Chemistry:Xenon oxydifluoride
From HandWiki
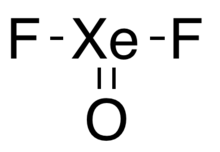
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
difluoro(oxo)xenon
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F2OXe | |
| Molar mass | 185.289 g·mol−1 |
| Structure | |
| T-shape | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Xenon oxytetrafluoride Xenon dioxydifluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Xenon oxydifluoride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula XeOF2. The first definitive isolation of the compound was published on 3 March 2007, producing it by the previously-examined route of partial hydrolysis of xenon tetrafluoride.[1]
- XeF
4 + H
2O → XeOF
2 + 2 HF
The compound has a T-shaped geometry and does not form polymers, though it does form an adduct with acetonitrile and with hydrogen fluoride.[1]
Although stable at low temperatures, it rapidly decomposes upon warming, either by losing the oxygen atom or by disproportionating into xenon difluoride and xenon dioxydifluoride:[1]
- 2 XeOF
2 → 2 XeF
2 + O
2 - 2 XeOF
2 → XeF
2 + XeO
2F
2
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brock, David S.; Bilir, Vural; Mercier, Hélène P. A.; Schrobilgen, Gary J. (2007). "XeOF2, F2OXeN≡CCH3, and XeOF2·nHF: Rare Examples of Xe(IV) Oxide Fluorides". Journal of the American Chemical Society 129 (12): 3598–3611. doi:10.1021/ja0673480. PMID 17335282. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja0673480.
 |

