Chemistry:Iodine nitrate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodo nitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| INO3 | |
| Molar mass | 188.908 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
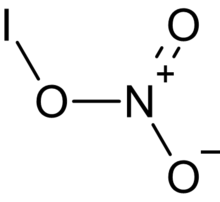
Iodine nitrate is a chemical with formula INO3.[1] It is a covalent molecule with a structure of I–O–NO2.[2]
Preparation
The compound was first produced by the reaction of mercury(II) nitrate and iodine in ether.[1]
Other nitrate salts and solvents can also be used.[1]
As a gas it is slightly unstable, decaying with a rate constant of −3.2×10−2 s−1.[2] The possible formation of this chemical in the atmosphere and its ability to destroy ozone have been studied. Potential reactions in this context are:[3]
- IONO2 → IO + NO2
- IONO2 → I + NO3
- I + O3 → IO + O2
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hassner, Alfred (15 April 2001). "Iodine Nitrate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: ri016. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ri016. ISBN 9780470842898.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Barnes, Ian; Becker, Karl H.; Starcke, Juergen (November 1991). "Fourier-transform IR spectroscopic observation of gaseous nitrosyl iodine, nitryl iodine, and iodine nitrate". The Journal of Physical Chemistry 95 (24): 9736–9740. doi:10.1021/j100177a026.
- ↑ Allan, B. J.; Plane, J. M. C. (September 2002). "A Study of the Recombination of IO with NO2 and the Stability of INO3: Implications for the Atmospheric Chemistry of Iodine". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 106 (37): 8634–8641. doi:10.1021/jp020089q. Bibcode: 2002JPCA..106.8634A.
Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO3)−4 | C | NO−3, NH4NO3 |
O | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)3, Fe(NO3)2 |
Co(NO3)2, Co(NO3)3 |
Ni(NO3)2 | Cu(NO3)2 | Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y(NO3)3 | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd(NO3)2 | AgNO3 | Cd(NO3)2 | In | Sn | Sb(NO3)3 | Te | I | Xe(NO3)2 |
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg2(NO3)2, Hg(NO3)2 |
Tl(NO3)3, TlNO3 |
Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) |
Po | At | Rn | |
| FrNO3 | Ra(NO3)2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(NO3)3 | Ce(NO3)3, Ce(NO3)4 |
Pr | Nd(NO3)3 | Pm | Sm | Eu(NO3)3 | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb(NO3)3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac(NO3)3 | Th(NO3)4 | Pa | UO2(NO3)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

