Chemistry:Lithium lactate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lithium 2-hydroxypropanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5LiO3[1][2] | |
| Molar mass | 96.01 |
| Appearance | Amorphous solid |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Very soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Sodium lactate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
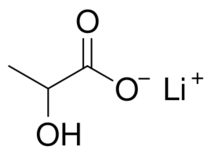
Lithium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of lithium and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOLi,[4] an amorphous solid, very soluble in water.[5]
Synthesis
Synthesis is by neutralization of lactic acid with lithium hydroxide:
- LiOH + CH3CH(OH)COOH → CH3CH(OH)COOLi + H2O
Physical properties
Lithium lactate forms an amorphous solid.
It dissolves very well in water[6] and organic solvents.
The compound demonstrates optical isomerism.
Lithium lactate emits acrid smoke when heated to decomposition.[7]
Chemical properties
Lithium lactate reacts with triphosgene to obtain lactic acid-O-internal anhydride.[8] It can be used as a precursor to prepare Li4SiO4,[9] Li4Ti5O12/C[10] and other materials.
Use
Lithium lactate is part of drugs that promote the excretion of uric acid from the body.[11]
It is also used as an Antipsychotic.[12]
References
- ↑ "867-55-0 CAS | LITHIUM LACTATE | Laboratory Chemicals | Article No. 04444". Loba Chemie. https://www.lobachemie.com/LaboratoryChemicals-04444/LITHIUM-LACTATE-CASNO-867-55-0.aspx.
- ↑ "27848-80-2 - L-(+)-Lactic acid lithium salt, Thermo Scientific - Lithium Lactate - J18160 - Alfa Aesar". Alfa Aesar. https://www.alfa.com/ru/catalog/J18160/.
- ↑ "Lithium lactate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/23673452#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "Lithium Lactate" (in en). American Elements. https://www.americanelements.com/lithium-lactate-867-55-0.
- ↑ "Lithium lactate". Sigma Aldrich. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/en/product/aldrich/440469.
- ↑ Lewis, Robert A. (31 May 2016) (in en). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary. John Wiley & Sons. p. 840. ISBN 978-1-118-13515-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=EwV0CgAAQBAJ&dq=lithium+lactate&pg=PA840. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ↑ Lewis, Richard J. (13 June 2008) (in en). Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference. John Wiley & Sons. p. 844. ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=WZeBDwAAQBAJ&dq=lithium+lactate&pg=PA844. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ↑ Nölle, Roman; Schmiegel, Jan-Patrick; Winter, Martin; Placke, Tobias (14 January 2020). "Tailoring Electrolyte Additives with Synergistic Functional Moieties for Silicon Negative Electrode-Based Lithium Ion Batteries: A Case Study on Lactic Acid O-Carboxyanhydride". Chemistry of Materials 32 (1): 173–185. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b03173. ISSN 0897-4756. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b03173. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ Yang, Xinwei; Liu, Wenqiang; Sun, Jian; Hu, Yingchao; Wang, Wenyu; Chen, Hongqiang; Zhang, Yang; Li, Xian et al. (2016). "Preparation of Novel Li4SiO4 Sorbents with Superior Performance at Low CO2 Concentration" (in en). ChemSusChem 9 (13): 1607–1613. doi:10.1002/cssc.201501699. ISSN 1864-564X. PMID 27312486. https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cssc.201501699. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ Stenina, I. A.; Sobolev, A. N.; Kuz’mina, A. A.; Kulova, T. L.; Yaroslavtsev, A. B. (1 August 2019). "Effect of the Carbon Source on the Electrochemical Properties of Li4Ti5O12/C Composites Prepared by Solid-State Synthesis" (in en). Inorganic Materials 55 (8): 803–809. doi:10.1134/S0020168519080156. ISSN 1608-3172. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134%2FS0020168519080156. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ Handler, J. S. (October 1, 1960). "The role of lactic acid in the reduced excretion of uric acid in toxemia of pregnancy". The Journal of Clinical Investigation 39 (10): 1526–1532. doi:10.1172/JCI104172. ISSN 0021-9738. PMID 13711188.
- ↑ Wang, Quan; Xu, Xinxiu; Li, Jun; Liu, Jing; Gu, Haifeng; Zhang, Ru; Chen, Jiekai; Kuang, Yin et al. (July 5, 2011). "Lithium, an anti-psychotic drug, greatly enhances the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells". Cell Research 21 (10): 1424–1435. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.108. ISSN 1748-7838. PMID 21727907.
 |

