Chemistry:Cenobamate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xcopri, Ontozry |
| Other names | YKP3089 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620021 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ≥88% |
| Protein binding | 60% |
| Metabolism | Mainly glucuronidation via UGT2B7 |
| Elimination half-life | 50–60 hours |
| Excretion | Mainly via urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H10ClN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 267.67 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
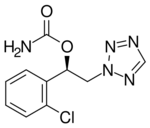
Cenobamate, sold under the brand names Xcopri (US) and Ontozry (EU), is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, a kind of epilepsy, in adults. It is taken by mouth.[2][6][7] Cenobamate (CNB), ([(R)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(2H-tetrazol-2-yl)ethyl], is a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative.[8]
Cenobamate was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2019[2][6][7][9] and placed in Schedule V of the Controlled Substances Act in March 2020.[10] Cenobamate was approved for medical use in the European Union in March 2021.[4]
Medical uses
In the United States, cenobamate is indicated for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in adults.[2]
In the European Union, it is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of focal-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults with epilepsy who have not been adequately controlled despite a history of treatment with at least two anti-epileptic medications.[4]
Contraindications
Cenobamate shortens the QT interval of the heart rhythm. It is therefore contraindicated in people with familial short QT syndrome, a very rare disease of the electrical system of the heart.[11][12]
Adverse effects
The most common side effects are drowsiness (in 37% of people taking the drug), dizziness (33%), and fatigue (24%). Sight disorders, headache and elevated potassium levels in the blood (over 5 mmol/L) are also common.[11] Hypersensitivity occurs in fewer than 1% of patients, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) in fewer than 0.1%.[12]
Patients treated with cenobamate may experience a shortening of the QT interval, and this new agent is contraindicated in patients with familial short QT syndrome because of the increased risk of ventricular dysrhythmias and sudden death. A dose-dependent QT-interval shortening was observed with cenobamate.[8]
Overdose
There are few data regarding cenobamate overdose. It is expected that the described adverse effects such as drowsiness, dizziness and fatigue would occur, as well as possibly problems with the heart rhythm. No specific antidote exists.[11][12]
Interactions
Using cenobamate together with other central nervous system depressants such as barbiturates, benzodiazepines or alcohol may result in increased drowsiness and other central nervous system symptoms.[11][12]
Cenobamate induces the enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 and can therefore decrease blood concentrations of drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes (for example midazolam and bupropion, respectively). Conversely, it inhibits the enzyme CYP2C19, potentially increasing concentrations of drugs metabolized by this enzyme (for example omeprazole).[11][12]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Cenobamate is a voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) blocker.[13] It is a selective blocker of the inactivated state of VGSCs, preferentially inhibiting persistent sodium current.[13] It has been proposed that cenobamate additionally enhances presynaptic release of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), thereby increasing inhibitory GABAergic neurotransmission.[13] Cenobamate is a positive allosteric modulator of high-affinity GABAA receptors, activated by GABA at a site independent of the benzodiazepine binding site, and efficiently enhances tonic conductance inhibition in hippocampal neurons.[8]
Pharmacokinetics
Cenobamate is absorbed from the gut to at least 88% and reaches highest concentrations in the blood plasma after one to four hours. When in the bloodstream, 60% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins, mostly to albumin. Cenobamate is inactivated mainly by glucuronidation via the enzyme UGT2B7 and to a lesser extent UGT2B4. The enzymes CYP2E1, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 play smaller roles in the drug's metabolism.[12]
Steady state conditions are reached after 14 days. Cenobamate and its metabolites are mostly eliminated via the urine and only to 5.2% via the faeces. The terminal half-life is 50 to 60 hours.[12]
History
The safety and efficacy of cenobamate to treat partial-onset seizures was established in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that enrolled 655 adults. In these studies, patients had partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization for an average of approximately 24 years and median seizure frequency of 8.5 seizures per 28 days during an 8-week baseline period. During the trials, doses of 100, 200, and 400 milligrams (mg) daily reduced the number of seizures per 28 days compared with the placebo group.[6]
Society and culture
Legal status
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved cenobamate in November 2019, and granted the application for Xcopri to SK Life Science Inc.[6][7][9][14]
On 28 January 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization.[15] The applicant for this medicinal product is Arvelle Therapeutics Netherlands B.V.[15] Ontozry was approved on 26 March 2021.[4][16]
References
- ↑ "Notice: Multiple additions to the Prescription Drug List (PDL) [2023-08-30"]. 26 October 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/drug-products/prescription-drug-list/notices-changes/multiple-additions-2023-08-30.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Xcopri Titration Pack- cenobamate kit Xcopri- cenobamate tablet, film coated Xcopri Maintenance Pack- cenobamate kit". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=565c2126-57ae-4e29-b443-723bbe7e2072.
- ↑ "Schedules of Controlled Substances: Placement of Cenobamate in Schedule V". 10 March 2020. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2020/03/10/2020-04963/schedules-of-controlled-substances-placement-of-cenobamate-in-schedule-v.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Ontozry EPAR". 25 January 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ontozry. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Ontozry Product information". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1530.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "FDA approves new treatment for adults with partial-onset seizures". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 21 November 2019. Archived from the original on 22 November 2019. Retrieved 21 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Drug Trials Snapshots: Xcopri". 3 December 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-trials-snapshots-xcopri.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Rissardo, Jamir Pitton; Fornari Caprara, Ana Letícia (2023-07-28). "Cenobamate (YKP3089) and Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Review of the Literature" (in en). Medicina 59 (8): 1389. doi:10.3390/medicina59081389. ISSN 1648-9144. PMID 37629678.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Drug Approval Package: Xcopri". 10 December 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2019/212839Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "2020 - Placement of Cenobamate in Schedule V". 10 March 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/rules/2020/fr0310_9.htm.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 Xcopri FDA Professional Drug Information. Accessed 2021-07-28.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 "Ontozry: EPAR – Product information". European Medicines Agency. 2021-06-02. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ontozry-epar-product-information_en.pdf.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 "A resurging boom in new drugs for epilepsy and brain disorders". Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 11 (1): 27–45. January 2018. doi:10.1080/17512433.2018.1386553. PMID 28956955.
- ↑ "Cenobamate FDA Approval Status". 13 November 2019. https://www.drugs.com/history/cenobamate.html.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Ontozry: Pending EC decision". 29 January 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/ontozry. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Ontozry". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1530.htm.
 |
