
| Date | Minimum possible approach |
Maximum possible approach |
|---|---|---|
| 2118-Jun-06 ± 2 days | 0.00089 astronomical unit|AU (133 thousand km)[1][13] | 0.041 AU (6.1 million km)[1] |
See also
- 99942 Apophis, a NEO that, for a few days, was thought to have a slight probability of striking the Earth in 2029. But the likelihood that would happen was quickly determined to be zero.
Notes
- ↑ v = 42.1219 √1/r − 0.5/a, where r is the distance from the Sun, and a is the major semi-axis. Average velocity is at r=a=1.7 AU.
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2007 VK184)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=2007VK184&view=OPC. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "MPEC 2007-V94 : 2007 VK184". IAU Minor Planet Center. 2007-11-13. http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/K07/K07V94.html. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "2007 VK184 Orbit". IAU Minor Planet Center. http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=2007+VK184. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 "2007 VK184 Earth Impact Risk Summary". Wayback Machine:NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. 2013-10-17. Archived from the original on October 17, 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20131017014439/http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/risk/2007vk184.html. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Date/Time Removed". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/risk/removed.html. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- ↑ "Horizons Batch for 24 Apr 2023 Opposition". JPL Horizons. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons_batch.cgi?batch=1&COMMAND=%272007+VK184%27&START_TIME=%272023-04-01%27&STOP_TIME=%272023-04-30%27&STEP_SIZE=%271%20day%27&QUANTITIES=%279,20,23,29%27. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- ↑ "MPEC 2014-F50 : 2007 VK184". IAU Minor Planet Center. 2014-03-28. http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K14/K14F50.html. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
- ↑ "WayBack Machine archive from 10 Jan 2008". Wayback Machine. 2008-01-10. Archived from the original on January 10, 2008. https://web.archive.org/web/20080110092256/http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/risk/2007vk184.html. Retrieved 2013-02-20.
- ↑ "2012 VK184 Ephemerides for 23 May 2014". NEODyS (Near Earth Objects – Dynamic Site). https://newton.spacedys.com/neodys/index.php?pc=1.1.3.1&n=2007VK184&oc=500&y0=2014&m0=5&d0=1&h0=0&mi0=0&y1=2014&m1=6&d1=1&h1=0&mi1=0&ti=1.0&tiu=days. Retrieved 2013-02-21.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Asteroid 2007 VK184 Eliminated as Impact Risk to Earth". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. 2014-04-02. Archived from the original on 2015-11-08. https://web.archive.org/web/20151108094215/http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news183.html. Retrieved 2014-04-03.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Robert Marcus; H. Jay Melosh (2010). "Earth Impact Effects Program". Imperial College London / Purdue University. http://impact.ese.ic.ac.uk/ImpactEffects/. Retrieved 2013-02-20. (solution using 130 meters, 2600 kg/m3, 19.2 km/s, 45 degrees, target: sedimentary rock)
- ↑ "Horizons Batch for 2048-Jun-02". JPL Horizons. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons_batch.cgi?batch=1&COMMAND=%272007+VK184%27&START_TIME=%272048-Jun-02%27&STOP_TIME=%272048-Jun-03%27&STEP_SIZE=%272%20day%27&QUANTITIES=%2720,39%27. Retrieved 2022-07-29. RNG_3sigma = uncertainty range in km. (JPL#25/Soln.date: 2021-Apr-15 generates RNG_3sigma = 18862 km for 2048-Jun-02.)
- ↑ "Close approaches for 2007VK184 from 1950 to 2122". European Space Agency. https://neo.ssa.esa.int/search-for-asteroids?tab=closeapp&des=2007VK184. Retrieved 2022-07-30.
External links
- List Of The Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs), Minor Planet Center
- 2007 VK184 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 2007 VK184 at ESA–space situational awareness
- 2007 VK184 at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |