Astronomy:HR 8832
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cassiopeia |
| Right ascension | 23h 13m 16.97632s[1] |
| Declination | +57° 10′ 06.0823″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.574[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K3V[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.902[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.983[2] |
| Variable type | Suspected[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –18.5[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +2075.07±0.33[1] mas/yr Dec.: +295.45±0.25[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 152.76 ± 0.29[1] mas |
| Distance | 21.35 ± 0.04 ly (6.55 ± 0.01 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 6.46[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.81±0.03[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.778±0.005[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.2646[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.567±0.018[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 4699[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.11 (± 0.04)[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 6.94[8] km/s |
| Age | 11.0[7] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HR 8832 (or HD 219134, or Gliese 892) is a main sequence star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is smaller and less luminous than our Sun, with a spectral class of K3V, which makes it an orange-red hued star. HR 8832 is relatively close to our system, with an estimated distance of 21.25 light years. This star is close to the limit of apparent magnitude that can still be seen by the unaided eye. The limit is considered to be magnitude 6 for most observers.
Companions
This star has a magnitude 9.4 companion at an angular separation of 106.6 arcseconds.[10] The star is reported to host a rocky super-Earth, HD 219134 b, based on size (1.6 times the size of Earth), and density (6.4 grams per cubic cm).[11][12] A further three exoplanets, two super-Earths and one Jovian world, have been deduced using Harps-N radial velocity data.[13] Two more were discovered two months later.[14] A total of four independent studies regarding the planetary system of HR 8832 have been done, with many of their results conflicting with each other. As of March 2017, the star is known to have at least 5 planets, two of them (HD 219134 b and c) known to be transiting, rocky Super-Earths. Two previously reported planets, HD 219134 e and HD 219134 g, were not found in following HARPS-N analyses in March 2017 by Gillon et al.[15]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius [23] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 4.74 (± 0.19) M⊕ | 0.038764 (± 0.0047) | 3.092926 | 0 (fixed) | 85.058 (± 0.08)° | 1.602 (± 0.055) R⊕ |
| c | 4.36 (± 0.22) M⊕ | 0.06530 (± 0.0008) | 6.76458 (± 0.00033) | 0.062 (± 0.039) | 87.28 (± 0.10)° | 1.511 (± 0.047) R⊕ |
| f | >7.30 (± 0.40) M⊕ | 0.1463 (± 0.0018) | 22.717 (± 0.015) | 0.148 (± 0.047) | — | — |
| d | >16.17 (± 0.64) M⊕ | 0.2370 (± 0.003) | 46.859 (± 0.028) | 0.138 (± 0.025) | — | — |
| g (unconfirmed) | >10.8 M⊕ | 0.3753 (± 0.0004) | 94.2 (± 0.2) | ~0 | — | — |
| e (retracted candidate) | >3.72 M⊕ | 2.56+3.41−0.15 | 1842.0+4199.0−292.0 | 0.34 (± 0.17) | — | — |
| h | >76.0 M⊕ | 2.96 | 2121.0 | 0.06±0.04 | — | — |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Oja, T. (August 1986), "UBV photometry of stars whose positions are accurately known. III", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 65 (2): 405–409, Bibcode: 1986A&AS...65..405O.
- ↑ Frasca, A. et al. (December 2009), "REM near-IR and optical photometric monitoring of pre-main sequence stars in Orion. Rotation periods and starspot parameters", Astronomy and Astrophysics 508 (3): 1313–1330, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913327, Bibcode: 2009A&A...508.1313F.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V. et al. (1981), "Nachrichtenblatt der Vereinigung der Sternfreunde e.V. (Catalogue of suspected variable stars)", Nachrichtenblatt der Vereinigung der Sternfreunde e.V. (1981) (Moscow: Academy of Sciences USSR Shternberg): 0, Bibcode: 1981CSV...C......0K.
- ↑ Wielen, R. et al. (1999), "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions", Veröff. Astron. Rechen-Inst. Heidelb (Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg) 35 (35): 1, Bibcode: 1999VeARI..35....1W.
- ↑ Holmberg, J. et al. (July 2009), "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the solar neighbourhood. III. Improved distances, ages, and kinematics", Astronomy and Astrophysics 501 (3): 941–947, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811191, Bibcode: 2009A&A...501..941H.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 "HD 219134". exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu. https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/DisplayOverview/nph-DisplayOverview?objname=HD+219134&type=PLANET_HOST. Retrieved 2017-12-24.
