Chemistry:Potassium amide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium amide
| |
| Other names
Potassamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KNH 2 | |
| Molar mass | 55.121 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Odor | ammonia-like |
| Density | 1.57 g/cm 3 |
| Melting point | 338 °C (640 °F; 611 K) |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | ammonia: 3.6 g/(100 mL) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-128.9 kJ/mol |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Lithium amide Sodium amide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Potassium amide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNH
2. Like other alkali metal amides, it is a white solid that hydrolyzes readily. It is a strong base.[1]
Production
Potassium amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with potassium. The reaction typically requires a catalyst.[2]
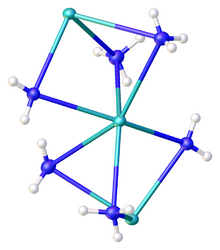
Structure
Traditionally KNH
2 is viewed as a simple salt, but it has significant covalent character and is highly aggregated in ammonia solution. The compound has been characterized by X-ray crystallography as the solvent-free form[3] as well as the mono- and diammonia solvates. In KNH
2 · 2NH
3, the potassium centers are each bonded to two amido ligands and four ammonia ligands, all six of which bridge to adjacent potassium centers. The result is a chain of hexacoordinate potassium ions. The K–NH
2 distances are 2.7652(11) whereas the K–NH
3 distances are respectively 2.9234(11) and 3.0698(11) Å.[4]
References
- ↑ Takaki, Katherine S. (2001). "Potassium Amide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp193. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ O. Glemser, H. Sauer (1963). "Silver Amide". in G. Brauer. Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed.. 1. NY, NY: Academic Press. pp. 1043.
- ↑ Juza, R.; Jacobs, H.; Klose, W. (1965). "Die Kristallstrukturen der Tieftemperaturmodifikationen von Kalium- und Rubidiumamid". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 338 (3–4): 171–178. doi:10.1002/zaac.19653380309.
- ↑ Kraus, Florian; Korber, Nikolaus (2005). "Hydrogen Bonds in Potassium Amide-Ammonia(1/2), KNH2.2NH3". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 631 (6–7): 1032–1034. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400467.
 |
