Chemistry:Xenon tetrafluoride

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Xenon tetrafluoride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| XeF4 | |||
| Molar mass | 207.2836 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 4.040 g cm−3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 117 °C (243 °F; 390 K) sublimes[1] | ||
| Reacts | |||
| Structure | |||
| D4h | |||
| square planar | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S |
146 J·mol−1·K−1[2] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−251 kJ·mol−1[2] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Xenon tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with chemical formula XeF4. It was the first discovered binary compound of a noble gas.[3] It is produced by the chemical reaction of xenon with fluorine:[4][5]
- Xe + 2 F2 → XeF4
This reaction is exothermic, releasing an energy of 251 kJ/mol.[3]
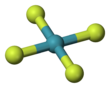
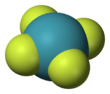
Xenon tetrafluoride is a colorless crystalline solid that sublimes at 117 °C. Its structure was determined by both NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography in 1963.[6][7] The structure is square planar, as has been confirmed by neutron diffraction studies.[8] According to VSEPR theory, in addition to four fluoride ligands, the xenon center has two lone pairs of electrons. These lone pairs are mutually trans.
Synthesis
The original synthesis of xenon tetrafluoride occurred through direct 1:5-molar-ratio combination of the elements in a nickel (Monel) vessel at 400 °C.[9] The nickel does not catalyze the reaction,[citation needed] but rather protects the container surfaces against fluoride corrosion. Controlling the process against impurities is difficult, as xenon difluoride (XeF2), tetrafluoride, and hexafluoride (XeF6) are all in chemical equilibrium, the difluoride favored at low temperatures and little fluorine and the hexafluoride favored at high temperatures and excess fluorine.[9][10] Fractional sublimation (xenon tetrafluoride is particularly involatile) or other equilibria generally allow purification of the product mixture.[9]
The elements combine more selectively when γ- or UV-irradiated in a nickel container or dissolved in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride with catalytic oxygen. That reaction is believed selective because dioxygen difluoride at standard conditions is too weak an oxidant to generate xenon(VI) species.[9]
Alternatively, fluoroxenonium perfluorometallate salts pyrolyze to XeF4.[9]
Reactions
Xenon tetrafluoride hydrolyzes at low temperatures to form elemental xenon, oxygen, hydrofluoric acid, and aqueous xenon trioxide:[11]
It is used as a precursor for synthesis of all tetravalent Xe compounds.[9] Reaction with tetramethylammonium fluoride gives tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate, which contains the pentagonal XeF−5 anion. The XeF−5 anion is also formed by reaction with cesium fluoride:[12]
- CsF + XeF4 → CsXeF5
Reaction with bismuth pentafluoride (BiF5) forms the XeF+3 cation:[13]
- BiF5 + XeF4 → XeF3BiF6
The XeF+3 cation in the salt XeF3Sb2F11 has been characterized by NMR spectroscopy.[14]
At 400 °C, XeF4 reacts with xenon to form XeF2:[10]
- XeF4 + Xe → 2 XeF2
The reaction of xenon tetrafluoride with platinum yields platinum tetrafluoride and xenon:[10]
- XeF4 + Pt → PtF4 + Xe
Applications
Xenon tetrafluoride has few applications. It has been shown to degrade silicone rubber for analyzing trace metal impurities in the rubber. XeF4 reacts with the silicone to form simple gaseous products, leaving a residue of metal impurities.[15]
References
- ↑ Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon (2001). Wiberg, Nils. ed. Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. p. 394. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles (6th ed.). Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Zumdahl (2007). Chemistry. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. p. 243. ISBN 978-0-618-52844-8.
- ↑ Claassen, H. H.; Selig, H.; Malm, J. G. (1962). "Xenon Tetrafluoride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 84 (18): 3593. doi:10.1021/ja00877a042.
- ↑ Chernick, C. L.; Claassen, H. H.; Fields, P. R.; Hyman, H. H.; Malm, J. G.; Manning, W. M.; Matheson, M. S.; Quarterman, L. A. et al. (1962). "Fluorine Compounds of Xenon and Radon". Science 138 (3537): 136–138. doi:10.1126/science.138.3537.136. PMID 17818399. Bibcode: 1962Sci...138..136C.
- ↑ Brown, Thomas H.; Whipple, E. B.; Verdier, Peter H. (1963). "Xenon Tetrafluoride: Fluorine-19 High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Spectrum". Science 140 (3563): 178. doi:10.1126/science.140.3563.178. PMID 17819836. Bibcode: 1963Sci...140..178B.
- ↑ Ibers, James A.; Hamilton, Walter C. (1963). "Xenon Tetrafluoride: Crystal Structure". Science 139 (3550): 106–107. doi:10.1126/science.139.3550.106. PMID 17798707. Bibcode: 1963Sci...139..106I.
- ↑ Burns, John H.; Agron, P. A.; Levy, Henri A (1963). "Xenon Tetrafluoride Molecule and Its Thermal Motion: A Neutron Diffraction Study". Science 139 (3560): 1208–1209. doi:10.1126/science.139.3560.1208. PMID 17757912. Bibcode: 1963Sci...139.1208B.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Haner, Jamie; Schrobilgen, Gary J. (2015). "The Chemistry of Xenon(IV)". Chem. Rev. 115 (2): 1255–1295. doi:10.1021/cr500427p. ISSN 0009-2665. PMID 25559700.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Bard, Allen J.; Parsons, Roger; Jordan, Joseph; International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (1985). Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution. CRC Press. pp. 767–768. ISBN 0-8247-7291-1. https://archive.org/details/standardpotentia0000unse/page/767.
- ↑ Williamson; Koch, C. W. (Mar 1963). "Xenon Tetrafluoride: Reaction with Aqueous Solutions". Science 139 (3559): 1046–1047. doi:10.1126/science.139.3559.1046. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17812981. Bibcode: 1963Sci...139.1046W.
- ↑ Harding, Charlie; Johnson, David Arthur; Janes, Rob (2002). Elements of the p Block. Molecular World. 9. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 93. ISBN 0-85404-690-9.
- ↑ Suzuki, Hitomi; Matano, Yoshihiro (2001). Organobismuth chemistry. Elsevier. p. 8. ISBN 0-444-20528-4.
- ↑ Gillespie, R. J.; Landa, B.; Schrobilgen, G. J. (1971). "Trifluoroxenon(IV) µ-fluoro-bispentafluoroantimonate(V): the XeF+3 cation". Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications (23): 1543–1544. doi:10.1039/C29710001543.
- ↑ Rigin, V.; Skvortsov, N. K.; Rigin, V. V. (March 1997). "Xenon tetrafluoride as a decomposition agent for silicone rubber for isolation and atomic emission spectrometric determination of trace metals". Analytica Chimica Acta 340 (1–3): 1–3. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(96)00563-6. Bibcode: 1997AcAC..340....1R.
External links
 |