- ↑ Martínez-Arnáiz, R. et al. (September 2010), "Chromospheric activity and rotation of FGK stars in the solar vicinity. An estimation of the radial velocity jitter", Astronomy and Astrophysics 520: A79, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913725, Bibcode: 2010A&A...520A..79M, http://eprints.ucm.es/37826/1/davidmontes17libre.pdf.
- ↑ "HR 8832". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=HR+8832.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ "PIA19832: Location of Nearest Rocky Exoplanet Known". NASA. 30 July 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19832. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ↑ Chou, Felicia; Clavin, Whitney (30 July 2015). "NASA's Spitzer Confirms Closest Rocky Exoplanet". NASA. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4672. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ↑ "Cassiopeia's Hidden Gem". Harvard. 30 July 2015. https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2015-16. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ↑ Vogt (25 September 2015). "A Six-Planet System Orbiting HD 219134". The Astrophysical Journal 814: 12. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/814/1/12. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...814...12V.
- ↑ http://backalleyastronomy.blogspot.com/2017/04/hd-219134-scorecard-5-planets-2.html?m=1
- ↑ "The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia — HD 219134 b". http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_b/.
- ↑ "The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia — HD 219134 c". http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_c/.
- ↑ "The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia — HD 219134 d". http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_d/.
- ↑ "The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia — HD 219134 e". http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_e/.
- ↑ "Planet HD 219134 f". Exoplanet.eu. http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_f/#12486. Retrieved 2015-11-17.
- ↑ "Planet HD 219134 g". Exoplanet.eu. http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_g. Retrieved 2015-11-17.
- ↑ "Planet HD 219134 h". Exoplanet.eu. http://exoplanet.eu/catalog/hd_219134_h. Retrieved 2015-11-17.
- ↑ Gillon, Michaël et al. (2017). "Two massive rocky planets transiting a K-dwarf 6.5 parsecs away". Nature Astronomy 1: 0056. doi:10.1038/s41550-017-0056. Bibcode: 2017NatAs...1E..56G.
Notes
External links
- "BD+56 2966 / HR 8832". SolStation. http://www.solstation.com/stars/hr8832.htm. Retrieved November 7, 2005.
| Constellation | |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
| Abbreviation | Cas |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Cassiopeiae |
| Symbolism | the Seated Queen |
| Right ascension | 22h 57m 04.5897s– 03h 41m 14.0997s[1] |
| Declination | 77.6923447°–48.6632690°[1] |
| Area | 598 sq. deg. (25th) |
| Main stars | 5 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 53 |
| Stars with planets | 14 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 4 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 7 |
| Brightest star | α Cas (Schedar)[lower-alpha 1] (2.24m) |
| Messier objects | 2 |
| Meteor showers | Perseids |
| Bordering constellations | Camelopardalis Cepheus Lacerta Andromeda Perseus |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −20°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of November. | |
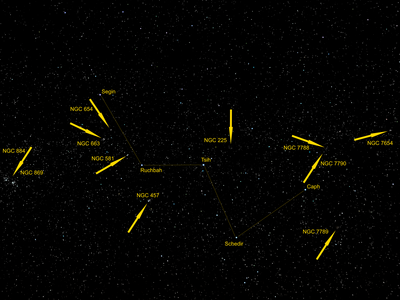
Cassiopeia (![]() listen) is a constellation and asterism in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars.
listen) is a constellation and asterism in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars.
Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North.
At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yellow hypergiants Rho Cassiopeiae and V509 Cassiopeiae and white hypergiant 6 Cassiopeiae. In 1572, Tycho Brahe's supernova flared brightly in Cassiopeia.[2] Cassiopeia A is a supernova remnant and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. Fourteen star systems have been found to have exoplanets, one of which—HD 219134—is thought to host six planets. A rich section of the Milky Way runs through Cassiopeia, containing a number of open clusters, young luminous galactic disc stars, and nebulae. IC 10 is an irregular galaxy that is the closest known starburst galaxy and the only one in the Local Group of galaxies.
