Physics:Deucravacitinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /duːˌkrævəˈsɪtɪnɪb/ doo-KRA-və-SI-ti-nib |
| Trade names | Sotyktu |
| Other names | BMS-986165 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 99% |
| Protein binding | 82–90% |
| Metabolism | Liver (primarily CYP1A2) |
| Metabolites | BMT-153261 (active) |
| Elimination half-life | 10 hours |
| Excretion | Feces, urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
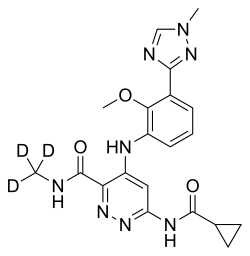
| Formula | C20H19D3N8O3 |
| Molar mass | 425.466 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Deucravacitinib, sold under the brand name Sotyktu, is medication used for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.[6] It is a tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor and it is taken by mouth.[6] It was developed by Bristol Myers Squibb.[8]
Deucravacitinib was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2022,[6][9][10] and in Australia in December 2022.[1] The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[11][12]
Medical uses
Deucravacitinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.[6]
Mechanism of action
It acts as a highly selective allosteric inhibitor of non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase 2 (TYK2).[13]
Molecule design
The chemical structure of deucravacitinib contains a methyl amide in which all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by deuterium.[14]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 26 January 2023, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Sotyktu, intended for the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.[15] The applicant for this medicinal product is Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EEIG.[15] Deucravacitinib was approved for medical use in the European Union in March 2023.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Sotyktu". 14 December 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspmd/sotyktu.
- ↑ "Sotyktu (Bristol-Myers Squibb Australia Pty Ltd)". 13 January 2023. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/prescription-medicines-registrations/sotyktu-bristol-myers-squibb-australia-pty-ltd.
- ↑ "Notice: Multiple Additions to the Prescription Drug List (PDL) [2023-03-08"]. 8 March 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/drug-products/prescription-drug-list/notices-changes/mutliple-additions-2023-03-08.html.
- ↑ "Summary Basis of Decision - Sotyktu". 10 March 2023. https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/summary-basis-decision-detailTwo.php?linkID=SBD00628&lang=en.
- ↑ "Sotyktu Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". 13 July 2023. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/14871/smpc.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 "Sotyktu- deucravacitinib tablet, film coated". 9 September 2022. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=ff4d7258-5068-4cdf-9692-8cae04c3198e.
- ↑ "Sotyktu". 27 March 2023. https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1718.htm.
- ↑ "U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Sotyktu (deucravacitinib), Oral Treatment for Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis" (Press release). Bristol Myers Squibb. 10 September 2022. Archived from the original on 10 September 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Sotyktu". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 October 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2022/214958Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ "Deucravacitinib: The First FDA-Approved Oral TYK2 Inhibitor for Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy: 10600280231153863. June 2023. doi:10.1177/10600280231153863. PMID 37341177.
- ↑ "Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2022". 10 January 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/new-drugs-fda-cders-new-molecular-entities-and-new-therapeutic-biological-products/new-drug-therapy-approvals-2022.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ (PDF) New Drug Therapy Approvals 2022 (Report). January 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/164429/download. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Selectivity Profile of the Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor Deucravacitinib Compared with Janus Kinase 1/2/3 Inhibitors". Dermatology and Therapy 11 (5): 1763–1776. October 2021. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00596-8. PMID 34471993.
- ↑ "First de novo deuterated drug poised for approval". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery 21 (9): 623–625. September 2022. doi:10.1038/d41573-022-00139-6. PMID 35974147.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Sotyktu: Pending EC decision". 26 January 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/sotyktu.
 |
