Chemistry:Boron triiodide
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
triiodoborane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| BI3 | |||
| Molar mass | 391.52 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 3.35 g/cm3 (50 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 49.9 °C (121.8 °F; 323.0 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) | ||
| soluble,hydrolysis | |||
| Solubility | soluble in CCl4, CS2, benzene, chloroform | ||
| 0D | |||
| Structure | |||
| hexagonal | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
71 J/mol K | ||
Std molar
entropy (S |
200 J/mol K | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-37.2 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −18 °C (0 °F; 255 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Boron trifluoride Boron trichloride Boron tribromide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
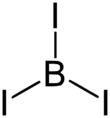
Boron triiodide is a chemical compound of boron and iodine with chemical formula BI3. It has a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
Preparation
Boron triiodide can be prepared by the reaction of boron with iodine at 209.5 °C or 409.1 °F.[citation needed] It can also be prepared by reacting hydroiodic acid with boron trichloride:
- 3HI + BCl
3 → BI
3 + 3HCl (reaction requires high temperature)
Another method is by reacting lithium borohydride with iodine. As well as boron triiodide, this reaction also produces lithium iodide, hydrogen and hydrogen iodide:[2]
- 3LiBH
4 + 8I
2 → 3LiI + 3BI
3 + 4H
2 + 4HI
Properties
In its pure state, boron triiodide forms colorless, otherwise reddish, shiny, air and hydrolysis-sensitive[3] crystals, which have a hexagonal crystal structure (a = 699.09 ± 0.02 pm, c = 736.42 ± 0.03 pm, space group P63/m (space group no. 176)).[4] Boron triiodide is a strong Lewis acid and soluble in carbon disulfide.[2]
Boron triiodide reacts with water and decomposes to boric acid and hydriodic acid:
- BI
3 + 3H
2O ⇌ B(OH)
3 + 3HI
Its dielectric constant is 5.38 and its heat of vaporization is 40.5 kJ/mol. At extremely high pressures, BI3 becomes metallic at ~23 GPa and is a superconductor above ~27 GPa.[5]
Applications
Boron triiodide can be used to produce other chemical compounds and as a catalyst (for example in coal liquefaction).[6]
References
- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Handbuch der präparativen anorganischen Chemie. 2 (3., umgearb. Aufl ed.). Stuttgart: Enke. 1978. ISBN 978-3-432-87813-3.
- ↑ "Beiträge zur Chemie der Bor-Stickstoff-Verbindungen". http://www-brs.ub.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/netahtml/HSS/Diss/StangeBernd/diss.pdf.
- ↑ Albert, Barbara; Schmitt, Konny (May 2001). "Die Kristallstruktur von Bortriiodid, BI3" (in de). Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 627 (5): 809–810. doi:10.1002/1521-3749(200105)627:5<809::AID-ZAAC809>3.0.CO;2-J. ISSN 0044-2313. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/1521-3749(200105)627:53.0.CO;2-J.
- ↑ Hamaya, Nozomu; Ishizuka, Miyuki; Onoda, Suzue; Guishan, Jiang; Ohmura, Ayako; Shimizu, Katsuya (2010). "Pressure-induced phase transition, metallization, and superconductivity in boron triiodide". Physical Review B 82 (9): 094506. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.82.094506. Bibcode: 2010PhRvB..82i4506H.
- ↑ "Kohleverflüssigung – Innovations Report". https://www.innovations-report.de/fachgebiete/biowissenschaften-chemie/bericht-53763/.
External links
- MSDS (link is broken)
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |