Chemistry:Moracizine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ethmozine |
| Other names | Moricizine (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601214 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 34–38% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Elimination half-life | 3–4 hours (healthy volunteers), 6–13 hours (cardiac disease) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
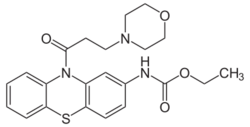
| Formula | C22H25N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 427.52 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Moracizine[1] or moricizine, sold under the trade name Ethmozine, is an antiarrhythmic of class IC.[2] It was used for the prophylaxis and treatment of serious and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias,[3] but was withdrawn in 2007 for commercial reasons.[4]
Pharmacology
Moracizine, a phenothiazine derivative, undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism and is also extensively metabolized after it has entered the circulation. It may have pharmacologically active metabolites. A clinical study has shown that moracizine is slightly less effective than encainide or flecainide in suppressing ventricular premature depolarizations.[citation needed] Compared with disopyramide and quinidine, moracizine was equally or more effective in suppressing premature ventricular contractions, couplets, and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia.[citation needed]
In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST), a large study testing the influence of antiarrhythmics on mortality, showed a statistically non-significant increase of mortality from 5.4 to 7.2% under moracizine. This is in line with other class IC antiarrhythmics.[5]
Synthesis
Note: The carbamate structure reminds the reader of Gastrophenzine or particularly Ethacizine.

The amide formation between Phenothiazine-2-ethylcarbamate [37711-29-8] (1) and 3-Chloropropionyl chloride [625-36-5] (2) gives ethyl N-[10-(3-chloropropanoyl)phenothiazin-2-yl]carbamate [119407-03-3] [34749-22-9] (3). Displacement of the remaining ω-halogen by morpholine (4) then completes the synthesis of Moricizine (5).
References
- ↑ "The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances". World Health Organization. 2009. p. 103. https://www.who.int/medicines/services/inn/StemBook2009.pdf.
- ↑ "Analysis of moricizine block of sodium current in isolated guinea-pig atrial myocytes. Atrioventricular difference of moricizine block". Vascular Pharmacology 38 (3): 131–41. March 2002. doi:10.1016/S1537-1891(02)00213-6. PMID 12402511.
- ↑ British National Formulary (59th ed.). British Medical Journal Publishing Group, Pharmaceutical Press. 2010.
- ↑ "Shire Announces Ethmozine will be Available until December 31, 2007". Heart Rhythm Society. http://www.hrsonline.org/policy/devicesdrugsfda/drugs/ethmozine_discontinued.cfm.
- ↑ Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial II Investigators (July 1992). "Effect of the antiarrhythmic agent moricizine on survival after myocardial infarction". The New England Journal of Medicine 327 (4): 227–33. doi:10.1056/NEJM199207233270403. PMID 1377359.
- ↑ Gritsenko, A.N., Ermakova, Z.I. & Zhuravlev, S.V. Pharm Chem J (1972) 6: 575.
- ↑ Anna Nikitichna Gritsenko, 5 More », U.S. Patent 3,740,395 (1973).
- ↑ Gary O. Page, U.S. Patent 5,202,435 (1993 to Roberts Laboratories Inc, Bristol Myers Squibb Pharma Co).
- ↑ L.P. Nikitenkov, et al. RU patent 2159771 (2000 to).
 |
