Chemistry:Iodous acid
From HandWiki
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (August 2024) |
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodous acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
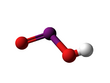
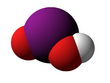
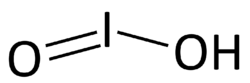
| HIO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 159.911 | ||
| Conjugate base | Iodite | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Iodous acid is the chemical compound with the formula HIO2. Its salts are named iodites; these are exceedingly unstable and have been observed but never isolated.[1] They will rapidly disproportionate to molecular iodine and iodates.
Other oxyacids
Iodous acid is part of a series of oxyacids in which iodine can assume oxidation states of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7. A number of neutral iodine oxides are also known.
| Iodine oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hydrogen iodide | Hypoiodous acid | Iodous acid | Iodic acid | Periodic acid |
| Formula | HI | HIO | HIO2 | HIO3 | HIO4 or H5IO6 |
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
 |