Chemistry:Ethyldichloroarsine
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethylarsonous dichloride | |||
| Other names
ED
Dichloroethylarsane; DICK | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1892 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5AsCl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 174.8893 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, mobile liquid | ||
| Density | 1.742 @ 14 °C | ||
| Melting point | −65 °C (−85 °F; 208 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) (decomposes) | ||
| Soluble in alcohol, benzene, ether, and water | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Highly toxic, irritant | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
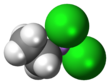
Ethyldichloroarsine, sometimes abbreviated "ED" and also known as ethyl Dick,[1] is an organoarsenic compound with the formula CH3CH2AsCl2. This colourless volatile liquid is a highly toxic obsolete vesicant or blister agent that was used during World War I in chemical warfare.[2] The molecule is pyramidal with the Cl-As-Cl and C-As-Cl angles approaching 90° (see image). Ethyldichloroarsine has high chronic toxicity, similar to lewisite.[3]
References
- ↑ "Chemical Warfare-A Chemical and Toxicological Review". American Journal of Public Health and the Nation's Health 34 (5): 455–60. May 1944. doi:10.2105/AJPH.34.5.455. PMID 18015982.
- ↑ "Methyldichloroarsine". NorthShore University HealthSystem. http://www.northshore.org/healthresources/encyclopedia/bioterrorism/ch018200.aspx.
- ↑ "In-Line Reactions and Ionizations of Vaporized Diphenylchloroarsine and Diphenylcyanoarsine in Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry". Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 27 (7): 1219–26. July 2016. doi:10.1007/s13361-016-1394-0. PMID 27098411.
 |