Mythology

The constellation is named after Cassiopeia, the queen of Aethiopia. Cassiopeia was the wife of King Cepheus of Aethiopia[2] and mother of Princess Andromeda. Cepheus and Cassiopeia were placed next to each other among the stars, along with Andromeda. She was placed in the sky as a punishment after enraging Poseidon with the boast that her daughter Andromeda was more beautiful than the Nereids or, alternatively, that she herself was more beautiful than the sea nymphs.[3] She was forced to wheel around the north celestial pole on her throne, spending half of her time clinging to it so she does not fall off, and Poseidon decreed that Andromeda should be bound to a rock as prey for the monster Cetus. Andromeda was then rescued by the hero Perseus, whom she later married.[4][5]
Cassiopeia has been variously portrayed throughout her history as a constellation. In Persia, she was drawn by al-Sufi as a queen holding a staff with a crescent moon in her right hand, wearing a crown, as well as a two-humped camel. In France, she was portrayed as having a marble throne and a palm leaf in her left hand, holding her robe in her right hand. This depiction is from Augustin Royer's 1679 atlas.[4]
In Chinese astronomy, the stars forming the constellation Cassiopeia are found among three areas: the Purple Forbidden enclosure (紫微垣, Zǐ Wēi Yuán), the Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武, Běi Fāng Xuán Wǔ), and the White Tiger of the West (西方白虎, Xī Fāng Bái Hǔ).
The Chinese astronomers saw several figures in what is modern-day Cassiopeia. Kappa, Eta, and Mu Cassiopeiae formed a constellation called the Bridge of the Kings; when seen along with Alpha and Beta Cassiopeiae, they formed the great chariot Wang-Liang. The charioteer's whip was represented by Gamma Cassiopeiae, sometimes called "Tsih", the Chinese word for "whip".[4]
In Hindu Mythology, Cassiopeia was associated with the mythological figure Sharmishtha – the daughter of the great Devil (Daitya) King Vrishparva and a friend to Devayani (Andromeda).
In Welsh Mythology Llys Dôn (literally "The Court of Dôn") is the traditional Welsh name for the constellation. At least three of Dôn's children also have astronomical associations: Caer Gwydion ("The fortress of Gwydion") is the traditional Welsh name for the Milky Way, and Caer Arianrhod ("The Fortress of Arianrhod") being the constellation of Corona Borealis.[6]
In the 17th century, various Biblical figures were depicted in the stars of Cassiopeia. These included Bathsheba, Solomon's mother; Deborah, an Old Testament prophet; and Mary Magdalene, a follower of Jesus.[4]
A figure called the "Tinted Hand" also appeared in the stars of Cassiopeia in some Arab atlases. This is variously said to represent a woman's hand dyed red with henna, as well as the bloodied hand of Muhammad's daughter Fatima. The hand is made up of the stars α Cas, β Cas, γ Cas, δ Cas, ε Cas, and η Cas. The arm is made up of the stars α Per, γ Per, δ Per, ε Per, η Per, and ν Per.[4]
Another Arab constellation that incorporated the stars of Cassiopeia was the Camel. Its head was composed of Lambda, Kappa, Iota, and Phi Andromedae; its hump was Beta Cassiopeiae; its body was the rest of Cassiopeia, and the legs were composed of stars in Perseus and Andromeda.[4]
Other cultures see a hand or moose antlers in the pattern.[7] These include the Sámi, for whom the W of Cassiopeia forms an elk antler. The Chukchi of Siberia similarly saw the five main stars as five reindeer stags.[4]
The people of the Marshall Islands saw Cassiopeia as part of a great porpoise constellation. The main stars of Cassiopeia make its tail, Andromeda and Triangulum form its body, and Aries makes its head.[4] In Hawaii, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Cassiopeiae were named. Alpha Cassiopeiae was called Poloahilani, Beta Cassiopeiae was called Polula, and Gamma Cassiopeiae was called Mulehu. The people of Pukapuka saw the figure of Cassiopeia as a distinct constellation called Na Taki-tolu-a-Mataliki.[8]
Characteristics

File:Cassiopeia.4m-10m.webm Cassiopeia had a supernova, Cassiopeia A, SN 1572.
Covering 598.4 square degrees and hence 1.451% of the sky, Cassiopeia ranks 25th of the 88 constellations in area.[9] It is bordered by Cepheus to the north and west, Andromeda to the south and west, Perseus to the southeast and Camelopardalis to the east, and also shares a short border with Lacerta to the west.
