Astronomy:R Lyrae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Lyra |
| Right ascension | 18h 55m 20.101223s[1] |
| Declination | +43° 56′ 45.9215″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.00[2] (3.9 - 5.0[3]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M5 III[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | −0.90[2] |
| U−B color index | +1.41[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.59[2] |
| Variable type | SRb[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −27.15[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 21.05[1] mas/yr Dec.: 82.06[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.94 ± 0.12[1] mas |
| Distance | 298 ± 3 ly (91 ± 1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.1[4] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.80[6] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 4,168[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.47[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,313[6] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
R Lyrae, also known as its Flamsteed designation 13 Lyrae, is a 4th magnitude semiregular variable star in the constellation Lyra, approximately 350 light years away from Earth. It is a red giant star of the spectral type M5III, meaning it has a surface temperature of under 3,500 kelvins. It is much larger and brighter, yet cooler, than the Sun. In the near-infrared J band, it is brighter than the nearby Vega.
R Lyrae is unusual in that it is a red star with a high proper motion, greater than 50 milliarcseconds a year.[8]
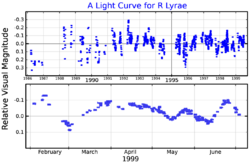
The variability is not consistent and regular, but periods of 46, 64, 378, and 1,000 days have been reported, with the 46-day period being the strongest.[4][10]
It is calculated that R Lyrae was a 2.0 M☉ star on the main sequence. It is considered an oxygen-rich asymptotic giant branch star, with both hydrogen and helium shells fusing.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Van Leeuwen, Floor (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy & Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "GCVS Query=R Lyr". General Catalogue of Variable Stars @ Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow, Russia. http://www.sai.msu.su/gcvs/cgi-bin/search.cgi?search=R+Lyr. Retrieved 2012-08-22.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Yeşilyaprak, C.; Aslan, Z. (2004). "Period-luminosity relation for M-type semiregular variables from Hipparcos parallaxes". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 355 (2): 601. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08344.x. Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.355..601Y.
- ↑ Famaey, B.; Pourbaix, D.; Frankowski, A.; Van Eck, S.; Mayor, M.; Udry, S.; Jorissen, A. (2009). "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants,. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations". Astronomy and Astrophysics 498 (2): 627. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698. Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..627F.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Halabi, Ghina M.; Eid, Mounib El (2015). "Exploring masses and CNO surface abundances of red giant stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 451 (3): 2957. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1141. Bibcode: 2015MNRAS.451.2957H.
- ↑ Prugniel, Ph.; Vauglin, I.; Koleva, M. (2011). "The atmospheric parameters and spectral interpolator for the MILES stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 531: A165. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116769. Bibcode: 2011A&A...531A.165P.
- ↑ Jiménez-Esteban, F. M.; Caballero, J. A.; Dorda, R.; Miles-Páez, P. A.; Solano, E. (2012). "Identification of red high proper-motion objects in Tycho-2 and 2MASS catalogues using Virtual Observatory tools". Astronomy & Astrophysics 539: 12. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118375. Bibcode: 2012A&A...539A..86J.
- ↑ Percy, John R.; Wilson, Joseph B.; Henry, Gregory W. (August 2001). "Long-Term VRI Photometry of Small-Amplitude Red Variables. I. Light Curves and Periods". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 113 (786): 983–996. doi:10.1086/322153. Bibcode: 2001PASP..113..983P. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2001PASP..113..983P. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ Glass, I. S.; Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Semiregular variables in the solar neighbourhood". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 378 (4): 1543–1549. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11903.x. Bibcode: 2007MNRAS.378.1543G.
 |