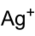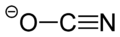Chemistry:Silver cyanate
|
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Silver(I) cyanate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| AgOCN | |||
| Molar mass | 149.885 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colourless | ||
| Density | 4g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 652 °C (1,206 °F; 925 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 1,085 °C (1,985 °F; 1,358 K) | ||
| Soluble in ammonia, nitric acid, potassium cyanide, ammonium hydroxide. Insoluble in alcohol and dilute acids.[1] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms | GHS07 | ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| HH302+H312+H332Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |||
| PP261Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP270Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP280Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP301+P312+P330Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP302+P352+P312Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP304+P340+P312Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP362+P364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, PP501Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Silver cyanate is the cyanate salt of silver. It can be made by the reaction of potassium cyanate with silver nitrate in aqueous solution, from which it precipitates as a solid.
- AgNO
3 + KNCO → Ag(NCO) + K+
+ NO−
3
Alternatively, the reaction
analogous to the reaction used for the industrial production of sodium cyanate, may be used.[2]
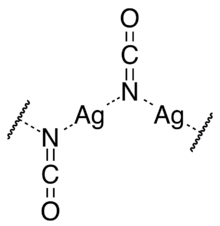
Silver cyanate is a beige to gray powder. It crystallises in the monoclinic crystal system in space group P21/m with parameters a = 547.3 pm, b = 637.2 pm, c = 341.6 pm, and β = 91°. Each unit cell contains two cyanate ions and two silver ions. The silver ions are each equidistant from two nitrogen atoms forming a straight N–Ag–N group. The nitrogen atoms are each coordinated to two silver atoms, so that there are zigzag chains of alternating silver and nitrogen atoms going in the direction of the monoclinic "b" axis, with the cyanate ions perpendicular to that axis.[3]
Silver cyanate reacts with nitric acid to form silver nitrate, carbon dioxide, and ammonium nitrate.[4]
- AgNCO + 2 HNO
3 + H
2O → AgNO
3 + CO
2 + NH
4NO
3
See also
References
- ↑ "3315-16-0 - Silver cyanate, 98% - 45411 - Alfa Aesar". https://www.alfa.com/en/catalog/045411/.
- ↑ Willy Kühne (1868) (in German), Lehrbuch der physiologischen Chemie, https://books.google.com/books?id=q8U9AAAAYAAJ&pg=PA470
- ↑ D. Britton, J. D. Dunitz: The crystal structure of silver cyanate, Acta Crystallogr. (1965). 18, 424–428, doi:10.1107/S0365110X65000944
- ↑ J. Milbauer: Bestimmung und Trennung der Cyanate, Cyanide, Rhodanide und Sulfide in Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry 42 (1903) 77–95, doi:10.1007/BF01302741.
 |