The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, is "Cas".[10] The official constellation boundaries, as set by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte in 1930,[lower-alpha 2] are defined by a polygon of 30 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 00h 27m 03s and 23h 41m 06s, while the declination coordinates are between 77.69° and 46.68°.[1] Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellation is visible to observers north of 12°S.[9][lower-alpha 3] High in the northern sky, it is circumpolar (that is, it never sets in the night sky) to viewers in the British Isles, Canada and the northern United States.[12]
Features
Stars

The German cartographer Johann Bayer used the Greek letters Alpha through Omega, and then A and B, to label the most prominent 26 stars in the constellation. Upsilon was later found to be two stars and labelled Upsilon1 and Upsilon2 by John Flamsteed. B Cassiopeiae was in fact the supernova known as Tycho's Supernova.[13] Within the constellation's borders, there are 157 stars brighter than or equal to apparent magnitude 6.5.[lower-alpha 4][9]
'W' asterism
The five brightest stars of Cassiopeia – Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Epsilon Cassiopeiae – form the characteristic W-shaped asterism.[12] All five are prominent naked eye stars, three are noticeably variable, and a fourth is a suspected low amplitude variable. The asterism is oriented as a W when below Polaris during northern spring and summer nights. In northern winter, and when seen from southern latitudes, it is "above" Polaris (i.e. closer to the zenith) and the W appears inverted.
Alpha Cassiopeiae, traditionally called Schedar (from the Arabic Al Sadr, "the breast"), is a four-star system. The primary dominates, an orange-hued giant of magnitude 2.2, 228 ± 2 light-years from Earth.[15] With a luminosity of around 771 times that of the Sun, it has swollen and cooled after exhausting its core hydrogen over its 100 to 200 million-year lifespan, spending much of it as a blue-white B-type main-sequence star.[16] Magnitude 8.9 yellow dwarf companion (B) is widely separated; companions (C and D) are closer and magnitudes 13 and 14 respectively.[17]
Beta Cassiopeiae, or Caph (meaning "hand"), is a white-hued star of magnitude 2.3, 54.7 ± 0.3 light-years from Earth.[15] Around 1.2 billion years old, it has used up its core hydrogen and begun expanding and cooling off the main sequence. It is around 1.9 times as massive as the Sun, and around 21.3 times as luminous. Rotating at about 92% of its critical speed, Caph completes a full rotation every 1.12 days. This is giving the star an oblate spheroid shape with an equatorial bulge that is 24% larger than the polar radius.[18] It is a Delta Scuti variable with a small amplitude and period of 2.5 hours.[19]
Gamma Cassiopeiae is the prototype Gamma Cassiopeiae variable star, a type of variable star that has a variable disc of material flung off by the high rotation rate of the star. Gamma Cassiopeiae has a minimum magnitude of 3.0 and a maximum magnitude of 1.6, but is generally near magnitude 2.2, with unpredictable fades and brightenings. It is a spectroscopic binary, with an orbital period of 203.59 days and a companion with a calculated mass about the same as the Sun. However, no direct evidence of this companion has been found, leading to speculation that it might be a white dwarf or other degenerate star.[20] It is 550 ± 10 light-years from Earth.
Delta Cassiopeiae, also known as Ruchbah or Rukbat, meaning "knee," is a possible Algol-type eclipsing binary star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 2.7. It has been reported to show eclipses of less than 0.1 magnitudes with a period of 2 years and 1 month.,[21] but this has never been confirmed. It is 99.4 ± 0.4 light-years from Earth.[15]
Epsilon Cassiopeiae has an apparent magnitude of 3.3. Located 410 ± 20 light-years from Earth,[15] it is a hot blue-white star of spectral type B3 III with a surface temperature of 15,680 K. It is 6.5 times as massive and 4.2 times as wide as the Sun, and belongs to a class of stars known as Be stars—rapidly spinning stars that throw off a ring or shell of matter.[22]
Fainter stars

The next seven brightest stars in Cassiopeia are also all confirmed or suspected variable stars, including 50 Cassiopeiae which was not given a Greek letter by Bayer and is a suspected variable with a very small amplitude. Zeta Cassiopeiae (Fulu[23]) is a suspected slowly pulsating B-type star. Eta Cassiopeiae (Achird[23]) is a spectroscopic binary star with a period of 480 years, and a suspected RS Canum Venaticorum variable. The primary is a yellow-hued star of magnitude 3.5 and the secondary is a red-hued star of magnitude 7.5. The system is 19 light-years from Earth. Kappa Cassiopeiae is a blue supergiant of spectral type BC0.7Ia that is some 302,000 times as luminous as the Sun and has 33 times its diameter.[24] It is a runaway star, moving at around 2.5 million mph relative to its neighbors (1,100 kilometers per second).[25] Its magnetic field and wind of particles creates a visible bow shock 4 light-years ahead of it, colliding with the diffuse, and usually invisible, interstellar gas and dust. The dimensions of the bow shock are vast: around 12 light-years long and 1.8 light-years wide.[26] Theta Cassiopeiae, named Marfak, is a suspected variable star whose brightness changes by less than a tenth of a magnitude. Iota Cassiopeiae is a triple star 142 light-years from Earth. The primary is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.5 and an α2 Canum Venaticorum variable, the secondary is a yellow-hued star of magnitude 6.9, and the tertiary is a star of magnitude 8.4. The primary and secondary are close together but the primary and tertiary are widely separated. Omicron Cassiopeiae is a triple star and the primary is another γ Cassiopeiae variable.
