Chemistry:Ibrexafungerp
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /aɪˌbrɛksəˈfʌndʒɜːrp/ eye-BREKS-ə-FUN-jurp |
| Trade names | Brexafemme |
| Other names | SCY-078 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, intravenous |
| Drug class | Antifungal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hydroxylation (CYP3A4) then conjugation (glucuronidation, sulfation)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
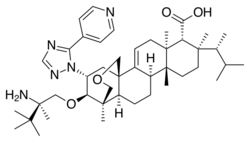
| Formula | C44H67N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 730.051 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ibrexafungerp, sold under the brand name Brexafemme, is an antifungal medication used to treat vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) (vaginal yeast infection).[1] It is taken orally (by mouth).[1] It is also currently undergoing clinical trials for other indications via an intravenous (IV) formulation. An estimated 75% of women will have at least one episode of VVC and 40 to 45% will have two or more episodes in their lifetime.[2]
Ibrexafungerp acts via inhibition of glucan synthase, which prevents formation of the fungal cell wall.[1]
Ibrexafungerp was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2021.[1][3] It is the first non-azole oral antifungal drug to be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of vaginal yeast infections.[3] The FDA considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[4]
Medical uses
Ibrexafungerp is indicated for the treatment of adult and postmenarchal pediatric females with vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).[1][3]
Ibrexafungerp is currently undergoing late-stage clinical trials for an intravenous formulation for the treatment of various fungal diseases, including life-threatening fungal infections caused primarily by Candida (including C. auris) and Aspergillus species. It has demonstrated broad-spectrum antifungal activity, in vitro and in vivo, against multidrug-resistant pathogens, including azole- and echinocandin-resistant strains.[5]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Ibrexafungerp is a triterpenoid antifungal agent.[1] It acts via inhibition of the enzyme glucan synthase, which is involved in the formation of 1,3-β-D-glucan—an essential component of the fungal cell wall.[1] The compound has concentration-dependent fungicidal activity against Candida species.[1]
Pharmacokinetics
Ibrexafungerp has a time to maximal concentrations of 4 to 6 hours.[1] It is metabolized by hydroxylation via CYP3A4 and subsequently by glucuronidation and sulfation.[1] The medication has an elimination half-life of approximately 20 hours.[1]
Synthesis

References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 "Brexafemme- ibrexafungerp tablet, film coated". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c33be3a1-c4fd-512c-e053-2995a90a63eb.
- ↑ "Vulvovaginal Candidiasis - STI Treatment Guidelines" (in en-us). U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 22 July 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/candidiasis.htm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Scynexis Announces FDA Approval of Brexafemme (ibrexafungerp tablets) as the First and Only Oral Non-Azole Treatment for Vaginal Yeast Infections". Scynexis, Inc. (Press release). 2 June 2021. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 2 June 2021.
- ↑ (PDF) Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021 (Report). 13 May 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/155227/download. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "SCYNEXIS Announces Successful Completion of Phase 1 Trial Evaluating Intravenous (IV) Formulation of Ibrexafungerp". Scynexis inc.. 9 November 2021. https://www.scynexis.com/news-media/press-releases/detail/260/scynexis-announces-successful-completion-of-phase-1-trial.
- ↑ "Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2021". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (American Chemical Society (ACS)) 66 (15): 10150–10201. August 2023. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00501. PMID 37528515.
Further reading
- "Oral Ibrexafungerp: an investigational agent for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 29 (9): 893–900. September 2020. doi:10.1080/13543784.2020.1791820. PMID 32746636.
- "Ibrexafungerp: A novel oral glucan synthase inhibitor". Medical Mycology 58 (5): 579–592. July 2020. doi:10.1093/mmy/myz083. PMID 31342066.
- "Combination Therapy with Ibrexafungerp (Formerly SCY-078), a First-in-Class Triterpenoid Inhibitor of (1→3)-β-d-Glucan Synthesis, and Isavuconazole for Treatment of Experimental Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 64 (6). May 2020. doi:10.1128/AAC.02429-19. PMID 32179521.
External links
- "Ibrexafungerp". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/ibrexafungerp.
- Clinical trial number NCT03734991 for "Efficacy and Safety of Oral Ibrexafungerp (SCY-078) vs. Placebo in Subjects With Acute Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VANISH 303)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03987620 for "Efficacy and Safety of Oral Ibrexafungerp (SCY-078) vs. Placebo in Subjects With Acute Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Vanish 306)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |

