Biology:Iridovirus
| Iridovirus | |
|---|---|
| |
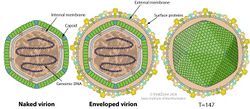
| Schematic drawings of Iridovirus virions | |

| |
| Armadillidium vulgare symptomatic of Invertebrate iridescent virus 31 (above) among individuals with typical colouration (below) | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Varidnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Bamfordvirae |
| Phylum: | Nucleocytoviricota |
| Class: | Megaviricetes |
| Order: | Pimascovirales |
| Family: | Iridoviridae |
| Subfamily: | Betairidovirinae |
| Genus: | Iridovirus |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Iridovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Iridoviridae.[1] Insects serve as natural hosts. Currently, only two species are placed in this genus. Invertebrate iridescent virus 6 (IIV-6) was recognised as the type species until such a designation was abolished. IIV-6 is hosted by mosquitos and usually causes covert (inapparent) infection that reduces fitness.[1][2] The remaining species Invertebrate iridescent virus 31 (IIV-31) is hosted by isopods and causes patent (apparent) infection characterised by blue to bluish-purple iridescence and a shortened lifespan.
Taxonomy
Group: dsDNA
- Family: Iridoviridae
- Genus: Iridovirus
- Invertebrate iridescent virus 6
- Invertebrate iridescent virus 31
Former species Invertebrate iridescent virus 1 (IIV-1) has been removed from Iridovirus. Its current status is a tentative member of Chloriridovirus.[4]
Structure
Viruses in Iridovirus are enveloped, with icosahedral and polyhedral geometries, and T=147 symmetry. Their diameter is around 185 nm. Genomes are linear, around 213 kb in length. The genome codes for 211 proteins.[1][2]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iridovirus | Polyhedral | T=147 | Linear | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Viral replication is nucleocytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral proteins to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the DNA strand displacement model. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. Invertebrates serve as their natural hosts.[2]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iridovirus | Invertebrates | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Lysis; budding | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | Contact |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Iridoviridae" (in en). https://ictv.global/report/chapter/iridoviridae/iridoviridae.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Viral Zone". ExPASy. http://viralzone.expasy.org/all_by_species/581.html. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ↑ ICTV: Master Species List 2018b.v2, on: ICTVonline: MSL #34 as of February 2019
- ↑ ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Invertebrate iridescent virus 1 (ZIP)
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q18819341 entry
 |