Sigma Cassiopeiae is a binary star 1500 light-years from Earth. It has a green-hued primary of magnitude 5.0 and a blue-hued secondary of magnitude 7.3. Psi Cassiopeiae is a triple star 193 light-years from Earth. The primary is an orange-hued giant star of magnitude 4.7 and the secondary is a close pair of stars that appears to be of magnitude 9.0.[21]
Rho Cassiopeiae is a semi-regular pulsating variable yellow hypergiant, among the most luminous stars in the galaxy at approximately 500,000 L☉.[27] It has a minimum magnitude of 6.2 and a maximum magnitude of 4.1; its period is approximately 320 days. It has around 450 times the Sun's diameter and 17 times its mass, having begun life 45 times as massive as the Sun. Rho Cassiopeiae is about 10,000 light-years from Earth. Cassiopeia includes V509 Cassiopeiae, a second example of the extremely rare yellow hypergiants, which is around 400,000 times as luminous as the Sun and 14 times as massive,[27] as well as 6 Cassiopeiae which is a hotter white hypergiant. It also hosts the red supergiant PZ Cassiopeiae, which is one of the largest known stars with an estimate of 1,190–1,940 R☉ and is also a semiregular variable.[28] Between 240,000 and 270,000 times as luminous as the Sun, it is around 9,160 light-years distant from Earth.[29]
AO Cassiopeiae is a binary system composed of an O8 main sequence star and an O9.2 bright giant that respectively weigh anywhere between 20.30 and 57.75 times and 14.8 and 31.73 times the mass of the Sun.[30] The two massive stars are so close to each other they distort each other into egg-shapes.[31]
Tycho Brahe's supernova was visible within Cassiopeia, and the star Tycho G is suspected of being the donor of the material that triggered that explosion.
Deep-sky objects
File:Potw1327a.tif A rich section of the Milky Way runs through Cassiopeia, stretching from Perseus towards Cygnus, and it contains a number of open clusters, young luminous galactic disc stars, and nebulae.
The Heart Nebula and the Soul Nebula are two neighboring emission nebulae about 7,500 light-years away.
