Chemistry:Robinin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
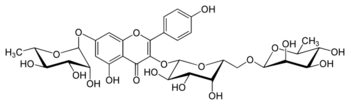
4′,5-Dihydroxy-3-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-galactopyranosyloxy]-7-(α-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)flavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(12S,13R,14R,15R,16S,52S,53R,54S,55R,56R,82R,83R,84R,85R,86S)-13,14,15,35,53,54,55,83,84,85-Decahydroxy-32-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-16,86-dimethyl-34H-2,4,7-trioxa-3(7,3)-[1]benzopyrana-1,8(2),5(2,6)-tris(oxana)octaphan-34-one | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H40O19 | |
| Molar mass | 740.66 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Robinin is a chemical compound. It can be isolated from Vinca erecta[1] or from the common locust Robinia pseudoacacia.[2] It is a flavone glycoside based on kaempferol.
References
- ↑ Akhmedzhanova, V. (1986). "Robinin and kaempfereol fromVinca erecta". Chemistry of Natural Compounds 22 (5): 601–602. doi:10.1007/BF00599275.
- ↑ Sando, Charles E. (1932). "The Plant Coloring Matter, Robinin". Journal of Biological Chemistry 94 (3): 675–680. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(18)76392-8.
 |

