Chemistry:Benzyl iodide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Iodomethyl)benzene | |
| Other names
Fraissite, iodotoluol, α-iodotoluene, phenylmethyliodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7I | |
| Molar mass | 218.037 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Low-melting crystals or colorless liquid |
| Melting point | 24.5 °C |
| Boiling point | 218 °C (424 °F; 491 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | WARNING |
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
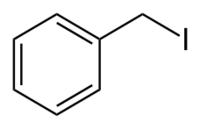
Benzyl iodide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H7I.[1][2] The compound consists of a benzene ring with an attached iodidemethyl group. The substance is an alkyl halide and is a constitutional isomer of the iodotoluenes.
Synthesis
Benzyl iodide can be obtained via the Finkelstein reaction from benzyl chloride and sodium iodide in acetone.

Properties
Benzyl iodide forms colorless to yellow needles, melting at 24.5 °C.[3] As a liquid, the compound has the high refractive index of 1.6334. Benzyl iodide is also a powerful lachrymator.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ "BENZYL IODIDE". chemicalbook.com. http://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB2305798.htm.
- ↑ "Benzyl iodide". webbook.nist.gov. http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C620053&Mask=8.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90. Edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009, ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0, Section 3, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, p. 3-306.
- ↑ Bauta, William E. (2001). "Benzyl Iodide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. onlinelibrary.wiley.com. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb060. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ↑ Fieser, Louis F.; Fieser, Mary (1982) (in de). Organische Chemie. ISBN 978-3-527-25075-2.
 |
