Biology:Glucan 1,4-alpha-maltohydrolase
From HandWiki
| Glucan 1,4-alpha-maltohydrolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.2.1.133 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 160611-47-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Glucan 1,4-alpha-maltohydrolase (EC 3.2.1.133, maltogenic alpha-amylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan alpha-maltohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name 4-alpha-D-glucan alpha-maltohydrolase.[1][2] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- hydrolysis of (1->4)-alpha-D-glucosidic linkages in polysaccharides so as to remove successive alpha-maltose residues from the non-reducing ends of the chains
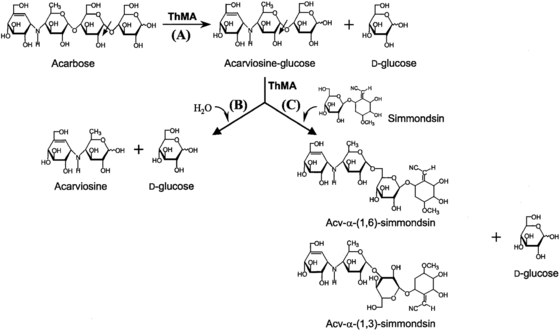
This enzyme acts on starch and related polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. Maltogenic amylases from Bacillus stearothermophilus,[3] Thermus sp.[4] and Geobacillus thermoleovorans[5] are able to degrade acarbose to glucose and acarviosine-glucose.
References
- ↑ "Cloning of a maltogenic α-amylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus". FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 56: 53–59. 1988. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb03149.x.
- ↑ "Properties and application of a thermostable maltogenic amylase produced by a strain of Bacillus modified by recombinant-DNA techniques". Stärke 36 (12): 405–411. 1984. doi:10.1002/star.19840361202.
- ↑ "Molecular and enzymatic characterization of a maltogenic amylase that hydrolyzes and transglycosylates acarbose". European Journal of Biochemistry 253 (1): 251–262. April 1998. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2530251.x. PMID 9578484.
- ↑ "Modes of action of acarbose hydrolysis and transglycosylation catalyzed by a thermostable maltogenic amylase, the gene for which was cloned from a Thermus strain" (in EN). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65 (4): 1644–1651. April 1999. doi:10.1128/AEM.65.4.1644-1651.1999. PMID 10103262. Bibcode: 1999ApEnM..65.1644K.
- ↑ "Dimerization mediates thermo-adaptation, substrate affinity and transglycosylation in a highly thermostable maltogenic amylase of Geobacillus thermoleovorans". PLOS ONE 8 (9): e73612. 2013-09-19. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073612. PMID 24069213. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...873612M.
External links
- Glucan+1,4-alpha-maltohydrolase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |