Chemistry:Xenon oxytetrafluoride
| |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| XeOF4 | |
| Molar mass | 223.23 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 3.17 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −46.2 °C (−51.2 °F; 227.0 K) |
| Reacts with water | |
| Structure | |
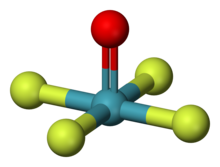
| square pyramidal[1][2] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Xenon oxytetrafluoride (XeOF4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is an unstable colorless liquid[2][3] with a melting point of −46.2 °C (−51.2 °F; 227.0 K)[4] that can be synthesized by partial hydrolysis of XeF6, or the reaction of XeF6 with silica[3] or NaNO3:[5]
A high-yield synthesis proceeds by the reaction of XeF6 with POF3 at −196 °C (−320.8 °F; 77.1 K).[6]
Like most xenon oxides, it is extremely reactive, and it hydrolyses in water to give hazardous and corrosive products, including hydrogen fluoride:
In addition, some ozone and fluorine is formed.
Reactions
XeOF4 reacts with H2O in the following steps:
The XeO3 formed is a dangerous explosive, decomposing explosively to Xe and O2:
- 2 XeO3 → 2 Xe + 3 O2
In its liquid form, XeOF4 exhibits amphoteric behaviour, forming complexes with both strong Lewis bases like CsF and strong Lewis acids like SbF5.[7] It forms a 1:1 adduct with XeF2, isostructural with XeF2·IF5,[8] as well as various heavy alkali metal fluorides.[4]
The reaction of XeOF4 with XeO3 provides a convenient synthesis route for XeO2F2.[9]
External links
- Xenon tetrafluoride oxide in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), http://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved 2022-04-13)
References
- ↑ Martins, Joseph; Wilson, E. Bright Jr. (1964). "Microwave Spectrum of Xenon Oxytetrafluoride" (in en). The Journal of Chemical Physics 41 (570): 570–571. doi:10.1063/1.1725910. ISSN 0021-9606. Bibcode: 1964JChPh..41..570M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Smith, D. F. (1963-05-24). "Xenon Oxyfluoride" (in en). Science 140 (3569): 899–900. doi:10.1126/science.140.3569.899. ISSN 0036-8075. OCLC 1644869. PMID 17810680. Bibcode: 1963Sci...140..899S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ibers, James A. (October 1965). "Molecular Structure". Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 16: 375–396. doi:10.1146/annurev.pc.16.100165.002111. ISSN 0066-426X. OCLC 1373069. Bibcode: 1965ARPC...16..375I.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Selig, Henry (1966-02-01). "Complexes of Xenon Oxide Tetrafluoride" (in en). Inorganic Chemistry 5 (2): 183–186. doi:10.1021/ic50036a004. ISSN 0020-1669.
- ↑ Christe, Karl O.; Wilson, William W. (April 1988). "Convenient synthesis of xenon oxide tetrafluoride" (in en). Inorganic Chemistry 27 (7): 1296–1297. doi:10.1021/ic00280a043. ISSN 0020-1669.
- ↑ Nielsen, Jon B.; Kinkead, Scott A.; Eller, P. Gary (1990-09-01). "A New Synthesis of Xenon Oxytetrafluoride, XeOF4" (in en). Inorganic Chemistry 29 (18): 3621–3622. doi:10.1021/ic00343a063. ISSN 0020-1669.
- ↑ Martin-Rovet, D.; Angelié, C.; Cauchetier, M.; Schrobilgen, G. J. (September 1982). "Various aspects of the reactivity of the xenon(VI) oxyfluoride: XeOF4" (in en). Journal of Fluorine Chemistry 21 (1): 10. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)85330-0. ISSN 0022-1139.
- ↑ Bartlett, N.; Wechsberg, M. (October 1971). "The Xenon Difluoride Complexes XeF2 · XeOF4; XeF2 · XeF6 · AsF5 and XeF2 · 2 XeF6 · 2 AsF5 and Their Relevance to Bond Polarity and Fluoride Ion Donor Ability of XeF2 and XeF6" (in en). Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 385 (1). doi:10.1002/zaac.19713850103. ISSN 0044-2313. OCLC 1770423.
- ↑ Huston, John L. (September 1967). "Xenon dioxide difluoride: isolation and some properties" (in en). The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 71 (10): 3339–3341. doi:10.1021/j100869a035. ISSN 1089-5639.
 |