Two Messier objects, M52 (NGC 7654) and M103 (NGC 581), are located in Cassiopeia; both are open clusters. M52, once described as a "kidney-shaped" cluster, contains approximately 100 stars and is 4600 light-years from Earth.[32] Its most prominent member is an orange-hued star of magnitude 8.0 near the cluster's edge. M103 is far poorer than M52, with only about 25 stars included. It is also more distant, between 8000 and 9500 light-years from Earth.[33] Its most prominent member is actually a closer, superimposed double star; it consists of a 7th-magnitude primary and 10th-magnitude secondary.[21]
The other prominent open clusters in Cassiopeia are NGC 457 and NGC 663, both of which have about 80 stars. NGC 457 is looser, and its brightest member is Phi Cassiopeiae, a white-hued supergiant star of magnitude 5.0. However, it is uncertain whether Phi Cassiopeiae is part of the open cluster or not.[34] The stars of NGC 457, arrayed in chains, are approximately 10,000 light-years from Earth. NGC 663 is both closer, at 8200 light-years from Earth, and larger, at 0.25 degrees in diameter.[21]
There are two supernova remnants in Cassiopeia. The first, designated 3C 10 or just Tycho's Supernova Remnant, is the aftermath of the supernova called Tycho's Star. It was observed in 1572 by Tycho Brahe and now exists as a bright object in the radio spectrum.[21] Within the 'W' asterism formed by Cassiopeia's five major stars lies Cassiopeia A (Cas A). It is the remnant of a supernova that took place approximately 300 years ago (as observed now from Earth; it is 10,000 light-years away),[35] and has the distinction of being the strongest radio source observable outside the Solar System. It was perhaps observed as a faint star in 1680 by John Flamsteed. It was also the subject of the first image returned by the Chandra X-Ray Observatory in the late 1990s. The shell of matter expelled from the star is moving at 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) per second; it has a temperature of 30,000 kelvins on average.[35]
NGC 457 is another open cluster in Cassiopeia, also called the E.T. Cluster, the Owl Cluster, and Caldwell 13. The cluster was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel. It has an overall magnitude of 6.4 and is approximately 10,000 light-years from Earth, lying in the Perseus arm of the Milky Way. However, its most prominent member, the double star Phi Cassiopeiae, is far closer – between 1000 and 4000 light-years away. NGC 457 is fairly rich; it is a Shapley class e and Trumpler class I 3 r cluster. It is concentrated towards its center and detached from the star field. It contains more than 100 stars, which vary widely in brightness.[36]
Two members of the Local Group of galaxies are in Cassiopeia. NGC 185 is a magnitude 9.2 elliptical galaxy of type E0, 2 million light-years away. Slightly dimmer and more distant NGC 147 is a magnitude 9.3 elliptical galaxy, like NGC 185 it is an elliptical of type E0; it is 2.3 million light-years from Earth. Though they do not appear in Andromeda, both dwarf galaxies are gravitationally bound to the far larger Andromeda Galaxy.[37]
IC 10 is an irregular galaxy that is the closest known starburst galaxy and the only one in the Local Group of galaxies.[38]
Cassiopeia also contains part of the closest galaxy group to our Local Group, the IC 342/Maffei Group. The galaxies Maffei 1 and Maffei 2 are located just to the south of the Heart and Soul nebulae. As a result of this location in the Zone of Avoidance, both are surprisingly faint despite both being within 10 million light-years away (Maffei 2 is below the range of most amateur telescopes).[39]
- The constellation Cassiopeia with star clusters
Meteor shower
The December Phi Cassiopeiids are a recently discovered early December meteor shower that radiates from Cassiopeia. Phi Cassiopeiids are very slow, with an entry velocity of approximately 16.7 kilometers per second. The shower's parent body is a Jupiter family comet, though its specific identity is unknown.[40]
Namesakes
USS Cassiopeia (AK-75) was a United States Navy Crater-class cargo ship named after the constellation.
In Pokémon Scarlet and Violet, the villainous team, Team Star, is divided into five squads named after the brightest stars in the constellation: Segin Squad, Schedar Squad, Ruchbah Squad, Navi Squad, and Caph Squad. In addition, the character Penny's alias, Cassiopeia, is named after the constellation.
Cassiopeia is also the name of a song by London-based band Bears in Trees. Although the lyrics of the song mainly refer to the ancient Greek woman, the album cover shows the constellation.[41]
See also
- Cassiopeia (Chinese astronomy)
References
Explanatory notes
- ↑ γ Cas is variable and occasionally brighter than α.
- ↑ Delporte had proposed standardising the constellation boundaries to the International Astronomical Union, who had agreed and gave him the lead role[11]
- ↑ While parts of the constellation technically rise above the horizon to observers between the latitudes of 12°S and 43°S, stars within a few degrees of the horizon are to all intents and purposes unobservable.[9]
- ↑ Objects of magnitude 6.5 are among the faintest visible to the unaided eye in suburban-rural transition night skies.[14]
Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Cassiopeia, Constellation Boundary". The Constellations (International Astronomical Union). https://www.iau.org/public/themes/constellations/#cas. Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Cassiopeia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 460.
- ↑ Chen, P.K. (2007). A Constellation Album: Stars and Mythology of the Night Sky. p. 82. ISBN 9781931559386.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Staal 1988, pp. 14–18
- ↑ Chen 2007, pp. 82–83
- ↑ Squire, Charles (2013). Celtic Myth and Legend. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-12209-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=nyjDAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT169.
