Chemistry:Potassium tartrate
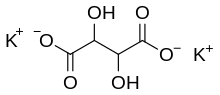
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dipotassium 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
| |
| Other names
Dipotassium tartrate; Argol; E336
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4K2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 226.268 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless, slightly opaque crystals |
| Density | 1.984 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.550 |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Potassium tartrate, dipotassium tartrate or argol has formula K2C4H4O6. It is the potassium salt of tartaric acid. It is often confused with potassium bitartrate, also known as cream of tartar. As a food additive, it shares the E number E336 with potassium bitartrate.[1]
Potassium bitartrate, also referred to as potassium acid tartrate or cream of tartar,[2] is the potassium acid salt of l-( + )-tartaric acid. It is obtained as a byproduct of wine manufacture during the fermentation process. Approved by the FDA as a direct food substance, potassium bitartrate is used as an additive, stabilizer, pH control agent, antimicrobial agent, processing aid, or thickener in various food products. Potassium bitartrate has a long history of medical use as a laxative administered as a rectal suppository and is an approved third-class OTC drug in Japan.
Potassium bitartrate was one of active ingredients in Phexxi, a non-hormonal contraceptive agent that was approved by the FDA in May 2020.[3]
Manufacturing
Potassium tartrate is produced by the reaction of tartaric acid with potassium sodium tartrate (rochelle salt), and potassium sulfate, followed by filtration, purification, precipitation and drying.
Other compounds
Tartar emetic is produced when potassium tartrate is heated with antimony trioxide. Tartar emetic causes intense nausea, prostration and vomiting by irritating the gastrointestinal mucosa.https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB11107
References
- ↑ PubChem. "Potassium tartrate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/8984.
- ↑ PubChem. "Potassium acid tartrate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/23681127.
- ↑ "Phexxi (lactic acid, citric acid and potassium bitartrate) FDA Approval History" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/history/phexxi.html.
 |