- ↑ Ptak, Robert (1998). Sky Stories Ancient and Modern. New York: Nova Science Publishers. p. 104.
- ↑ Makemson, Maud Worcester (1941). The Morning Star Rises: an account of Polynesian astronomy. Yale University Press. p. 281. Bibcode: 1941msra.book.....M.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Ian Ridpath. "Constellations: Andromeda–Indus". Star Tales. self-published. http://www.ianridpath.com/constellations1.html.
- ↑ Russell, Henry Norris (1922). "The New International Symbols for the Constellations". Popular Astronomy 30: 469. Bibcode: 1922PA.....30..469R.
- ↑ Ridpath, Ian. "Constellation boundaries: How the modern constellation outlines came to be". Star Tales. self-published. http://www.ianridpath.com/boundaries.html.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Arnold, H.J.P; Doherty, Paul; Moore, Patrick (1999). The Photographic Atlas of the Stars. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-7503-0654-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=YjcvJUfnWBAC&pg=PA20.
- ↑ Wagman, Morton (2003). Lost Stars: Lost, Missing and Troublesome Stars from the Catalogues of Johannes Bayer, Nicholas Louis de Lacaille, John Flamsteed, and Sundry Others. Blacksburg, Virginia: The McDonald & Woodward Publishing Company. pp. 91–92. ISBN 978-0-939923-78-6.
- ↑ Bortle, John E. (February 2001). "The Bortle Dark-Sky Scale". Sky & Telescope. Sky Publishing Corporation. http://www.skyandtelescope.com/resources/darksky/3304011.html?page=1&c=y.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the New Hipparcos Reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–64. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ↑ Professor James B. (Jim) Kaler. "SHEDAR (Alpha Cassiopeiae)". University of Illinois. http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/shedar.html.
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3466. doi:10.1086/323920. Bibcode: 2001AJ....122.3466M.
- ↑ Che, X.; Monnier, J. D.; Zhao, M.; Pedretti, E.; Thureau, N.; Mérand, A.; ten Brummelaar, T.; McAlister, H. et al. (2011). "Colder and Hotter: Interferometric Imaging of β Cassiopeiae and α Leonis". The Astrophysical Journal 732 (2): 68. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/732/2/68. Bibcode: 2011ApJ...732...68C.
- ↑ Kaler, James B. (Jim). "Caph". Stars. University of Illinois. http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/caph.html.
- ↑ Harmanec, P.; Habuda, P.; Štefl, S.; Hadrava, P.; Korčáková, D.; Koubský, P.; Krtička, J.; Kubát, J. et al. (2000). "Properties and nature of Be stars. XX. Binary nature and orbital elements of gamma Cas". Astronomy and Astrophysics 364: L85–L88. Bibcode: 2000A&A...364L..85H.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 Ridpath & Tirion 2001, pp. 106–108.
- ↑ Catanzaro, G. (2013). "Spectroscopic atlas of Hα and Hβ in a sample of northern Be stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 550 (A79): 18. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220357. Bibcode: 2013A&A...550A..79C.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Naming Stars". IAU.org. https://www.iau.org/public/themes/naming_stars/.
- ↑ Searle, S. C.; Prinja, R. K.; Massa, D.; Ryans, R. (2008). "Quantitative studies of the optical and UV spectra of Galactic early B supergiants. I. Fundamental parameters". Astronomy and Astrophysics 481 (3): 777. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077125. Bibcode: 2008A&A...481..777S.
- ↑ Clavin, Whitney (21 February 2014). "The bow shock of Kappa Cassiopeiae, a massive, hot supergiant". Phys.org. http://phys.org/news/2014-02-kappa-cassiopeiae-massive-hot-supergiant.html.
- ↑ Peri, C. S.; Benaglia, P.; Brookes, D. P.; Stevens, I. R.; Isequilla, N. L. (2012). "E-BOSS: An Extensive stellar BOw Shock Survey. I. Methods and first catalogue". Astronomy & Astrophysics 538: A108. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118116. Bibcode: 2012A&A...538A.108P.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Stothers, Richard B. (2012). "Yellow Hypergiants Show Long Secondary Periods?". The Astrophysical Journal 751 (2): 151. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/751/2/151. Bibcode: 2012ApJ...751..151S.
- ↑ Levesque, Emily M.; Massey, Philip; Olsen, K. A. G.; Plez, Bertrand; Josselin, Eric; Maeder, Andre; Meynet, Georges (August 2005). "The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought". The Astrophysical Journal 628 (2): 973–985. doi:10.1086/430901. Bibcode: 2005ApJ...628..973L.
- ↑ Kusuno, K.; Asaki, Y.; Imai, H.; Oyama, T. (2013). "Distance and Proper Motion Measurement of the Red Supergiant, Pz Cas, in Very Long Baseline Interferometry H2O Maser Astrometry". The Astrophysical Journal 774 (2): 107. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/774/2/107. Bibcode: 2013ApJ...774..107K.
- ↑ Hohle, M.M.; Neuhäuser, R.; Schutz, B.F. (2010). "Masses and luminosities of O- and B-type stars and red supergiants". Astronomische Nachrichten 331 (4): 349. doi:10.1002/asna.200911355. Bibcode: 2010AN....331..349H.
- ↑ Astronomy and Cosmogony. CUP Archive. 1928. pp. 125–. GGKEY:KFJRG3PWW14. https://books.google.com/books?id=M988AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA125.
- ↑ Wu, Zhen-Yu et al. (November 2009), "The orbits of open clusters in the Galaxy", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 399 (4): 2146–2164, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15416.x, Bibcode: 2009MNRAS.399.2146W.
- ↑ Sanner, J.; Geffert, M.; Brunzendorf, J.; Schmoll, J. (1999). "Photometric and kinematic studies of open star clusters. I. NGC 581 (M 103)". Astronomy and Astrophysics 349: 448–456. Bibcode: 1999A&A...349..448S.
- ↑ Zhang, X. B.; Luo, C. Q.; Fu, J. N. (2012). "B-Type Variables in the Young Open Cluster Ngc 457". The Astronomical Journal 144 (3): 86. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/144/3/86. Bibcode: 2012AJ....144...86Z.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Wilkins, Jamie; Dunn, Robert (2006). 300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe (1st ed.). Buffalo, New York: Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1-55407-175-3.
- ↑ Levy 2005, pp. 92–93.
- ↑ Levy 2005, pp. 180–181.
- ↑ Nidever, David L.; Ashley, Trisha; Slater, Colin T.; Ott, Jürgen; Johnson, Megan; Bell, Eric F.; Stanimirović, Snežana; Putman, Mary et al. (2013). "Evidence for an interaction in the nearest starbursting dwarf irregular galaxy IC 10". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 779 (2): L15. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/779/2/L15. Bibcode: 2013ApJ...779L..15N.
- ↑ I. D. Karachentsev (2005). "The Local Group and Other Neighboring Galaxy Groups". Astronomical Journal 129 (1): 178–188. doi:10.1086/426368. Bibcode: 2005AJ....129..178K.
- ↑ Jenniskens, Peter (September 2012). "Mapping Meteoroid Orbits: New Meteor Showers Discovered". Sky & Telescope: 25.
- ↑ "Cassiopeia". https://bearsintreesofficial.bandcamp.com/track/cassiopeia.
General and cited sources
- Krause, O; Rieke, GH; Birkmann, SM; Le Floc'h, E; Gordon, KD; Egami, E; Bieging, J; Hughes, JP et al. (2005). "Infrared echoes near the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A". Science 308 (5728): 1604–6. doi:10.1126/science.1112035. PMID 15947181. Bibcode: 2005Sci...308.1604K.
- Levy, David H. (2005), Deep Sky Objects, Prometheus Books, ISBN 1-59102-361-0, https://archive.org/details/deepskyobjects00davi
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2001), Stars and Planets Guide, Princeton University Press, ISBN 0-691-08913-2
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2007). Stars and Planets Guide. London: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-725120-9.
- Staal, Julius D. W. (1988). The New Patterns in the Sky: Myths and Legends of the Stars. The McDonald and Woodward Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-939923-04-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Cassiopeia
- The clickable Cassiopeia
- Star Tales – Cassiopeia
- Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (ca 160 medieval and early modern images of Cassiopeia)
Template loop detected: Template:Stars of Cassiopeia
Coordinates: ![]() 01h 00m 00s, +60° 00′ 00″
01h 00m 00s, +60° 00′ 00″
 |
Coordinates: ![]() 23h 13m 16.98s, +57° 10′ 06.1″
23h 13m 16.98s, +57° 10′ 06.1″